
Stock. Title. Fixed income refers to any type of investment under which the borrower or issuer is obliged to make payments of a fixed amount on a fixed schedule. For example, the borrower may have to pay interest at a fixed rate once a year, and to repay the principal amount on maturity. Fixed-income securities can be contrasted with equity securities – often referred to as stocks and shares – that create no obligation to pay dividends or any other form of income.
What is the best fixed income investment?
- fixed income
- bonds
- real estate
- active management
What are the types of fixed income securities?
Types of Fixed Income Securities. Debt Mutual Funds; Debt Mutual funds pool in resources from investors and invest the corpus primarily in various debt instruments such as bonds, fixed income securities,etc. Investment in these instruments ensures fixed returns for the investor. Also, these funds invest in debt securities with good credit ratings.
What stocks should I invest in?
Key Points
- AbbVie and Medical Properties Trust are two healthcare stocks that offer juicy dividends.
- Energy stocks Devon and Enterprise Products Partners have especially attractive dividends right now.
- Telecom giant Verizon not only pays a solid dividend but its stock is cheap as well.
Why invest in fixed income investments?
While the diversification benefits of investing in fixed income securities are substantial over time, it’s difficult to justify investing in bonds in the current environment with yields set to rise and inflation eating away at any nominal return.
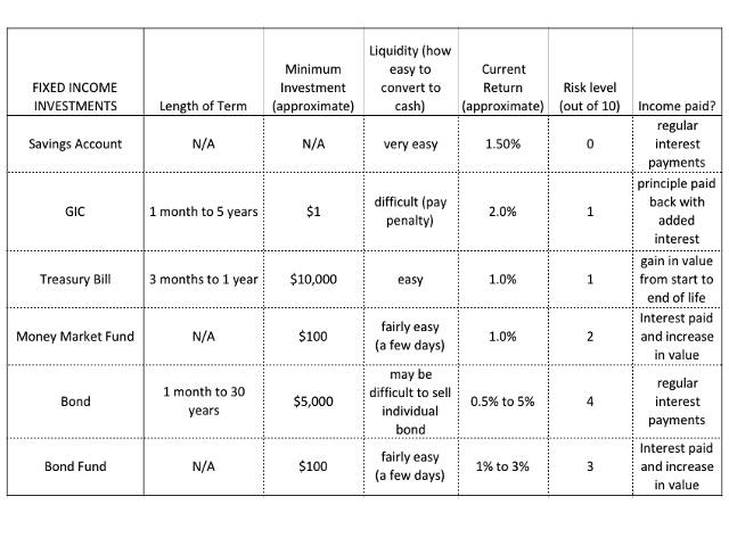
What is an example of a fixed income investment?
Treasury bonds and bills, municipal bonds, corporate bonds, and certificates of deposit (CDs) are all examples of fixed-income products. Bonds trade over-the-counter (OTC) on the bond market and secondary market.
Are fixed income investments safe?
The U.S. Treasury guarantees government fixed-income securities and considered safe-haven investments in times of economic uncertainty. On the other hand, corporate bonds are backed by the financial viability of the company. In short, corporate bonds have a higher risk of default than government bonds.
Can fixed income funds lose money?
The Bottom Line. Can you lose money on bonds and other fixed-income investments? Yes, indeed; there are far more ways to lose money in the bond market than people imagine.
What is the disadvantage of a fixed income investment?
Disadvantages of Fixed Income Investments Interest rate risk: Fixed income investments are subject to the interest rate risk. This risk arises when the interest rate in the market in which the person has invested rises.
What is the safest investment with the highest return?
9 Safe Investments With the Highest ReturnsCertificates of Deposit.Money Market Accounts.Treasury Bonds.Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities.Municipal Bonds.Corporate Bonds.S&P 500 Index Fund/ETF.Dividend Stocks.More items...•
What are pros and cons of fixed-income investing?
Pros and cons of fixed income investingProsConsLower risksPotentially lower returnsSteady returnsInterest rate riskPotential tax benefitsIssues with access to cashMay 11, 2022
Can I retire on 500000?
Key Takeaways. It may be possible to retire at 45 years of age, but it will depend on a variety of factors. If you have $500,000 in savings, according to the 4% rule, you will have access to roughly $20,000 per year for 30 years.
Where can I invest my fixed-income now?
8 great fixed-income funds to buy for 2022:Vanguard Inflation-Protected Securities (VIPSX)Invesco National AMT-Free Municipal Bond ETF (PZA)Vanguard Intermediate-Term Bond ETF (BIV)iShares Core Total USD Bond Market ETF (IUSB)Dimensional Core Fixed-Income ETF (DFCF)More items...
Which is the best fund to invest now?
Here's the list of the five best mutual funds for SIP:Fund Name3-year Return (%)*Parag Parikh Flexi Cap Fund Direct-Growth20.52%InvestPGIM India Flexi Cap Fund Direct-Growth20.13%InvestMirae Asset Emerging Bluechip Fund Direct-Growth17.47%InvestSBI Focused Equity Fund Direct Plan-Growth13.58%Invest3 more rows
Should I have fixed-income in my portfolio?
Fixed income serves four key roles in a portfolio: Diversification from equities, capital preservation, income and inflation protection. Many investors would benefit from evaluating whether their bond holdings are meeting these goals.
How does a fixed-income investment work for you?
A fixed-income investment is essentially a loan that an investor gives to an issuer. The issuer can be a government or corporate borrower. The borrower pays the investor a fixed amount of interest until the maturity date. Once the maturity date is reached, the borrower repays the investor the principal amount.
Is fixed-income safer than equities?
Individual investors often have better access to equity markets than fixed-income markets. Equity markets offer higher expected returns than fixed-income markets, but they also carry higher risk.
Why is fixed income better than stocks?
This is because fixed income assets are generally less sensitive to macroeconomic risks, such as economic downturns and geopolitical events.
What are the risks of fixed income?
There are four major risks associated with fixed income: 1 Interest rate risk#N#When interest rates rise, bond prices fall, meaning the bonds you hold lose value. Interest rate movements are the major cause of price volatility in bond markets. 2 Inflation risk#N#Inflation is another source of risk for bond investors. Bonds provide a fixed amount of income at regular intervals. But if the rate of inflation outpaces this fixed amount of income, the investor loses purchasing power. 3 Credit risk#N#If you invest in corporate bonds, you take on credit risk in addition to interest rate risk. Credit risk (also known as business risk or financial risk) is the possibility that an issuer could default on its debt obligation. If this happens, the investor may not receive the full value of their principal investment. 4 Liquidity risk#N#Liquidity risk is the chance that an investor might want to sell a fixed income asset, but they’re unable to find a buyer.
What happens to bonds when interest rates rise?
When interest rates rise, bond prices fall, meaning the bonds you hold lose value. Interest rate movements are the major cause of price volatility in bond markets. Inflation is another source of risk for bond investors. Bonds provide a fixed amount of income at regular intervals.
What happens to the investor when the rate of inflation outpaces this fixed amount of income?
But if the rate of inflation outpaces this fixed amount of income, the investor loses purchasing power. Credit risk. If you invest in corporate bonds, you take on credit risk in addition to interest rate risk.
What is floating rate loan?
One of the attractions to the bank loan market is that it is generally a floating rate market. Floating rate means that rather than fixed, as interest rates rise, the coupons on your loans in this case can rise as well.
Can fixed income investments cause inflation?
However, you should be mindful of inflation risk, which can cause your investments to lose value over time. Fixed income investments can help you generate a steady source of income. Investors receive a fixed amount of income at regular intervals in the form of coupon payments on their bond holdings.
What is fixed income?
Fixed income is an investment that provides a steady stream of cash flows. Common examples include defined-benefit pensions, bonds, and loans. Fixed income also includes certificates of deposit, savings accounts, money market funds, and fixed-rate annuities. You can invest in fixed-income securities via bond mutual funds, ...
What is long term fixed income investment?
Long-term fixed-income investments is called a bond. This type of instrument reflects a debt arrangement between a corporate or government issuer and an investor (creditor). For corporate issues, the interest rates offered depend on Treasury rates as well as the credit risk and duration risk associated with the issue.
What is fixed rate annuity?
Fixed-rate annuities are an insurance product that guarantees you a fixed payment over an agreed-upon period. These are increasing since fewer workers receive pensions. One variation of this product that can provide some long-term upside is a variable annuity. In certain cases, it can offer an agreed-upon fixed payout stream, which is underwritten based on a basket of equities funded with your initial contribution. The basket of equities can increase the value of the annuity in the event of a major increase in the equity market, but still provide a base level fixed income.
How does fixed income affect the economy?
How Fixed Income Affects the U.S. Economy. Fixed income provides most of the liquidity that keeps the U.S. economy humming. Businesses go to bond markets to raise funds to grow (for shorter term needs, they use the money markets, which are also comprised of very near-term fixed-income securities).
What is bond mutual fund?
An example is a European company issuing bonds in Japan, which are denominated in U.S. dollars. Bond mutual funds are mutual funds that own a large number of bonds.
What is interest rate swap?
Interest rate swaps are contracts that allow investors to swap their future interest rate payments (or receipts). Oftentimes, this arrangement involves a payer (or receiver) of a fixed-rate stream of interest bond and a payer (or receiver) of a floating-rate stream of interest. They trade OTC.
Why do banks use money market instruments?
They use money market instruments to get the cash needed for day-to-day operations. Treasury bills, notes, and bonds serve as benchmarks for other interest rates. When demand for Treasury debt declines, yields rise. Investors then demand higher interest rates on other, fixed-income products.
What is fixed income securities?
Fixed income securities are a type of debt instrument that provides returns in the form of regular, or fixed, interest payments and repayments of the principal when the security reaches maturity. The instruments are issued by governments, corporations, and other entities to finance their operations.
What is fixed income?
The term fixed income refers to the interest payments that an investor receives, which are based on the creditworthiness of the borrower and current interest rates. Generally speaking, fixed income securities such as bonds pay a higher interest, known as the coupon. Bond Pricing Bond pricing is the science of calculating a bond's issue price based ...
What is bond pricing?
Bond pricing allows investors. , the longer their maturities are. The borrower is willing to pay more interest in return for being able to borrow the money for a longer period of time. At the end of the security’s term or maturity, the borrower returns the borrowed money, known as the principal or “par value.”.
What is ABS in financial terms?
ABS represents a collection of such assets that have been packaged together in the form of a single fixed-income security. For investors, asset-backed securities are usually an alternative to investing in corporate debt.
What is the safest short term debt instrument?
Treasury Bills. Considered the safest short-term debt instrument, Treasury bills are issued by the US federal government. With maturities ranging from one to 12 months, these securities most commonly involve 28, 91, and 182-day (one month, three months, and six months) maturities. These instruments offer no regular coupon, or interest, payments.
What are the principal risks associated with fixed income securities?
Principal risks associated with fixed-income securities concern the borrower’s vulnerability to defaulting on its debt. Such risks are incorporated in the interest or coupon that the security offers, with securities with a higher risk of default offering higher interest rates to investors.
What are money market instruments?
Money market instruments include securities such as commercial paper, banker’s acceptances, certificates of deposit (CD), and repurchase agreements (“repo”). Treasury bills are technically included in this category, but due to the fact that they are traded in such high volume, they have their own category here.
What is fixed income investment?
Fixed-income investments. 1. U.S. Treasuries. Issued by the federal government, U.S. Treasuries pay interest semiannually until the bond matures and the principal is repaid in full. The tenor of a U.S. Treasury bond can vary from as little as one month, known as a U.S. Treasury bill, all the way up to a 30-year U.S. Treasury bond.
What is investment grade bond?
Investment-grade corporate bonds. Companies often need to borrow money for periods spanning years, rather than mere weeks or months. When they do, companies issue bonds that offer a stated rate of interest on a fixed schedule, typically paying interest semiannually.
What is high yield bond?
Junk bonds are those issued by entities that have a credit rating of BB+/Ba1 or lower, or don't have a credit rating at all. These bonds are typically scheduled to pay interest semiannually and mature in only a few years.
What is the best way to invest in short term debt?
2. Money market funds. Money market funds invest in the short-term debt of the U.S. government and respected large companies. Generally, money market funds seek to invest in debt that matures in less than one year, thus providing safety from interest-rate fluctuations and reducing the risk that a borrower will default.
What are the three strategies investors use to find the best balance of risk and reward?
Here are three common strategies investors use. 1. Laddering strategy.
What is income stock?
An income stock is an equity security that pays regular, often steadily increasing dividends. Income stocks usually offer a high yield that may generate the majority of the security's overall returns. While there is no specific breakpoint for classification, most income stocks have lower levels of volatility than the overall stock market, ...
Where do income stocks come from?
Any excess cash flow from profits can be directed back to investors on a regular basis. Income stocks can come from any industry, but investors commonly find them within real estate (through real estate investment trusts, or REITs), energy sectors, utilities, natural resources and financial institutions.
Why do conservative investors invest in income stocks?
Many conservative investors seek income stocks, because they want some exposure to corporate profit growth. At the same time, these stocks have steady streams of revenue that allow for a low risk and consistent source of revenue, perhaps for investors who are older and do not have regular salaries anymore.
Do growth stocks pay dividends?
In contrast with income stocks, growth stocks usually do not pay dividends. Instead, company management often prefers to reinvest retained earnings into capital projects .
What is fixed income?
Fixed-income securities typically have lower risks, which means they provide lower returns. They generally involve default risk, i.e., the risk that the issuer will not meet the cash flow obligations. The only fixed-income securities that involve virtually no default risk are government treasury securities. Treasury securities include treasury bills (that mature in one year), notes (that mature in 1 to 10 years), and long-term bonds (that mature in more than 10 years).
Which fixed income securities have no default risk?
The only fixed-income securities that involve virtually no default risk are government treasury securities. Treasury securities include treasury bills (that mature in one year), notes (that mature in 1 to 10 years), and long-term bonds (that mature in more than 10 years).
What is equity account?
Both equity#N#Equity Accounts Equity accounts consist of common stock, preferred stock, share capital, treasury stock, contributed surplus, additional paid-in capital, #N#and fixed-income#N#Fixed Income Bond Terms Definitions for the most common bond and fixed income terms. Annuity, perpetuity, coupon rate, covariance, current yield, par value, yield to maturity. etc.#N#products are financial instruments that can help investors achieve their financial goals. Equity investments generally consist of stocks#N#Stock What is a stock? An individual who owns stock in a company is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever be dissolved). The terms "stock", "shares", and "equity" are used interchangeably.#N#or stock funds, while fixed income securities generally consist of corporate or government bonds.
What are common stocks?
Common stocks, the securities that are traded most often, grant the owners the right to claim the issuing company’s assets, receive dividends, and vote at shareholders’ meetings.
What is equity investment?
Equity. Equity investments allow investors to hold partial ownership of issuing companies. As one of the principal asset classes, equity plays a vital role in financial analysis and portfolio management. Equity investments come in various forms, such as stocks and stock mutual funds.
How to calculate cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. owners are entitled to dividends before common stock owners, although holders of both stocks can only receive dividends after all creditors of the company have been satisfied.
What are the two variables used to describe the risk and return of an equity instrument?
We generally use two variables – expected return (E) and standard deviation (σ) – to describe the risk-and-return characteristics of an equity instrument. In constructing a portfolio, we consider these two variables of each asset class to determine their respective weights.
What is fixed income investment?
A fixed-income investment involves an issuer or a borrower making payments to a lender or investor at a set date for a set amount. In the current low interest rate environment, most financial advisors suggest investors hold short- and intermediate-term funds that will offer buyers some flexibility if rates rise.
How long does a fixed income fund last?
The fund can hold investments that run up to five years in maturity, but the vast majority of holdings are very short-term durations – in the zero-to-three months time frame – or will mature in one to three years.
How long does FXNAX hold bonds?
dollar-denominated bonds with at least one year until maturity. McDonald also says that FXNAX holds bonds with "reasonable" durations of five to seven years, which means the fund won't be too affected by rising interests.
Is FXNAX a bond?
FXNAX can act as a core investment-grade bond holding in a portfolio. McDonald notes that the fund focuses on high-quality investments, "so that internal losses, due to default, are nearly impossible.".
/shutterstock_314942846-5bfc3ae546e0fb00511dcb1a.jpg)