How to find the historical PE ratio for any stock?
The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better. However, the long answer is more nuanced than that.
What does a PE ratio tell you?
PE ratio stands for the price-earnings ratio. It is a valuation metric that provides investors with information about whether a company's shares are trading at an attractive price given their prospective earnings growth rate. P/E ratio or price to earnings ratio is …
What is the current PE ratio?
PEG Ratio PEG Ratio is the P/E ratio of a company divided by the forecasted Growth in earnings (hence "PEG"). It is useful for adjusting high growth companies. The ratio adjusts the traditional P/E ratio by taking into account the growth rate in earnings per …
What can P/E ratio tell you?

What is a good PE ratio for stocks?
Is a PE ratio of 100 good?
Is it better to have a higher or lower PE ratio?
Is 30 a good PE ratio?
A P/E of 30 is high by historical stock market standards. This type of valuation is usually placed on only the fastest-growing companies by investors in the company's early stages of growth. Once a company becomes more mature, it will grow more slowly and the P/E tends to decline.
What is Uber's PE ratio?
Should I buy a stock with high PE ratio?
Whats a good dividend yield?
Why PE ratio is important?
What PE ratio is too high?
Who is the most accurate stock analyst?
How do you know if a stock is overvalued?
Price Earnings Ratio Formula
P/E = Stock Price Per Share / Earnings Per ShareorP/E = Market Capitalization / Total Net EarningsorJustified P/E = Dividend Payout Ratio / R – Gwh...
P/E Ratio Formula Explanation
The basic P/E formula takes current stock price and EPS to find the current P/E. EPS is found by taking earnings from the last twelve months divide...
Why Use The Price Earnings Ratio?
Investors want to buy financially sound companies that offer cheap shares. Among the many ratios, the P/E is part of the research process for selec...
Limitations of Price Earnings Ratio
Finding the true value of a stock cannot just be calculated using current year earnings. The value depends on all expected future cash flows and ea...
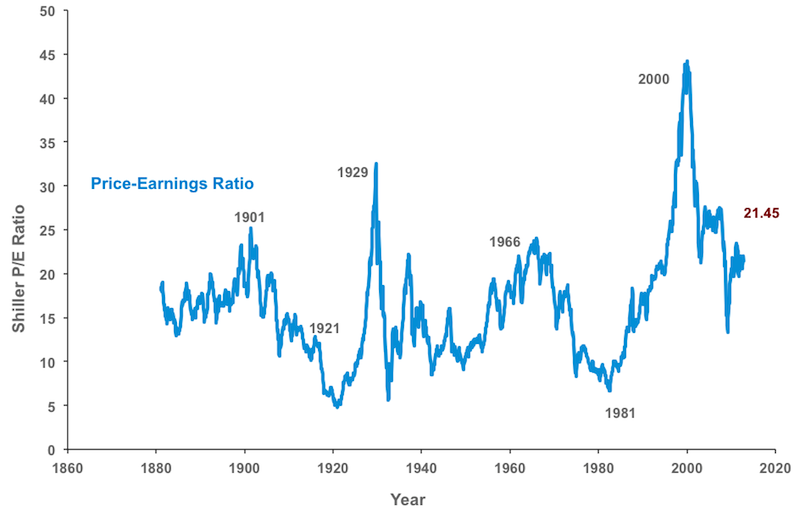
When to use historical PE ratio?
Historical PE ratios are often used with the S&P 500 when analyzing trends and deciding whether the overall market is “expensive” or “cheap.”
What is the P/E ratio of Booking Holdings?
However, it’s not as expensive as other travel website stocks. Booking Holdings has a P/E ratio of 12. Keep that in mind.
Why is a PEG ratio of 1 or less considered an undervalued investment?
A PEG ratio of 1 or less is generally considered an undervalued investment because its price is low compared to growth expectations.
Why is the P/E ratio skewy?
This can skew the P/E ratio. Finally, the downside to the P/E is that just because the P/E ratio suggests a stock is “cheap” doesn ’t mean the investor should buy it.
Why do utilities have lower P/E?
Utility companies tend to have lower P/E ratios given their low historical earnings . Meanwhile, technology companies have enjoyed higher P/E ratios due to their higher earnings growth.
What is industry PE?
Industry PE ratios are the average (mean) P/E ratio of all the companies that operate within a certain industry.
What is earnings yield?
The earnings yield is displayed as a percentage and allows investors to compare a stock to other assets, such as fixed income securities.
What is the PE Ratio?
The price-earnings (PE) ratio is the most popular measure of stock-market valuation. It shows what you are paying for each dollar of earnings. If the PE ratio is high, then investors think that yields will be increased in future and vice versa.
Fundamentals of PE Ratio
P/E ratio is the price of a company's share divided by its earnings per share. The earnings, as the company reports them, are gross earnings.
How is PE Ratio calculated?
The PE ratio is calculated by dividing the market price of a share by its earnings per share. The result is then multiplied by 100. A PE ratio of 8, for example, means that for every rupee of profit earned by the company, the shares are being sold at 8 rupees. A PE ratio of 15 means it's being sold at 15 rupees for every rupee of profit.
How to Use PE Ratios for Stock Market Investing?
The price-to-earnings ratio, or pe ratio, is the most common way to value a stock. It's also one of the concepts in finance that's hardest to understand.
Understanding the PE Ratio
The most commonly used method to determine the fair market value of a share of common stock is to find its intrinsic value based on future cash inflows discounted at the risk-free rate. The resulting value is divided by the number of shares outstanding to get the fair market value per share (often called the intrinsic value).
Why Do Investors Look at PE Ratios?
Investors look at PE Ratio while taking an investment decision. They invest in companies where earnings are growing faster than the stock price. In such a case, they believe that its earnings will ultimately justify its high price tag.
Wrapping Up
PE Ratio is an important financial term. It denotes the relative "cheapness" or "expensiveness" of a company compared to its competitors. Diving into the numbers of a company represents some risk for making mistakes in a company's actual earnings. Understanding PE Ratio will facilitate your investment decisions.
What is a peg ratio?
PEG Ratio PEG Ratio is the P/E ratio of a company divided by the forecasted Growth in earnings (hence "PEG"). It is useful for adjusting high growth companies. The ratio adjusts the traditional P/E ratio by taking into account the growth rate in earnings per share that are expected in the future. Examples, and guide to PEG
What does low P/E mean in stocks?
Companies with a low Price Earnings Ratio are often considered to be value stocks. It means they are undervalued because their stock price trade lower relative to its fundamentals. This mispricing will be a great bargain and will prompt investors to buy the stock before the market corrects it. And when it does, investors make a profit as a result of a higher stock price. Examples of low P/E stocks can be found in mature industries that pay a steady rate of dividends#N#Dividend A dividend is a share of profits and retained earnings that a company pays out to its shareholders. When a company generates a profit and accumulates retained earnings, those earnings can be either reinvested in the business or paid out to shareholders as a dividend.#N#.
What is justified P/E ratio?
The justified P/E ratio#N#Justified Price to Earnings Ratio The justified price to earnings ratio is the price to earnings ratio that is "justified" by using the Gordon Growth Model. This version of the popular P/E ratio uses a variety of underlying fundamental factors such as cost of equity and growth rate.#N#above is calculated independently of the standard P/E. In other words, the two ratios should produce two different results. If the P/E is lower than the justified P/E ratio, the company is undervalued, and purchasing the stock will result in profits if the alpha#N#Alpha Alpha is a measure of the performance of an investment relative to a suitable benchmark index such as the S&P 500. An alpha of one (the baseline value is zero) shows that the return on the investment during a specified time frame outperformed the overall market average by 1%.#N#is closed.
What is a growth stock?
Companies with a high Price Earnings Ratio are often considered to be growth stocks. This indicates a positive future performance, and investors have higher expectations for future earnings growth and are willing to pay more for them. The downside to this is that growth stocks are often higher in volatility, and this puts a lot of pressure on companies to do more to justify their higher valuation. For this reason, investing in growth stocks will more likely be seen as a risky#N#Risk Aversion Risk aversion refers to the tendency of an economic agent to strictly prefer certainty to uncertainty. An economic agent exhibiting risk aversion is said to be risk averse. Formally, a risk averse agent strictly prefers the expected value of a gamble to the gamble itself.#N#investment. Stocks with high P/E ratios can also be considered overvalued.
How to find current P/E?
The basic P/E formula takes the current stock price and EPS to find the current P/E. EPS is found by taking earnings from the last twelve months divided by the weighted average shares outstanding#N#Weighted Average Shares Outstanding Weighted average shares outstanding refers to the number of shares of a company calculated after adjusting for changes in the share capital over a reporting period. The number of weighted average shares outstanding is used in calculating metrics such as Earnings per Share (EPS) on a company's financial statements#N#. Earnings can be normalized#N#Normalization Financial statements normalization involves adjusting non-recurring expenses or revenues in financial statements or metrics so that they only reflect the usual transactions of a company. Financial statements often contain expenses that do not constitute a company's normal business operations#N#for unusual or one-off items that can impact earnings#N#Net Income Net Income is a key line item, not only in the income statement, but in all three core financial statements. While it is arrived at through#N#abnormally. Learn more about normalized EPS#N#Normalized EPS Normalized EPS refers to adjustments made to the income statement to reflect the up and down cycles of the economy.#N#.
What is the difference between EPS and fair value?
It is a popular ratio that gives investors a better sense of the value. Fair Value Fair value refers to the actual value of an asset - a product, stock, or security - that is agreed upon by both the seller and the buyer.
What is equity research analyst?
Equity Research Analyst An equity research analyst provides research coverage of public companies and distributes that research to clients.