
When a stock’s market price rises above the strike price, a put option is out of the money. This means that, other than the premium, the option has no value and the price is close to nothing. The reason is simple: you would have to pay more for the shares than the strike price you would get by exercising the option to sell the shares.
How does a stock price actually go up or down?
Stock prices go up and down based on supply and demand. When people want to buy a stock versus selling it, the price goes up. If people want to sell a stock versus buying it, the price goes down. Forecasting whether there will be more buyers or sellers in a stock requires additional research, however. Buyers are attracted to stocks for any number of reasons, from low valuation to new product ...
What makes Stocks go up or down in price?
What causes a stock’s price to go up or down?
- Short-term factors that move stock prices. Legendary Wall Street analyst and mentor to Warren Buffett, Benjamin Graham, once said that in the short run the market is a voting machine, ...
- Long-term factors that move stock prices. So if the market is a weighing machine in the long term, what exactly is it weighing? ...
- Bottom line. ...
How does the expected return affect a stock price?
Key Points
- A company that is publicly traded must announce its earnings reports quarterly. ...
- Beta is a metric used to signal the risk in a particular stock. ...
- Analysts constantly assess the health of public companies to assess the value of its equity and debt instruments, and their outlook affects stock and bond prices in secondary markets.
How do you calculate the current price of a stock?
- Three ways to calculate the relative value of a stock. Many investors will use ratios to decide whether a stock represents relative value compared with its peers.
- Some more tips to help you value a company’s shares. As well as the above ratios, which give you an idea of a stock’s relative value in line with similar ...
- Ready to invest? ...
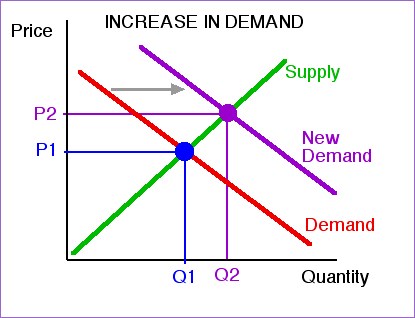
What causes share price to increase?
The main factors that determine whether a share price moves up or down are supply and demand. Essentially, if more people want to buy a share than sell it, the price will rise because the share is more sought-after (the 'demand' outstrips the 'supply').
How does increase in stock price help a company?
Higher stock price means fewer shares are paid for the same cash value. Attracts Investors: A higher share price increases the interest of customers because they expect a greater return from your company. Earns Employee's Trust: Companies with increasing stock prices have a tendency to attract better quality employees.
What happens if no one sells a stock?
When there are no buyers, you can't sell your shares—you'll be stuck with them until there is some buying interest from other investors. A buyer could pop in a few seconds, or it could take minutes, days, or even weeks in the case of very thinly traded stocks.
What does high stock price mean?
In general, a high stock price indicates good financial health and a low stock price indicates poor overall financial health. As a business grows and goes through hard times, its stock price usually rises and falls, respectively.
Why does a stock's price change?
A stock’s price can change because its multiple (s) change. This means that stock traders change their view of what a stock is worth without any underlying change in the stocks achieved revenues or earnings. For example the (trailing) P/E ratio or multiple changes, or the Price to Book value ratio changes. Generally this means that the outlook ...
What does it mean when a stock's fundamentals change?
2. A stock’s fundamentals change as a result of releasing updated financial data.
What is high expected growth?
Often companies with very high expected growth trade at high multiples such as 50 times earnings or more. In this case the investor is hoping that the earnings will grow very rapidly and therefore the stock price will rise even if the P/E multiple falls back somewhat. This is classic growth stock investing and generally involves buying stocks with high multiples.
How to know if a stock is undervalued?
1. You can look for stocks that seem under-valued based on their multiples. For example a company with a strong earnings outlook that is trading at (say) 10 times earnings and (say) 1.5 times book value could increase rapidly in price due to a “multiple expansion”. For example the market could suddenly recognize that the stock is under-valued and the P/E could jump from 10 to 20 as the stock price doubles. If you buy this stock at a P/E of 10 and then it rises to a P/E of 20, you have effectively out-smarted the investor who sold it. The company’s fundamentals may not have changed but the market’s view of what the company is worth has simply increased. This is classic value investing and generally involves buying stocks with low multiples.
Do all investors hope that every stock they buy will increase in price?
All Investors hope that every stock that they buy will increase in price. But few investors understand much about what would cause a stock price to increase.
Why do stocks increase or decrease in price?
Stocks increase or decrease in price on the basis of what investors think the stock is worth, not directly because the company is doing well or in response to analyses of worth. If Jim Cramer of "Mad Money" pitches a stock on CNBC, that almost always immediately drives up the price more than the company's increased earnings, ...
Why do investors drive up the price of a stock?
Because investors are both emotional and fallible, sometimes they drive up the price farther than the metrics warrant. At other times, because a company does business in an unglamorous or out-of-favor business sector or for other reasons, investors don't respond to the improved metrics, creating a "value" stock, one that on the basis of an objective analysis of its metrics ought to be priced higher. Warren Buffett, the fabled Omaha investor, generally invests in these underpriced companies and has become a multi-billionaire by taking advantage of the disparity between how investors feel about a stock and its intrinsic value.
What Gives a Stock Its Value?
One of the more interesting developments in stock market analysis over the past two to three decades is a decline among prominent economists in the belief that the market is fully rational – that by and large the price of every stock accurately represents its real value – the so-called "efficient market hypothesis." Increasingly, economists have come to see that the market isn't fully rational at all – that it's profoundly affected by what economists call "sentiment," meaning the various emotions investors bring to their stock purchases. Consequently, a revision of the earlier belief goes something like this: Every stock is worth what investors believe it's worth.
Why does a stock move up?
A stock moves up or down in price because of investor sentiment. If investors believe a stock is worth more than its current price, it moves up. If they believe it's worth less, it moves down.
How do stock metrics affect price?
In one sense, a stock's metrics determine its price movement: as a company's success in the market becomes known – with the release of quarterly reports, for example, or because of a favorable news release – investors respond to the good news. The volume of buy orders increases and, in response to increased demand, the price moves up.
How to see how investor emotions affect the market?
To see how investor emotions affect the market, consider Everyman, a typical investor. Begin by tracking Everyman's emotional state toward the end of a bear market. Research shows that at this point in the market cycle the average investor is profoundly pessimistic and risk-averse.
How long does the bull market last?
But the average bull market lasts more than eight years, and the first couple of years are particularly profitable for investors. Sooner or later, Everyman will be fully back in the market again and, as time goes on, investing with increasing confidence and boldness.
Why do stocks change?
So, why do stock prices change? The best answer is that nobody really knows for sure. Some believe that it isn't possible to predict how stocks will change in price while others think that by drawing charts and looking at past price movements, you can determine when to buy and sell. The only thing we do know as a certainty is that stocks are volatile and can change in price extremely rapidly.
What is the principal theory of stock price?
That being said, the principal theory is that the price movement of a stock indicates what investors feel a company is worth. Don't equate a company's value with the stock price. The value of a company is its market capitalization, which is the stock price multiplied by the number of shares outstanding. For example, a company that trades ...
How to determine the value of a stock?
The important things to grasp about this subject are the following: 1 At the most fundamental level, supply and demand in the market determine stock price. 2 Price times the number of shares outstanding (market capitalization) is the value of a company. Comparing just the share price of two companies is meaningless. 3 Theoretically earnings are what affect investors' valuation of a company, but there are other indicators that investors use to predict stock price. Remember, it is investors' sentiments, attitudes, and expectations that ultimately affect stock prices. 4 There are many theories that try to explain the way stock prices move the way they do. Unfortunately, there is no one theory that can explain everything.
What is price times the number of shares outstanding?
Price times the number of shares outstanding (market capitalization) is the value of a company. Comparing just the share price of two companies is meaningless. Theoretically earnings are what affect investors' valuation of a company, but there are other indicators that investors use to predict stock price. Remember, it is investors' sentiments, ...
Can earnings affect stock price?
Of course, it's not just earnings that can change the sentiment towards a stock (which, in turn, changes its price). It would be a rather simple world if this were the case! During the dot-com bubble, for example, dozens of Internet companies rose to have market capitalizations in the billions of dollars without ever making even the smallest profit. As we all know, these valuations did not hold, and most all Internet companies saw their values shrink to a fraction of their highs. Still, the fact that prices did move that much demonstrates that there are factors other than current earnings that influence stocks. Investors have developed literally hundreds of these variables, ratios and indicators. Some you may have already heard of, such as the P/E ratio , while others are extremely complicated and obscure with names like Chaikin Oscillator or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) .
What affects stock price?
High demand for a stock drives the stock price higher, but what causes that high demand in the first place? It's all about how investors feel:
What is demand increase in stocks?
Sometimes demand for stocks in general increases, or demand for stocks in a particular stock market sector increases. A broad-based demand increase can drive individual stocks higher without any company-specific news. One example: The COVID-19 pandemic led to consumers increasing spending online at the expense of brick-and-mortar stores. Some investors believe this change is here to stay, which led to an increase in demand and higher prices for e-commerce stocks across the board.
Why is demand for a stock so high?
Ultimately, demand for a stock is driven by how confident investors are about that stock's prospects. In the short term, things like quarterly earnings reports that beat expectations, analyst upgrades, and other positive business developments can lead investors to be willing to pay a higher price to acquire shares. On the flip side, disappointing earnings reports, analyst downgrades, and negative business developments can cause investors to lose interest, thus reducing demand and forcing sellers to accept lower prices.
Why should long term investors be laser focused on a company's potential to increase its profits over many years?
While a lot of ink is spilled about daily fluctuations in stock prices, and while many people try to profit from those short-term moves , long-term investors should be laser-focused on a company's potential to increase its profits over many years. Ultimately, it's rising profits that push stock prices higher.
Why is the value of a stock important?
In the long term, the value of a stock is ultimately tied to the profits generated by the underlying company. Investors who believe a company will be able to grow its earnings in the long run, or who believe a stock is undervalued, may be willing to pay a higher price for the stock today regardless of short-term developments. This creates a pool of demand undeterred by day-to-day news, which can push the stock price higher or prevent big declines.
Do long term investors care about short term developments?
Long-term investors, like those of us at The Motley Fool, don't much care about the short-term developments that push stock prices up and down each trading day. When you have many years or even decades to let your money grow, things such as analyst upgrades and earnings beats are irrelevant.
What could impact a stock's price?
Anything from a public relations crisis to breaking company news could impact a stock’s price. When investors, particularly at the hedge-fund level, sense cause for concern, we can watch that drama play out on the stock market. The same happens with factors like the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies, geopolitical events like wars and boycotts, and even factors like innovation and technology, such as the hype we see around cryptocurrency right now.
What factors influence share prices more than any other?
But one factor influences share prices more than any other: Profit.
How to measure market sentiment?
Plumb says we can measure market sentiment using the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), or the “fear index.” The higher the VIX goes, the higher the fear in traders. The lower the VIX, the lesser the fear. When the market is stressed, VIX goes up. The VIX averaged 15.4 in 2019 but reached an almost-record high of 82.69 at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020, according to Reuters.
Why invest in index funds?
One benefit of investing in index funds is that you can start building wealth even if you don’t have a lot of technical knowledge about the stock market. But for investors interested in adding individual stocks to their portfolio, it can be helpful to have a basic understanding of how to research stocks and monitor stock prices. That starts by paying attention to the news cycle, market conditions — and even your gut.
How does a breakout news story affect a stock's price?
Everything from a breakout news story to a shareholder meeting can impact a stock’s price. A lot of times, it has to do with supply and demand, such as we saw during the infamous GameStop surge, when a collective of small individual traders drove share prices up. While some lucky traders were able to sell the stock at its peak and profit, many traders hoping to make a quick buck instead lost money when the price eventually fell back down .
What is market sentiment?
Market sentiment, or investor sentiment, is the investor outlook regarding a particular stock’s performance in the market. Sentiment drives demand, which also influences supply.
Can hedge fund traders predict stock price?
Nobody can predict every element that goes into stock price fluctuations, though many try. That’s what a hedge fund trader’s entire job is all about: trying to pool money together to maximize returns on investments, all while predicting — or influencing, some say — what the market does.
What does it mean when a stock price decreases with higher volume?
People are not interested in those stocks. The stock’s whose price decreases with higher volume means a short build up has taken place in those stocks, and shorting those stocks is favorable. It is based on the technical analysis with fibonacci level.
Why does the price of a stock decrease with volume?
And when selling pressure increases, it leads to decrease in price.
Why is it easy to fluctuate the stock price of low traded stocks?
Since, it is always easy to fluctuate the stock price of low traded stocks as the volume of such stock is very low & hen ce,all that a broker needs to do is to create a small stimulus of either buying or selling the stock (manipulating the stock price) which later becomes the sentiment of the market & hence he ends up getting good profit either by buying at a lower price or selling at a higher price.
What does it mean when the volume of a stock increases?
But if volume increases in the inverse direction of the stock price, it indicates that current trend may be reversed. Hence increasing volume in the market indicates traders are not expecting current uptrend to follow, thus they start selling the stock which leads to downfall in the stock price.
How does volume affect trading?
If you see volume is increasing tremendously then it means smart money has entered into trade. Smart money in intraday trading refers to a big giant who's interested in the trade. If you see price of share is increasing with volume increasing then then smart money is interested in buying the share. And other way around if you see volume increasing and share price is going down then smart money is interested in selling. Sudden surge of volume is because of smart money. Normal traders like you and me buy or sell like 500 shares, 1000 shares, or even a lot. But smart money trades like 10,000,00 shares in one go. Which will huge reflection on the numbers or volume. If a retail trader wants to make some quick bucks then he should follow smart money. The catch here is entry and exit. Which you should be careful of.
What does volume mean in trading?
Volume is a secondary indicator which tells how many shares were bought and sold in a given time period - usually a day. The number of shares bought is always the same as the number of shares sold. Some short term traders and analysts think a large volume traded means a lot of conviction.
What happens if you see the option chain of the stock?
Any support in the downtrend will reverse the price. If you see the option chain of the stock’s price , you will see that at certain level selling is highest and at certain level , buying is highest. Those will act as support and resistance.
Interest rates are going up
Super-easy pandemic monetary policy gave strong support to asset prices. The prices of bonds in the secondary markets increased as new bonds could be issued at lower rates (and thus lower current yields - see example on how interest rates affect bonds).
How do stocks perform when interest rates rise?
Historically, when rates increase it's actually good for stocks overall. Again, the implications are that rates are going up to slow (not stop) the rate of economic growth. A strong economy can be very good for companies.
Diversification, my old friend
The purpose of diversification is because like broad-based market moves, there’s no way to know when certain sectors, styles, or factors are going to outperform or underperform, for how long, and to what extent.
