Stock Split
- Dividends and Stock Splits. A dividend is a distribution of earnings that a corporation makes to its shareholders. ...
- Increasing Shares. Both stock splits and stock dividends have the effect of increasing the number of outstanding shares of a company's stock.
- Reason for a Stock Split. ...
- Effects of a Stock Split. ...
How does stock split affect cash dividends?
While a stock split doesn't cause the value of a company's intrinsic value to rise, it can make the stock accessible to more investors, and often increase demand, which can push the stock price higher. Simply put, a stock's dividend per share will be reduced as a result of a stock split, but the total amount of dividends paid doesn't change.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of stock dividends?
Stock Split Advantages And Disadvantages
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Stock Dividends. ...
- Stock Dividend. ...
- Types Of Business : A Sole Proprietorship Business. ...
- Case 19 - Georgia Case Atlantic. ...
- Finance And Financial Management : The Major Sub Areas Of Finance. ...
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Stock Shares. ...
- Business Financing And The Capital Structure. ...
- Dividend Policy. ...
- Dividend Policy. ...
Which stock has the most splits?
Stock splits usually work, and the 20-for-1 split by Google’s parent company Alphabet may spark a wave. That’s according to analysis from Bank of America, which found that companies that have announced stock splits have outperformed the market.
What company pays the highest dividend?
Omega Healthcare and Lumen Technologies pay dividends far higher than that of the S&P 500. Both companies are facing challenges this year, so investors will want to monitor their progress. Dividend investors might rightly want to question companies with yields north of 5%. In many cases, there are considerable risks surrounding those payouts.
What is better stock split or stock dividend?
A stock dividend is issued to keep earnings in the company and make the company more valuable in the future. When a company is considered more valuable, stock prices rise. A stock split is performed because a company's stock is outperforming the company's goals.
What happens to dividend when stock splits?
In general, dividends declared after a stock split will be reduced proportionately per share to account for the increase in shares outstanding, leaving total dividend payments unaffected. The dividend payout ratio of a company shows the percentage of net income, or earnings, paid out to shareholders in dividends.
What does it mean that a stock split in the form of a dividend?
When a stock split is announced, companies often describe it as a one time special stock dividend. This is not to be confused with a quarterly cash dividend, and simply means the company will carry out the stock split by issuing additional shares to shareholders.
Who benefits from a stock split?
Although the number of outstanding shares increases and the price per share decreases, the market capitalization (and the value of the company) does not change. As a result, stock splits help make shares more affordable to smaller investors and provides greater marketability and liquidity in the market.
Is a stock split good for investors?
By splitting the stock, companies lower the price and make them more affordable to a greater number of investors. This expands the shareholder base through increased buying, which can lead to a rally in the share price.
Do you lose money when a stock splits?
A stock split doesn't add any value to a stock. Instead, it takes one share of a stock and splits it into two shares, reducing its value by half. Current shareholders will hold twice the shares at half the value for each, but the total value doesn't change.
What are the disadvantages of a stock split?
Downsides of stock splits include increased volatility, record-keeping challenges, low price risks and increased costs.
Does a stock split hurt shareholders?
When a stock splits, it has no effect on stockholders' equity. During a stock split, the company does not receive any additional money for the shares that are created. If a company simply issued new shares it would receive money for these, which would increase stockholders' equity.
Do stocks Go Up After split?
Although the intrinsic value of the stock is not changed by a forward split, investor excitement often drives the stock price up after the split is announced, and sometimes the stock rises further in post-split trading.
What does a 4 to 1 stock split mean?
If a company announces a 4-for-1 stock split, the shareholder will get three additional shares. The price of the original share will be divided by four, so that a share trading at $400 would trade at $100 after the split.
What does a 5 to 1 stock split mean?
5-for-1 split ratio: In a 5-for-1 stock split, each individual share of stock is split into five shares. The market price of those five new shares is one-fifth the price of the old share.
Why would a company do a stock split?
Companies typically engage in a stock split so that investors can more easily buy and sell shares, otherwise known as increasing the company's liquidity. Stock splits divide a company's shares into more shares, which in turn lowers a share's price and increases the number of shares available.
Stock Dividends
A stock dividend is one of the two ways in which a company grants dividends to shareholders. Companies can also issue cash dividends to investors. While cash dividends are the most common method to reward shareholders, some companies choose to offer stock dividends.
Stock Splits
A stock split is when a company divides existing shares into several units. By doing this, a company increases the total number of outstanding shares without adjusting the full value of those shares as the split doesn’t take cash into consideration.
What is Better?
A stock split is better for a small investor who can’t afford expensive stocks, such as stocks in Amazon and Google. If you only have a few hundred dollars to invest, you couldn’t buy even one share in such big companies. This is why a stock split would be great for you.
Final Thoughts
Both a stock dividend and a stock share lead to more total outstanding shares. The main differences are the reasons for the action and the method of increasing shares. A stock dividend is when people are allocated new shares based on their existing holdings. Dividends are used as an alternative to cash dividends.
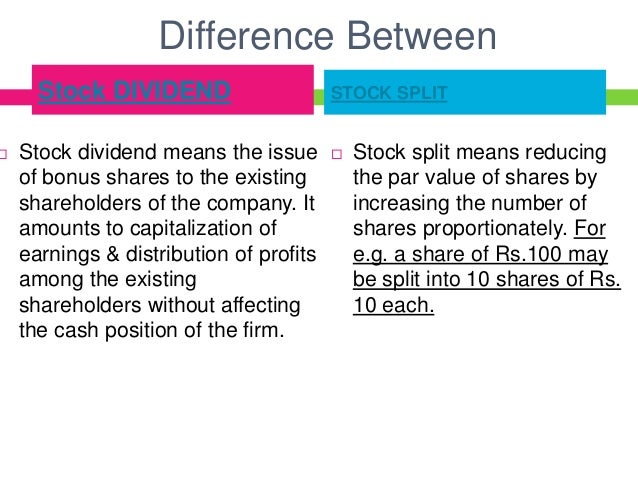
Key Difference – Stock Dividend vs Stock Split
Stock dividend and stock split are two aspects that are confused easily due to many similarities between them. Both result in an increase in the number of outstanding shares in the company without affecting the total market value.
What is Stock Dividend?
Stock dividend is one of the two principal ways in which companies can grant dividends to shareholders, the other been cash dividends. Even though cash dividend is the most widely used method, companies can offer stock dividend in years that they make little profits or losses.
What is Stock Split
Stock Split is a method where the company divides the existing shares into multiple units. As a result, the outstanding number of shares increase; however, there will be no change in the total value of shares since the split does not result in cash consideration.
What is the difference between Stock Dividend and Stock Split?
Stock split divides the existing shares into multiple shares with the intention of expanding the number of shares.
Summary – Stock Dividend vs Stock Split
Both stock dividend and stock split results in an increase in the total number of shares outstanding. The main difference between stock dividend and stock split mainly depends on the purpose they are issued for, as both result in similar outcomes.
What Happens to Dividends After a Stock Split?
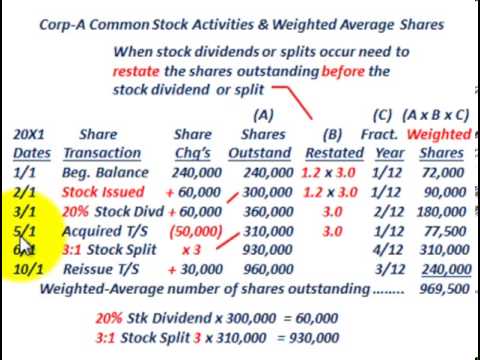
When a company decides to issue a stock split (or stock dividend ), any upcoming cash dividends can be affected in a couple of ways. In most cases, the dividend will be adjusted along with the share price. The factors to consider are the date of the stock split and the time of the cash dividend's record date.
Stock Splits After the Record Date
A stock split is an action taken by a company to divide its existing shares into multiple shares. For instance, if a stock is trading at $100 per share and the company initiates a two-for-one stock split, a holder of 100 shares before the split will hold 200 shares at $50 per share after the split.
Stock Splits Before the Record Date
As for situations when the stock split occurs before a dividend record date, the dividend will, for the most part, be paid out for the newly created shares as well. Except that the dividend likely will be split compared to previous time periods. This is due to the fact that companies want to maintain the number of dividends issued.
What Is a Stock Dividend?
A stock dividend is a dividend payment to shareholders that is made in shares rather than as cash. The stock dividend has the advantage of rewarding shareholders without reducing the company's cash balance, although it can dilute earnings per share.
How a Stock Dividend Works
Also known as a "scrip dividend," a stock dividend is a distribution of shares to existing shareholders in lieu of a cash dividend. This type of dividend may be made when a company wants to reward its investors but doesn't have the spare cash or wants to preserve its cash for other investments.
Dilution Effect
The board of a public company, for example, may approve a 5% stock dividend. That gives existing investors an additional share of company stock for every 20 shares they already own. However, this means that the pool of available stock shares in the company increases by 5%, diluting the value of existing shares.
Accounting for Small vs. Large Stock Dividends
When a stock dividend is issued, the total value of equity remains the same from both the investor's perspective and the company's perspective. However, all stock dividends require a journal entry for the company issuing the dividend.
An Example of Stock Dividends
For example, if a company were to issue a 5% stock dividend, it would increase the number of shares held by shareholders by 5% (one share for every 20 owned). If there are one million shares in a company, this would translate into an additional 50,000 shares. If you owned 100 shares in the company, you'd receive five additional shares.
What Is a Stock Dividend?
When a company issues a stock dividend, it is issuing a dividend in the form of shares, instead of cash. Also referred to as a scrip dividend, a stock dividend will grant a shareholder a fraction of shares in relation to their currently held shares.
Why Do Companies Issue Stock Dividends?
A company may issue a stock dividend if it has a limited supply of liquid cash reserves. It may also choose to issue a stock dividend if it is trying to preserve its existing supply of cash.
Impact of a Stock Dividend on Market Capitalization
Similar to a cash dividend, a stock dividend does not increase shareholder wealth or market capitalization Market Capitalization Market Capitalization (Market Cap) is the most recent market value of a company’s outstanding shares. Market Cap is equal to the current share price multiplied by the number of shares outstanding.
Example of a Stock Dividend
Colin is a shareholder of ABC Company and owns 1,000 shares. The board of directors of ABC Company recently announced a 10% stock dividend. Assuming that the current stock price is $10 and there are 100,000 total shares outstanding, what is the effect of a 10% stock dividend on Colin’s 1,000 shares?
Advantages of a Stock Dividend
A company that does not have enough cash may choose to pay a stock dividend in lieu of a cash dividend. In other words, a cash dividend allows a company to maintain its current cash position.
Disadvantages of a Stock Dividend
The market may perceive a stock dividend as a shortage of cash, signaling financial problems. Market participants may believe the company is financially distressed, as they do not know the actual reason for management issuing a stock dividend. This can put selling pressure on the stock and depress its price.
Journal Entries for a Stock Dividend
The journal entries for a stock dividend depends on whether the company is involved in a small stock dividend or a large stock dividend. The journal entries for both sizes are illustrated below:
More Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Stock Dividend. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
