Beta coefficient is a measure of sensitivity of a company's stock price to movement in the market. It is an indicator of a stock's systematic risk which is the undiversifiable risk inherent in the financial system as a whole. Beta coefficient is an important input in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM
Capital asset pricing model
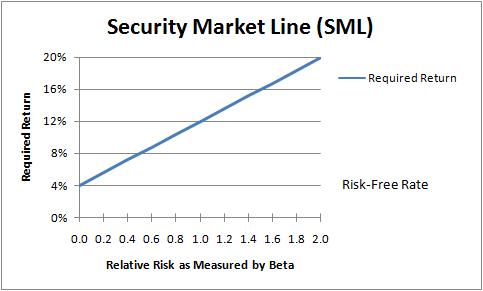
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is an empirical model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk.
How to easily calculate the beta of a stock?
Top 3 Formula to Calculate Beta
- Covariance/Variance Method. To calculate the covariance Calculate The Covariance Covariance is a statistical measure used to find the relationship between two assets and is calculated as the standard deviation ...
- By Slope Method in Excel. We can also calculate Beta by using the slope function in excel. ...
- Correlation Method. ...
How do you calculate the beta of a stock?
Part 1 Part 1 of 4: Calculating Beta Using a Simple Equation
- Find the risk-free rate. This is the rate of return an investor could expect on an investment in which his or her money is not at risk, such as ...
- Determine the respective rates of return for the stock and for the market or appropriate index. These figures are also expressed as percentages.
- Subtract the risk-free rate from the stock's rate of return. ...
How do you calculate beta of stock?
Stock Beta formula. Stock’s Beta is calculated as the division of covariance of the stock’s returns and the benchmark’s returns by the variance of the benchmark’s returns over a predefined period. Below is the formula to calculate stock Beta. Stock Beta Formula = COV(Rs,RM) / VAR(Rm)
What stocks have the highest beta?
- Microsoft has a beta of around 1.25. This means an investor can reasonably expect that this stock is 25% more volatile than the market. ...
- Walt Disney Company has a beta right around 1.03. This puts its volatility right in line with the broader market. ...
- In contrast, Duke Energy has a beta of around 0.27. ...

What does a stock beta of 1.5 mean?
Roughly speaking, a security with a beta of 1.5, will have move, on average, 1.5 times the market return. [More precisely, that stock's excess return (over and above a short-term money market rate) is expected to move 1.5 times the market excess return).]
What is a good beta coefficient?
A beta coefficient below 1 means that the stock has a systematic risk lower than the market, and hence would offer below-market return; and a beta coefficient greater than 1 shows that the stock has an above-average risk and hence, must provide above-average return.
What does a stock beta of 0.5 mean?
If a stock had a beta of 0.5, we would expect it to be half as volatile as the market: A market return of 10% would mean a 5% gain for the company. Here is a basic guide to beta levels: Negative beta: A beta less than 0, which would indicate an inverse relation to the market, is possible but highly unlikely.
What does a β of 1.3 mean?
The beta for a stock describes how much the stock's price moves compared to the market. If a stock has a beta above 1, it's more volatile than the overall market. For example, if an asset has a beta of 1.3, it's theoretically 30% more volatile than the market.
What does a beta of 0.7 mean?
A fund with a beta of 0.7 has experienced gains and losses that are 70% of the benchmark's changes. A beta of 1.3 means the total return is likely to move up or down 30% more than the index. A fund with a 1.0 beta is expected to move in sync with the index."
How do you read a stock beta?
A beta that is greater than 1.0 indicates that the security's price is theoretically more volatile than the market. For example, if a stock's beta is 1.2, it is assumed to be 20% more volatile than the market. Technology stocks and small cap stocks tend to have higher betas than the market benchmark.
What does a beta of 0.9 mean?
A beta that is greater than 1.0 means that the fund is more volatile than the benchmark index. A beta of less than 1.0 means that the fund is less volatile than the index. In theory, if the market goes up 10%, a fund with a beta of 1.0 should go up 10%; if the market drops 10%, the fund should drop by an equal amount.
What is a good PE ratio for stocks?
So, what is a good PE ratio for a stock? A “good” P/E ratio isn't necessarily a high ratio or a low ratio on its own. The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better.
What does a beta of 0.2 mean?
If your industry has a beta of 0.2, it is only 20% as risky as the index. That means if the S&P 500 loses 10%, your industry only loses about 2%.
What does a beta of 0.8 mean?
If the stock is more volatile than the market, its beta will be more than 1, and if it is less volatile than the market, its beta will be less than 1. For example, a stock with a beta of 0.8 would be expected to return 80% as much as the overall market.
What does a beta of 1.1 mean?
Each tenth of a point represents the percentage of volatility. For example, if a stock beta value is 1.1, then it is considered to have a 10 percent greater volatility than the market.
What does negative beta mean in stocks?
A negative beta correlation would mean an investment that moves in the opposite direction from the stock market. When the market rises, then a negative-beta investment generally falls. When the market falls, then the negative-beta investment will tend to rise.
Does a higher beta mean more risk?
Yes. A higher beta indicates higher volatility and hence a higher risk relative to the market.
Does a higher beta mean more reward?
It means a higher potential reward for a given move in the market, yes.
Does Beta only capture downside price volatility?
No. Beta captures relative volatility, which considers both directions.
What is beta in stocks?
Beta is a measure of the volatility — or systematic risk — of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole. Beta is used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), which describes the relationship between systematic risk and expected return for assets (usually stocks). CAPM is widely used as a method for pricing risky securities ...
What does it mean when a stock has a beta of less than 1.0?
Beta Value Less Than One. A beta value that is less than 1.0 means that the security is theoretically less volatile than the market. Including this stock in a portfolio makes it less risky than the same portfolio without the stock.
What is a beta of 1.0?
A stock with a beta of 1.0 has systematic risk. However, the beta calculation can’t detect any unsystematic risk. Adding a stock to a portfolio with a beta of 1.0 doesn’t add any risk to the portfolio, but it also doesn’t increase the likelihood that the portfolio will provide an excess return.
Why is beta important?
Beta is useful in determining a security's short-term risk, and for analyzing volatility to arrive at equity costs when using the CAPM. However, since beta is calculated using historical data points, it becomes less meaningful for investors looking to predict a stock's future movements.
How does beta work?
How Beta Works. A beta coefficient can measure the volatility of an individual stock compared to the systematic risk of the entire market. In statistical terms, beta represents the slope of the line through a regression of data points.
What is beta in capital asset pricing?
Beta, primarily used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), is a measure of the volatility–or systematic risk–of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole.
What does a negative beta mean?
Some stocks have negative betas. A beta of -1.0 means that the stock is inversely correlated to the market benchmark. This stock could be thought of as an opposite, mirror image of the benchmark’s trends. Put options and inverse ETFs are designed to have negative betas.
What is beta in stock market?
Stock Beta is one of the statistical tools that quantify the volatility in the prices of a security or stock with reference to the market as a whole or any other benchmark used for comparing the performance of the security. It is actually a component of Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
What does it mean when the beta of a stock is negative?
The Stock Beta can have three types of values: Beta < 0: If the Beta is negative, then this implies an inverse relationship between the stock and the underlying market or the benchmark in comparison. Both stock and the market or the benchmark will move in the opposite direction. Beta = 0: If the Beta is equal to zero, ...
What does a beta of 1 mean?
Beta of 1 implies that the volatility of the stock is exactly the same as that of the underlying market or the index in both qualitative and quantitative terms. Beta of greater than 1 implies that the stock is more volatile than the underlying market or index. A negative Beta is possible but highly unlikely.
What does it mean when the beta is greater than zero?
Beta > 0: If the Beta is greater than zero, then there is a strong direct relationship between the stock and the underlying market or the benchmark. Both stock and the market or the benchmark will move in the same direction. Some further insight is as follows:
What does it mean when the beta is 0?
Beta = 0: If the Beta is equal to zero, then this implies that there is no relation between the movement of the returns of the stock and the market or the benchmark, and hence both are too dissimilar to have any common pattern in price movements . Beta > 0: If the Beta is greater than zero, then there is a strong direct relationship between ...
Is a negative beta of gold a good thing?
A negative Beta is possible but highly unlikely. Most investors believe that gold and stock based on gold tend to perform better when the market dives. Whereas a Beta of zero is possible in the case of government bonds acting as risk-free securities providing a low yield to the investors.
What is beta coefficient?
Home » Accounting Dictionary » What is a Beta Coefficient? Definition: A beta coefficient measures how likely the price of a security or a stock will change to a movement in the market price. The Beta of a stock or security is also used to measure the systematic risks associated with that investment.
What is the beta of a stock?
The calculation of Beta is a form of regression analysis, as it typically represents the slope of the security’s characteristic line; a straight line which shows the relationship between the rate of return of a stock and the rate of return from the market.
What is the beta of Apple?
For example, Apple Inc’s (AAPL) beta is 1.44, meaning its stocks are more volatile and is 44% more likely to respond to a movement in the market. The Coca Cola Company (KO) has a β coefficient of 0.74, meaning its stocks are less volatile and is 26% less likely to respond to a movement in the market.
What is the beta of utilities stocks?
It must be noted that most utilities stocks have a beta of less than 1. On the other hand, most trades in technology, like listings on Nasdaq, have a β coefficient of greater than 1, indicating a likelihood of higher returns with more associated risks.
What happens if the coefficient is less than one?
If the coefficient is less that one, then the security’s returns are less likely to respond to movements in the market. If the β coefficient is greater than 1, then the security’s returns are more likely to respond to movements in the market; more volatile.
What is asset beta?
Unlevered Beta / Asset Beta Unlevered Beta (Asset Beta) is the volatility of returns for a business, without considering its financial leverage. It only takes into account its assets. , on the other hand, only shows the risk of an unlevered company relative to the market.
Why is equity beta called equity beta?
It is also commonly referred to as “equity beta” because it is the volatility of an equity based on its capital structure. Capital Structure Capital structure refers to the amount of debt and/or equity employed by a firm to fund its operations and finance its assets. A firm's capital structure.
What is leveraged beta?
Levered beta, also known as equity beta or stock beta, is the volatility of returns for a stock, taking into account the impact of the company’s leverage from its capital structure. It compares the volatility (risk) of a levered company to the risk of the market. Levered beta includes both business risk. Systemic Risk Systemic risk can be defined ...
Is a company with a 0f 0.79 more volatile than the market?
Also, a company with a β of 1.30 is theoretically 30% more volatile than the market. Similarly, a company with a β 0f 0.79 is theoretically 21% less volatile than the market.
What is beta in stocks?
What Is Beta? Beta is a measure of a stock's volatility in relation to the overall market. By definition, the market, such as the S&P 500 Index, has a beta of 1.0, and individual stocks are ranked according to how much they deviate from the market.
What does beta mean in investing?
Of course, when investors consider risk, they are thinking about the chance that the stock they buy will decrease in value. The trouble is that beta, as a proxy for risk, doesn't distinguish between upside and downside price movements. For most investors, downside movements are a risk, while upside ones mean opportunity.
What is beta in CAPM?
Beta is a component of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), which is used to calculate the cost of equity funding. The CAPM formula uses the total average market return and the beta value of the stock to determine the rate of return that shareholders might reasonably expect based on perceived investment risk.
Why is beta important?
To followers of CAPM, beta is useful. A stock's price variability is important to consider when assessing risk. If you think about risk as the possibility of a stock losing its value, beta has appeal as a proxy for risk. Intuitively, it makes plenty of sense.
Why does beta change over time?
A stock's beta will change over time because it compares the stock's return with the returns of the overall market. Benjamin Graham, the "father of value investing," and his modern advocates tried to spot well-run companies with a "margin of safety"—that is, an ability to withstand unpleasant surprises.
Why do analysts use beta?
Analysts use it often when they want to determine a stock's risk profile. However, while beta does say something about price risk, it has its limits for investors looking to determine fundamental risk factors.
What does value investor mean?
A value investor would argue that a company represents a lower-risk investment after it falls in value —investors can get the same stock at a lower price despite the rise in the stock's beta following its decline.
What does a beta of 1 mean?
A beta of 1 means that a stock's volatility matches up exactly with the markets. A higher beta indicates great volatility, and a lower beta indicates less volatility.
What does higher beta mean?
A higher beta indicates great volatility, and a lower beta indicates less volatility. Calculating beta for a given stock is not too difficult, despite the intimidating jargon. To calculate it, all you need is some market data over a period of time and a spreadsheet program. Why calculate beta yourself?
How long should you use beta?
If you're a buy and hold investor, you should use a longer time period to calculate beta, maybe five or even 10 years. If you're a trader, buying and selling frequently, you should use a beta over a much shorter time frame, potentially just a few weeks, days, or even less.
