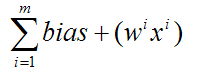
If you can’t track that down, ask the company’s investor services or your brokerage firm for information. Brokers must now keep cost-basis data for stocks bought in 2011 or later, but most have older records. You might also find clues in your tax files—for example, showing when you started paying taxes on the dividends.
What is cost basis in investing?
Cost basis is the total price you paid to buy an investment. You calculate your capital gain or loss by subtracting the price you paid to buy and from the price you sold the investment for. Total Price Sold – Total Price Paid = Capital Gain (positive) or Capital Loss (negative) Let’s say you buy 15,000 shares of stock at a price of $7 per share.
How do you find the average cost basis of a stock?
If you have a range of possible purchase dates, find the average price of your stock or bond during the date range. If you only have a purchase year, find the average price during that year. Once the cost basis is in your portfolio record, sell the securities.
How do I report the cost basis of a share purchase?
If you know a share’s sale price but not its purchase price, here are four options for how to report the cost basis of the transaction. If the share was issued by a publicly traded company (U.S. or foreign), look up the historical rate for the shares online and report the share price at the time when you purchased the shares.
What happens to the cost basis of a stock on death?
The stock was originally purchased for $10 per share and is valued at $50 on the date of death. In this case, the cost basis is “stepped up” to $50, essentially extinguishing the $40 per share gain. Keep in mind, estate and inheritance taxes could still apply.
How do I find the original cost basis of a stock?
You can calculate your cost basis per share in two ways: Take the original investment amount ($10,000) and divide it by the new number of shares you hold (2,000 shares) to arrive at the new per-share cost basis ($10,000/2,000 = $5).
How does the IRS know your cost basis?
You usually get this information on the confirmation statement that the broker sends you after you have purchased a security. You—the taxpayer—are responsible for reporting your cost basis information accurately to the IRS. You do this in most cases by filling out Form 8949.
Do I have cost basis for a stock I received for free?
The basis in the free stock is equal to the income you received when given the stock. You may need to adjust the cost basis as listed. The sale proceeds would be the amount reported on Form 1099-MISC.
What if my 1099-B does not show cost basis?
The Form 1099-B you receive may only report the date of the sale and the sales proceeds amount. If it does not report the date acquired or cost basis, you must still enter that information on Schedule D and/or Form 8949. As a result, you should keep and maintain this information with your tax records.
What to do if cost basis is missing?
What if cost or adjusted basis is "missing" from 1099-B form? Should I leave it blank? No, The cost basis is the amount that you paid for the investment. If you leave it blank you will be taxed on 100% of the proceeds.
Why is cost basis not reported to IRS?
Short Term sales with cost basis not reported to the IRS means that they and probably you did not have the cost information listed on your Form 1099-B.
How do I know if basis was reported to IRS?
Sample of Form 1099-B 1545-0715) SHORT-TERM TRANSACTIONS FOR WHICH BASIS IS REPORTED TO THE IRS–Report on Form 8949, Part I, with Box A checked. Section A indicates whether the cost basis for the transaction was reported to the IRS and if the transaction is a short-term or long-term transaction.
Why is my cost basis Zero?
Yes, if you are certain you didn't pay anything for these shares, then you can enter "0" as the Cost Basis. Before doing this, check with your employer's payroll department and make sure that the company did not include any "cost" for these shares in your taxable income (Box 1 of your Form W-2).
How do I find my cost basis on TD Ameritrade?
To access the platform, just log into your account at tdameritrade.com, go to My Account, and select Cost Basis.
What if cost basis is wrong?
If the cost basis you report is too low, then you will overpay taxes. The cost basis is especially tricky to understand when you sold stock you acquired from employee stock compensation, such as stock options, restricted stock units, or an employee stock purchase plan.
Do I have to report every stock transaction?
Regarding reporting trades on Form 1099 and Schedule D, you must report each trade separately by either: Including each trade on Form 8949, which transfers to Schedule D. Combining the trades for each short-term or long-term category on your Schedule D. Include a separate attached spreadsheet showing each trade.
When did brokerage firms start tracking cost basis?
In 2008, Congress enacted mandatory cost basis reporting for brokers and mutual funds.
How long do brokers keep records?
Brokers must keep records for six years, and some go back further (although you may have to pay a small fee to receive a duplicate statement). If your broker doesn't keep records that far back, try to remember when you bought the shares and see what they were selling for then.
When was PG&E stock purchased?
It was purchased between 1957 and 1980. I will be selling PG&E stock soon and have no idea what the cost basis is. It was purchased between 1957 and 1980. If you bought the stock yourself, your basis is what you paid for the shares, including brokerage commissions (different rules apply if you inherited the stock or received it as a gift).
Does AT&T have a basis page?
Some companies, like AT& T, have a special Web page just for tax basis information, which includes a link to worksheets that can help you figure out your basis -- a tricky task if the company has had any spin-offs or mergers since you bought the stock.
When is the cost basis stepped up?
When assets are inherited, the cost basis is stepped-up to the value on the date of death (or six months later if alternate valuation is used). For example, let’s assume that a parent leaves a stock to their child.
Can you gain or lose on a sale of a property if you use donor's adjusted basis?
According to the IRS, if you use the donor's adjusted basis for figuring a gain and get a loss, and then use the fair market value for figuring a loss and get a gain, you have neither a gain nor loss on the sale or disposition of the property.
How to avoid missing cost basis?
Still, you should do two things to avoid missing cost basis: Verify that your custodian records cost basis. You will usually find this information on their website. The records may be listed as cost basis or gains/loss. Save a copy of your gains/loss reports before transferring accounts from one custodian to another.
What is the goal of investing?
The goal of investing is to buy and sell at a profit. You want to make money. You report gains to the IRS when you sell. The gains determine the tax bill related to the investment you made.
What is cost basis?
Cost basis is the original value of a security, which typically represents its purchase price plus other costs you paid (such as commissions and fees) and any adjustments such as dividends and stock splits.
How to find unknown cost basis?
To find an unknown cost basis for stocks and bonds, you first must determine the purchase date. Look for any purchase-related records you might have, such as brokerage statements or receipts. If no purchase records exist, take an educated guess about when you might have bought the securities based on life events happening when they were purchased.
What happens if you don't know the principal of a stock?
But if you do not know what the investment principal was, you cannot provide a cost basis for the securities you sold. In that case, the Internal Revenue Service will assume that 100 percent of the sale proceeds is a taxable capital gain. This means you will pay tax on the principal originally invested in the stocks and bonds as well as on ...
Do you pay capital gains tax on a small investment?
Paying the Appropriate Tax. If yours is a small investment holding and you would have to spend much time and money to arrive at a cost basis, you may want to consider simply paying capital gains tax as if your securities’ cost basis was zero.
Do you pay taxes on stocks when you sell them?
When you sell stocks or bonds, you'll make a profit or take a loss. If you make a profit, you'll owe income tax on your capital gain. But before you know how much tax you owe, you first have to figure the security's "cost basis.".