
Stocks and bonds are the two main classes of assets investors use in their portfolios. Stocks offer an ownership stake in a company, while bonds are akin to loans made to a company (a corporate bond) or other organization (like the U.S. Treasury
United States Secretary of the Treasury
The secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury which is concerned with all financial and monetary matters relating to the federal government, and, until 2003, also included several major federal law enforcement agencies. This position in the feder…
How does a bond differ from stock?
Key Similarities
- Interest rate sensitivity. Both bonds and preferred stock prices fall when interest rates rise. ...
- Callability. Both securities may have an embedded call option (making them "callable") that gives the issuer the right to call back the security in case of a fall in interest ...
- Voting rights. ...
- Capital appreciation. ...
- Convertibility. ...
What are the differences between stocks and bonds?
Legal Resources
- 1. A Summary of the Key Points. ...
- 1.1 Participating Institutions. The Intra-Market Connect scheme involves arrangements for bond trading, registration, depository, clearing and settlement.
- 1.2 Qualified Investors. ...
- 1.3 Eligible Bonds. ...
- 3. ...
- 3.1 Nominee Accounts. ...
- 3.2 Bond Settlement. ...
What are the risks and benefits of stocks and bonds?
- Bonds tend to rise and fall less dramatically than stocks, which means their prices may fluctuate less.
- Certain bonds can provide a level of income stability.
- Some bonds, such as U.S. Treasuries, can provide both stability and liquidity.
What is the different between stock and mutual bond?
bonds, here are the advantages of bonds:
- You choose the desired bond’s safety
- You choose the desired bond’s yield
- Trading flexibility
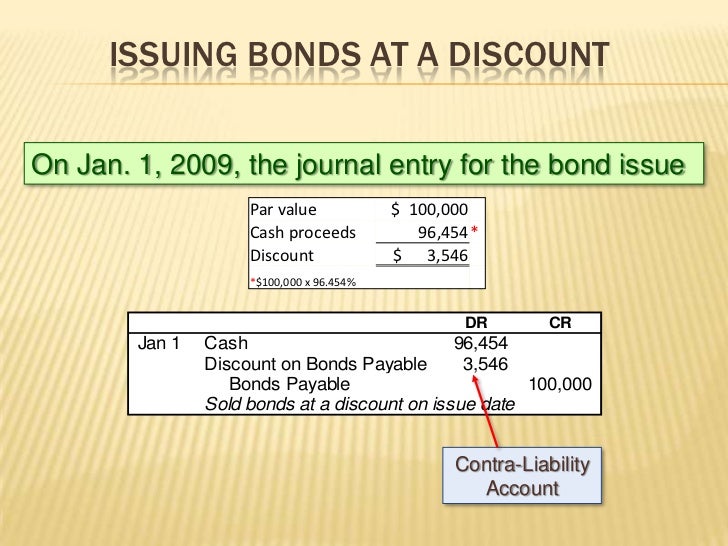
What is the idea behind bond?
The basic idea behind a bond is that an entity needs to raise money, and therefore, can sell a bond in return for the required funds. In return, they promise to pay back the initial amount that they borrowed, in addition to interest.
Why are stocks beneficial?
Stocks are beneficial for investors who have a higher risk appetite. Stocks are much more volatile, and there is a higher chance of losing your investment since equity holders are subordinated to debt holders if a company is forced to liquidate. However, in return for the risk, stockholders have a greater potential return.
What is the IPO of stocks?
Stocks are issued initially through an Initial Public Offering (IPO), and can subsequently be traded among investors in the secondary market. Stock markets are tightly regulated by the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S. and are subject to tight regulation in other countries as well.
What is the most popular stock exchange in the US?
Stocks are well known for being sold on various financial exchanges – in the United States, the most popular exchanges are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) is the largest securities exchange in the world, hosting 82% of the S&P 500, as well as 70 of the biggest.
What is the LSE?
London Stock Exchange (LSE) London Stock Exchange (LSE) The London Stock Exchange (LSE), which is based in London, the United Kingdom, is one of the leading stock markets in the world. Owned by the London Stock Exchange Group, the LSE was established in 1571, making it one of the oldest stock exchanges in the world.
What are the two most common asset classes?
Two of the most common asset classes for investments are bonds, also known as fixed-income instruments, and stocks, also known as equities. Both types of investments have a deep history within the capital markets. Capital Markets Capital markets are the exchange system platform that transfers capital from investors who want to employ their excess ...
What is interest in finance?
Interest represents the compensation rate that the investor, who is the lender in this situation, requires. They are also called fixed-income instruments because they provide a fixed amount of return, which comes in the form of interest.
What is the difference between a stock and a bond?
Stocks give you partial ownership in a corporation, while bonds are a loan from you to a company or government. The biggest difference between them is how they generate profit: stocks must appreciate in value and be sold later on the stock market, while most bonds pay fixed interest over time.
What is a bond?
Bonds are a loan from you to a company or government. There’s no equity involved, nor any shares to buy. Put simply, a company or government is in debt to you when you buy a bond, and it will pay you interest on the loan for a set period, after which it will pay back the full amount you bought the bond for.
How do bonds and stocks make money?
To make money from stocks, you’ll need to sell the company’s shares at a higher price than you paid for them to generate a profit or capital gain.
Why are bonds sold on the market?
Bonds can also be sold on the market for capital gains if their value increases higher than what you paid for them. This could happen due to changes in interest rates, an improved rating from the credit agencies or a combination of these.
What happens if you sell stock?
In this instance, if you sold them, you’d lose money. Stocks are also known as corporate stock, common stock, corporate shares, equity shares and equity securities. Companies may issue shares to the public for several reasons, but the most common is to raise cash that can be used to fuel future growth.
What does it mean to own stock?
Stocks represent partial ownership, or equity, in a company. When you buy stock, you’re actually purchasing a tiny slice of the company — one or more "shares." And the more shares you buy, the more of the company you own. Let’s say a company has a stock price of $50 per share, and you invest $2,500 (that's 50 shares for $50 each).
What is corporate bond?
A company’s ability to pay back debt is reflected in its credit rating, which is assigned by credit rating agencies like Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s. Corporate bonds can be grouped into two categories: investment-grade bonds and high-yield bonds. Investment grade. Higher credit rating, lower risk, lower returns.
What is the difference between a stock and a bond?
Key Differences. A stock is a financial instrument issued by a company depicting the right of ownership in return for funds provided as equity. A bond is a financial instrument issued for raising an additional amount of capital.
Why are bonds issued by the government?
Bonds issued by the government are extensively used and also depicts the financial stability of the country. If the yields offered are less it means the nation is in a good position to pay off its debt and does not need everyone to lend to them and vice-versa.
What is bond loan?
Bonds are actually loans that are secured by a specific physical asset. It highlights the amount of debt taken with a promise to pay the principal amount in the future and periodically offering them the yields at a pre-decided percentage. In this article, we shall understand the importance of Stocks vs Bonds and the differences between them.
Is a stock an equity or debt?
Stocks are treated as equity instruments whereas bonds are debt instruments. Debt Instruments Debt instruments provide finance for the company's growth, investments, and future planning and agree to repay the same within the stipulated time. Long-term instruments include debentures, bonds, GDRs from foreign investors.
Do stockholders have to pay DDT?
The stock market has a secondary market in place ensuring centralized trading as opposed to bonds in which trading is done Over the Counter (OTC). Stockholders may have to pay DDT (Dividend distribution tax) in case of the returns received which can further curtail the returns received but bonds are not exposed to such tax burdens.
Do bondholders get voting rights?
Bondholders are creditors to the company and do not get voting rights. The risk factor is high in stocks since the returns are not fixed or proportional ...
Do bonds have fixed returns?
On the other hand, bonds have fixed returns that have to be paid irrespective of the performance of the borrower since it is a debt amount.
What is the difference between bonds and stocks?
The difference between stocks and bonds. The difference between stocks and bonds is that stocks are shares in the ownership of a business, while bonds are a form of debt that the issuing entity promises to repay at some point in the future.
Why do you convert to stock?
Converting to stock also gives a former bond holder the right to vote on certain company issues. Both stocks and bonds may be traded on a public exchange.
Is it riskier to invest in stocks or bonds?
This means that stocks are a riskier investment than bonds. Periodic payments. A company has the option to reward its shareholders with dividends, whereas it is usually obligated to make periodic interest payments to its bond holders for very specific amounts.
Can bonds be traded on a public exchange?
Both stocks and bonds may be traded on a public exchange. This is a common occurrence for larger publicly-held companies, and much more rare for smaller entities that do not want to go through the inordinate expense of going public.
Is a stock a riskier investment than a bond?
This means that stocks are a riskier investment than bonds. Periodic payments. A company has the option to reward its ...
What is bond market?
The bond market is where investors go to trade (buy and sell) debt securities, prominently bonds, which may be issued by corporations or governments. The bond market is also known as the debt or the credit market. Securities sold on the bond market are all various forms of debt. By buying a bond, credit, or debt security, ...
What is the function of the stock market?
The primary function of the stock market is to bring buyers and sellers together into a fair, regulated, and controlled environment where they can execute their trades. This gives those involved the confidence that trading is done with transparency, and that pricing is fair and honest.
What is underwriting in bond market?
In the bond market, an underwriter buys securities from the issuers and resells them for a profit. Participants: These entities buy and sell bonds and other related securities. By buying bonds, the participant issues a loan for the length of the security and receives interest in return.
What is the difference between a bond rating and a bond rating?
This rating—expressed through a letter grade—tells investors how much risk a bond has of defaulting. A bond with a "AAA" or "A" rating is high-quality, while an "A"- or "BBB"-rated bond is medium risk. Bonds with a BB rating or lower are considered to be high-risk. 3 4
What is the Nasdaq?
Nasdaq, a global, electronic exchange that lists the securities of smaller capitalization companies from different parts of the world. Although technology and financial stock make up the bulk of the index, it also includes consumer goods and services, healthcare, and utilities.
Why do bonds fall?
Bonds, on the other hand, are more susceptible to risks such as inflation and interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall. If interest rates are high and you need to sell your bond before it matures, you may end up getting less than the purchase price.
What is mortgage bond?
A mortgage bond is a type of security backed by pooled mortgages, paying interest to the holder monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually.
What is bonding in finance?
A bond is a fixed income instrument that represents a loan made by an investor to a borrower (typically corporate or governmental). A bond could be thought of as an I.O.U. between the lender and borrower that includes the details of the loan and its payments. Bonds are used by companies, municipalities, states, ...
Who owns a bond?
Owners of bonds are debtholders, or creditors, of the issuer. Bond details include the end date when the principal of the loan is due to be paid to the bond owner and usually include the terms for variable or fixed interest payments made by the borrower.
Why is a callable bond riskier than a callable bond?
A callable bond is riskier for the bond buyer because the bond is more likely to be called when it is rising in value. Remember, when interest rates are falling, bond prices rise. Because of this, callable bonds are not as valuable as bonds that aren’t callable with the same maturity, credit rating, and coupon rate.
What is the bond coupon?
The interest payment (the coupon) is part of the return that bondholders earn for loaning their funds to the issuer.
Why does the price of a bond change?
The price of a bond changes in response to changes in interest rates in the economy. This is due to the fact that for a fixed-rate bond, the issuer has promised to pay a coupon based on the face value of the bond—so for a $1,000 par, 10% annual coupon bond, the issuer will pay the bondholder $100 each year.
What is the interest payment on a bond?
The interest payment (the coupon) is part of the return that bondholders earn for loaning their funds to the issuer. The interest rate that determines the payment is called the coupon rate . The initial price of most bonds is typically set at par, usually $100 or $1,000 face value per individual bond.
Why do bond prices fall?
When interest rates go up, bond prices fall in order to have the effect of equalizing the interest rate on the bond with prevailing rates, and vice versa.
How are bonds priced?
Bonds are priced in the secondary market based on their face value, or par. Bonds that are priced above par—higher than face value—are said to trade at a premium, while bonds that are priced below their face value—below par—trade at a discount. Like any other asset, bond prices depend on supply and demand.
Why do companies sell bonds?
Companies sell bonds to finance ongoing operations, new projects or acquisitions. Governments sell bonds for funding purposes, and also to supplement revenue from taxes. When you invest in a bond, you are a debtholder for the entity that is issuing the bond.
What are the different types of bonds?
We can further classify bonds according to the way they pay interest and certain other features: 1 Zero-Coupon Bonds: As their name suggests, zero-coupon bonds do not make periodic interest payments. Instead, investors buy zero-coupon bonds at a discount to their face value and are repaid the full face value at maturity. 2 Callable Bonds: These bonds let the issuer pay off the debt—or “call the bond”—before the maturity date. Call provisions are agreed to before the bond is issued. 3 Puttable Bonds: Investors have the option to redeem a puttable bond—also known as a put bond—earlier than the maturity date. Put bonds can offer single or several different dates for early redemption. 4 Convertible Bonds: These corporate bonds may be converted into shares of the issuing company’s stock prior to maturity.
What is the maturity of a bond?
Maturity: The date on which the bond issuer returns the money lent to them by bond investors. Bonds have short, medium or long maturities. Face value: Also known as par, face value is the amount your bond will be worth at maturity. A bond’s face value is also the basis for calculating interest payments due to bondholders.
Why is the coupon lower on a bond?
Generally speaking, the higher a bond’s rating, the lower the coupon needs to be because of lower risk of default by the issuer. The lower a bond’s ratings, the more interest an issuer has to pay investors in order to entice them to make an investment and offset higher risk.
What is fixed income bond?
Fixed income is a term often used to describe bonds, since your investment earns fixed payments over the life ...
Why do bond yields increase?
Changes in market interest rates add to the complexity. As market interest rates rise, bond yields increase as well, depressing bond prices.
