
What Are Dark Pools in Stocks and How Do They Work?
- Dark pools benefit institutional investors. Dark pool investing can save institutional investors money since they aren’t managed by a large public exchange and therefore avoid exchange fees.
- There are three types of dark pools. Dark pools are legal trading exchanges that are kept private. ...
- Pros of dark pools. ...
- Cons of dark pools. ...
What are dark pools in stock trading?
Dark pools, more loosely regulated trading venues in the United States ... trading these shares on a public exchange may result in a large decrease in the stock price, creating greater volatility in the market and an inferior execution price for the ...
How to trade dark pools in day trading?
Dark pool trading has much less pre-trade transparency as it does not show how much investors want to buy or at what price. Dark pools were designed to increase competition and cut transaction costs. With that said, dark pool trading needs traditional displayed markets to determine price benchmarks for stocks.
Are short sales by dark pools reported?
Ever since 2010, FINRA has collected short sale volume data from their TradeReporting Facilities (TRFs).† The TRFs receive data from exclusively off-exchange, or “dark,” venues. Some of these venues are Alternative Trading Systems (ATSs), or “dark pools” and some are “internalizers.” Since our analysis doesn't need to distinguish between types of off-exchange venues, we'll refer to all data from the TRFs as “dark pool” data.
What are dark pool trades?
Dark pool trades, or prints, are equity block trades executed over-the-counter (OTC) through a private exchange only available to institutional investors. These private exchanges (also called Alternative Trading Systems) are known as “dark pools” due to their complete lack of transparency.

Is dark pool trading good for a stock?
Pros. Market Impact: Trading through a dark pool generally causes less impact on a stock price than buying or selling large amounts on a public exchange. Lower Fees: Dark pools are often cheaper trading venues than the public markets.
How are dark pools legal?
Known as reg 19c3 the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission passed the regulation which would start on April 26, 1979. The new regulation allowed the emergence of dark pools through the 1980s that allowed investors to trade large block orders while avoiding market impact and giving up privacy.
How do dark pools make money?
In a dark pool trading system, investors place buy and sell orders without disclosing either the price of their trade or the number of shares. Dark pool trades are made “over the counter.” This means that the stocks are traded directly between the buyer and seller, oftentimes with the help of a broker.
Do dark pools still exist?
There are several different types of dark pools: broker or dealer-owned exchanges, such as Morgan Stanley's MS Pool and Goldman Sachs' Sigma X; independently owned exchanges offering private trading to their clients; and private exchange markets operated by public exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange's ...
What is dark pool?
Dark pools are a type of alternative trading system (ATS) that give certain investors the opportunity to place large orders and make trades without publicly revealing their intentions during the search for a buyer or seller.
When did dark pools start?
Dark pools emerged in the 1980s when the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) allowed brokers to transact large blocks of shares. Electronic trading and an SEC ruling in 2007 that was designed to increase competition and cut transaction costs have stimulated an increase in the number of dark pools.
Is a dark pool legal?
Although considered legal, dark pools are able to operate with little transparency. Those who have denounced HFT as an unfair advantage over other investors have also condemned the lack of transparency in dark pools, which can hide conflicts of interest. The Securities and Exchange Commission ( SEC) has stepped up its scrutiny of dark pools over complaints of illegal front-running that occurs when institutional traders place their order in front of a customer’s order to capitalize on the uptick in share prices. Advocates of dark pools insist they provide essential liquidity, allowing the markets to operate more efficiently.
What is a dark pool?
A dark pool is a financial exchange or hub that is privately organized where trading of financial securities is held . Dark pools are in stark contrast to public financial exchange markets, where there is a high degree of regulation and media attention. Dark pools allow investors to trade without any public exposure until after ...
Why are dark pools important?
Many private financial exchanges were established, and it facilitated traders who received very large orders and could not complete them on traditional public exchange s. Dark pools add to the efficiency of the market since there is additional liquidity for certain securities by getting them to list on the exchanges.
Why are dark pools so disadvantaged?
1. Lack of transparency. Since dark pools operate with very little oversight, they are heavily scrutinized for not putting as much regulation in place as other public exchanges. As a result, many feel that they are disadvantaged by investors who trade on the exchanges.
What are the advantages of dark pools?
Advantages of Dark Pools. Some advantages were touched on earlier, but the main advantages of dark pools are: 1. Private trading. Dark pools allow for trading execution away from the spotlight of public markets. Public markets tend to overreact or underreact due to news coverage and market sentiment.
What is block trade?
Block Trades. A block trade is simply just the sale or purchase of a very large number of securities between two parties. There are no criteria for a block trade. However, it is usually a trade that is so large that it may result in a tangible impact on the security price.
What is the benefit of dark pool trading?
2. In practice, dark pool trading provides some important benefits, such as the ability to trade a large volume of stocks while minimizing information leakage.
When was the dark pool created?
The first dark pool was created in 1986, with the launch of Instinet’s trading platform called After Hours Cross. It allowed investors to place anonymous orders that were matched after the markets closed. Just one year later, in 1987, a second platform emerged in the form of ITG’s POSIT.
Why are dark pools so popular?
The popularity of dark pools also stems from their specific trade execution formats and specialties. Almost all dark pools run as electronic limit order book markets. Some operate on a continuous trading basis throughout the day, while others are block trading-cross platforms.
What is institutional trading?
Institutional trading is global and can have a huge impact; the strategies and quantities of securities being traded can literally move their respective markets. To minimize this impact, institutional trading is often done in secret on legal, private, alternative trading systems (ATS), called “dark pools.”. Below, we’ll dive into how dark pools ...
What is a dark pool in 2021?
Dark pools are parallel, and largely opaque, institutional trading markets where large transactions in equities, bonds, and foreign currencies occur daily. They are invisible to the public and other participants in the dark pool. Institutional trading is global and can have a huge impact;
Why did traders create dark pools?
Traders wanted lower execution costs and did not want competitors to know what, when, the price, and quantity of instruments they were trading. As a result, dark pools were created so that prices were not publicly displayed .
Do dark pool exchanges affect individual investors?
They may not affect individual investors directly, but regulators worry about the negative impact on price discovery and market quality. Dark pool exchanges are highly specialized and cater to a variety of sophisticated trading strategies and different order execution models.
What is a dark pool?
Dark pools, or black pools, are privately organized and managed financial exchanges for trading securities. These dark pools aren’t accessible to the general public. Therefore, are basically unknown to retail and general investors.
When did dark pools start?
The origin of dark pools dates back to 1979. They decided to change financial regulations in the US. As a result, securities listed on one exchange could trade elsewhere. They no longer had to trade only on the exchange to which they were listed.
Why are dark pools important?
Dark pools are built to cater and provide additional liquidity and secrecy to big players trading huge blocks of securities. Dark pools allow big institutions placing large trades to avoid impacting the markets and prices. Any number of securities can be easily sold or bought away from the eye of the general public.
Why are dark pools created?
As a result dark pools were created. In fact, dark pools are also known as dark pools of liquidity. When trading huge block orders, institutions wanted to avoid impacting the markets. Hence, dark pool trading was born. Investors trading a large number of securities on the regular exchanges would move markets.
How many dark pools are there?
They allowed institutions to trade large orders without having any impact on the prices. Now there are more than fifty dark pools registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. Dark pool trading is different than being a market maker .
Why is the price of a security stable?
The price of the traded security remains stable because the trades aren’t known to retail traders. As a result, there’s no price overreaction or under reaction due to the executed order. Availability of Liquidity and Increased Efficiency. Liquidity and volume is a major part of trading any security.
What are the disadvantages of dark pools?
Let’s take a look at some of the disadvantages to dark pool trading. Total Lack of Transparency.
Why are dark pools used?
This is the main reason dark pools were created. Dark pool stocks are also used for HFT (high-frequency trading) and might help improve market efficiency.
Why is dark pool trading important?
The privacy of dark pool stock trading can be helpful in keeping details of large trades away from news media coverage. On the public market, these types of trades would likely “trigger price overreaction or underreaction,” according to Corporate Finance Institute.
Why do dark pools save money?
Dark pools benefit institutional investors. Dark pool investing can save institutional investors money since they aren’t managed by a large public exchange and therefore avoid exchange fees. Also, the intentions of their trades aren't public until after the trades are executed, which can also offer a price benefit for an institutional investor.
What is a dark pool in 2021?
ET. If you haven't heard of dark pool stocks, there’s a good reason for that. A “dark pool” is a private exchange used for trading securities in a non-public manner. The dark pools usually aren't available to the general public. They are more frequently used by large investors like hedge funds.
How many dark pools are there in 2020?
They might also be called alternative trading systems (ATS) or private trading networks. Investopedia reported that as of February 2020, over 50 dark pools were registered with the SEC, falling into three different categories. The three categories include:
What are the negatives of dark pools?
Certainly, a major negative aspect of dark pools is their lack of transparency. This leaves the dark pools “susceptible to conflicts of interest by their owners and predatory trading practices by HFT firms,” according to Investopedia.
Is the dark pool public?
The dark pools usually aren't available to the general public. They are more frequently used by large investors like hedge funds. Article continues below advertisement. Public stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange and the Nasdaq are heavily regulated and monitored by the SEC.
Dark Pools Explained in Less Than 4 Minutes
Jake Safane is a freelance writer with more than 10 years of experience in the journalism industry. He writes about investing, assets, markets, and more. Jake has been published in a variety of publications that focus on finance and sustainability.
Definition and Examples of Dark Pools
A dark pool is a place where securities transactions take place in the dark, metaphorically speaking. Within dark pools, traders typically can’t see other parties’ information regarding buying and selling securities until a transaction goes through.
How Do Dark Pools Work?
Dark pools work by having broker-dealers or other parties, such as stock exchanges, set up private electronic venues to conduct trades.
Criticisms of Dark Pools
While dark pools are legal, they have come under regulatory scrutiny because of their lack of transparency. Sometimes ATS/dark pool operators have engaged in dishonest behavior—like front-running orders (tipping off other traders about a dark-pool trade)—that’s led to enforcement from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. 1
What Do Dark Pools Mean for Individual Investors?
Individuals generally can’t access dark pools directly on their own, just as you can’t walk onto the floor of the NYSE to buy and sell stocks—orders have to go through financial professionals like brokers. Still, if your broker ultimately places your order through a dark pool, that can affect your returns.
What Is Dark Pool Investing?
Dark pools, otherwise known as Alternative Trading Systems (ATS), are legal private securities marketplaces. In a dark pool trading system investors place buy and sell orders without disclosing either the price of their trade or the number of shares.
Why do Dark Pools Exist?
Chiefly, dark pools exist for large scale investors that don’t want to influence the market through their trades.
Dark Pools and You
There’s no practical chance that an average retail trader will shift the market. Unless you manage a substantial portfolio, your influence on the market most likely isn’t going to drastically influence other investors. Technically, you buying a company’s stock will affect share prices, but practically, it won’t be to any measurable degree.
The Bottom Line
Dark pool investing isn’t usually something the average retail investor will take part in, but it may be useful for institutional investors and companies. When large scale investors plan to buy or sell a substantial amount of stock, it could influence other investors to do the same, affecting the entire market significantly.
Tips for Dark Pool Investors
If you’re interested in dark pool investing, consider working with a financial advisor to ensure it’s the right move for you. Finding the right financial advisor that fits your needs doesn’t have to be hard. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with financial advisors in your area in five minutes.
How Dark Pool Trading Works?
Dark pool trading is similar to other platforms, except they are not public. Most of the time, dark pool stocks are owned by mainstream financial companies such as Morgan Stanley or the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). But the difference is that the identity of the users is hidden during the transactions.
Examples
An example of dark pool stock trading can be quoted when an executive of a large company decides to sell 50% of his shares. He knows that this would directly impact the company he’s working for because this is a large number of shares, and his position would attract media attention to the trade.
Dark Pool Index (DIX)
The Dark pool index (DIX), is based on the same companies as the Standard & Poor’s 500 index. However, it uses the numbers from dark pools instead of the public stocks from these businesses.
Dark Pool Indicators (DIP)
The Dark Pool Indicator (DIP) is an indicator similar to the DIX, but it works differently. For starters, the DIX is based on the Standard & Poor’s 500 indexes, while the DIPs are based on how individual stocks are doing in the dark pool market.
Pros and Cons
These platforms may be attractive to investors who want to conceal their identity while they trade. However, they also have a few drawbacks. Here are the major pros and cons of trading in the dark pool:
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Dark Pool and its meaning. Here we explain how dark pool trading works along with examples, its index, and indicators. You can learn more from the following articles –
What is a dark pool?
Dark pools are an ominous sounding term for private exchanges or markets for securities trading. However, unlike stock exchanges, dark pools are not accessible by the investing public. Dark pools are also sometimes called “dark pools of liquidity”.
Why were dark pools invented?
Dark pools were invented to facilitate block trading by institutional investors who did not wish to impact the markets with their large orders and obtain adverse prices for their trades. Dark pool data does NOT provide us with INTENT, we do not know if the large block trade or sweep was a buy or sell.
Why do you want options flow on the same screen as dark pool trades?
You also want a tool that displays options flow on the same screen as the dark pool trades because options flow will also help you determine if a dark pool print was a buy or sell order. What happens is that large institutions often front-run their own dark pool orders with large option sweeps and block orders.
What does it mean to cross a block in a dark pool?
When a trader speaks of a “cross” or “crossing a block”, it means to match and execute a block trade or “crossing a board lot”. Once an order has been crossed it is referred to as a “fill”.
Do dark pool block orders give us INTENT?
Remember, dark pool block orders do NOT give us INTENT. Often times an institutional trader is building a large position for a client and that can take time. We will see repeat orders coming off the dark pool for a single stock but its price doesn’t really seem to do anything and stays somewhat range bound.
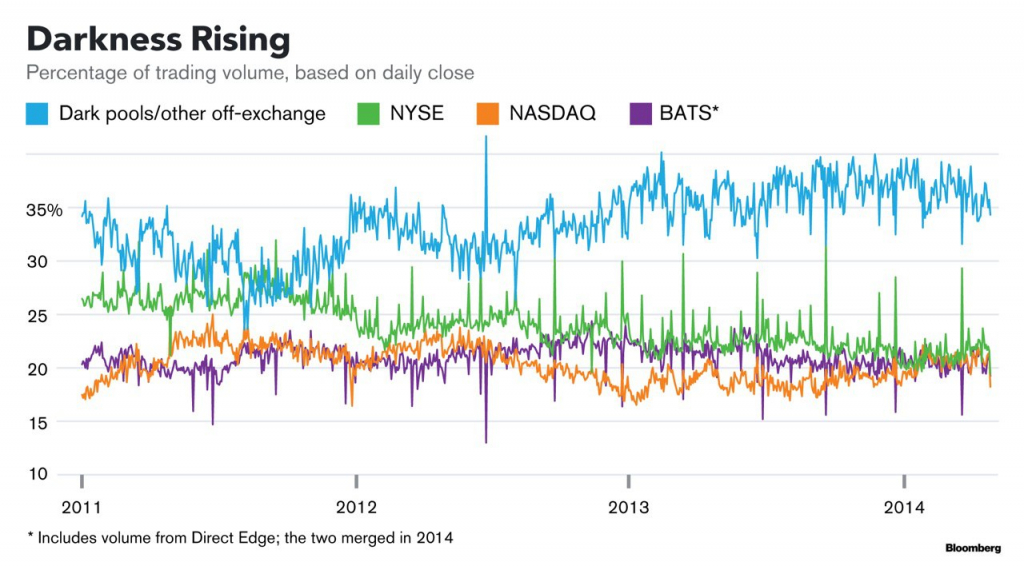
The Rationale For Dark Pools
Why Use A Dark Pool?
- Contrast this with the present-day situation, where an institutional investor can use a dark pool to sell a one million share block. The lack of transparency actually works in the institutional investor’s favor since it may result in a better-realized price than if the sale was executed on an exchange. Note that, as dark pool participants do not disclose their trading intention to the exch…
Types of Dark Pools
- As of February 2022, there were more than 60 dark pools registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). There are three types:34
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dark Pools
- The biggest advantage of dark pools is that market impact is significantly reduced for large orders. Dark pools may also lower transaction costs because dark pool trades do not have to pay exchange fees, while transactions based on the bid-ask midpoint do not incur the full spread.7 If the amount of trading in dark pools owned by broker-dealers and electronic market makersconti…
Regulating Dark Pools
- The recent HFT controversy has drawn significant regulatory attention to dark pools. Regulators have generally viewed dark pools with suspicion because of their lack of transparency. This controversy may lead to renewed efforts to curb their appeal. One measure that may help exchanges reclaim market share from dark pools and other off-exchange venues could be a pilo…
What Is A Dark Pool?
Understanding The Dark Pool
- Dark pools emerged in the 1980s when the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) allowed brokers to transact large blocks of shares. Electronic trading and an SEC ruling in 2005 that was designed to increase competition and cut transaction costs have stimulated an increase in the number of dark pools.12Dark pools can charge lower fees than exchanges because they are oft…
Dark Pools and High-Frequency Trading
- With the advent of supercomputers capable of executing algorithmic-based programs over the course of just milliseconds, high-frequency trading (HFT) has come to dominate daily trading volume. HFT technology allows institutional traders to execute their orders of multimillion-share blocks ahead of other investors, capitalizing on fractional upticks or downticks in share prices. …
Critiques of Dark Pools
- Although considered legal, dark pools are able to operate with little transparency. Those who have denounced HFT as an unfair advantage over other investors have also condemned the lack of transparency in dark pools, which can hide conflicts of interest. Due to complaints, the SEC conducted research and presented their 2015 report, scrutinizing dark pools for illegal front-runn…
Examples of Dark Pools
- There are several different types of dark pools: broker or dealer-owned exchanges, such as Morgan Stanley's MS Pool and Goldman Sachs' Sigma X; independently owned exchanges offering private trading to their clients; and private exchange markets operated by public exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange's Euronext. A privately-owned market will hav…