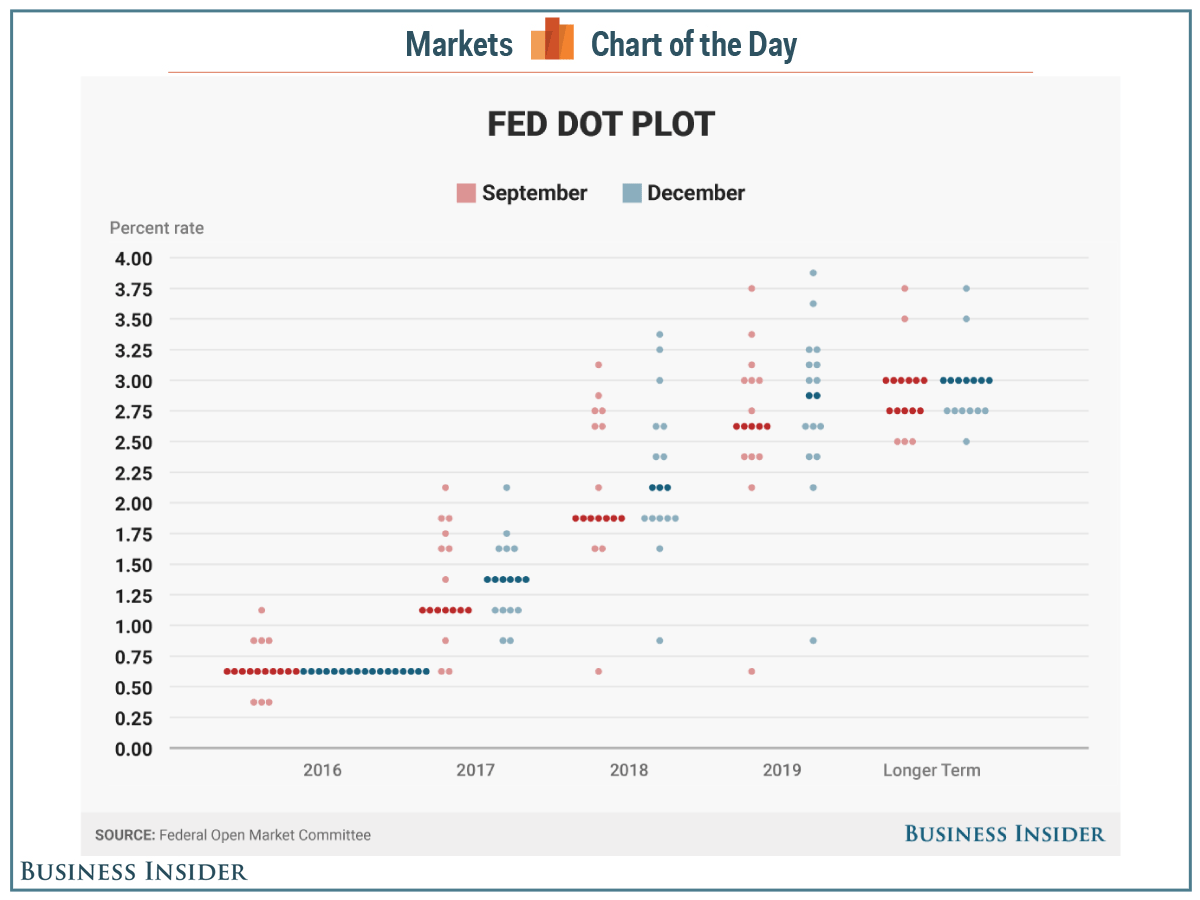
What happens to stocks when interest rates rise? When interest rates are rising, both businesses and consumers will cut back on spending. This will cause earnings to fall and stock prices to drop.
How will the Fed’s rate hike affect the stock market?
If the Fed believes the economy is lagging, it can cut the federal funds rate to make borrowing money cheaper for individuals and businesses. This move typically pushes up stock prices, rewarding investors better returns. The first months of the Covid-19 crisis provide the most recent example of this dynamic.
What happens to stocks when interest rates rise?
Historically, when rates increase it's actually good for stocks overall. Again, the implications are that rates are going up to slow (not stop) the rate of economic growth. A strong economy can be very good for companies.
What happens when stock prices go down?
If enough companies experience declines in their stock prices, the whole market, or the key indexes many people equate with the market—the Dow Jones Industrial Average, S&P 500, etc.—will go down. With a lowered expectation in the growth and future cash flows of a company, investors will not get as much growth from stock price appreciation.
How will a rate hike affect your mortgage rates?
Because longer-term 15-year and 30-year mortgage rates are fixed and tied to Treasury yields and the broader economy, those homeowners won’t be immediately impacted by a rate hike.
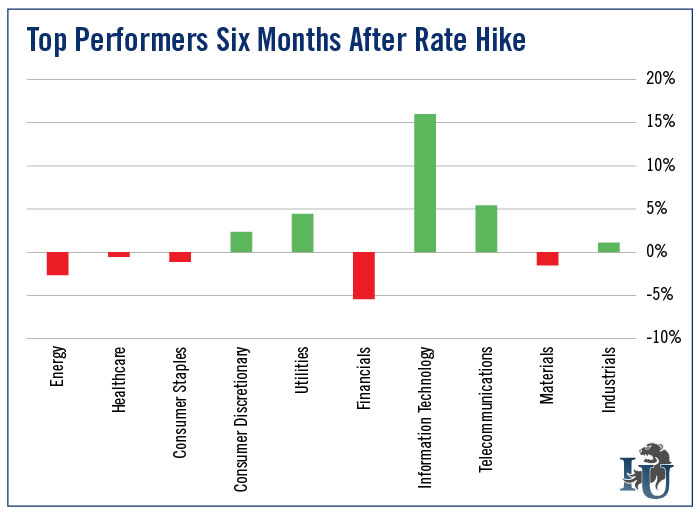
Is rate hike good for stocks?
Rising or falling interest rates can also impact the psychology of investors psychology. When the Federal Reserve announces a hike, both businesses and consumers will cut back on spending. This will cause earnings to fall and stock prices to drop, and the market may tumble in anticipation.
Do stocks go up when prices go up?
By this we mean that share prices change because of supply and demand. If more people want to buy a stock (demand) than sell it (supply), then the price moves up. Conversely, if more people wanted to sell a stock than buy it, there would be greater supply than demand, and the price would fall.
What happens when rates hike?
When Fed rate hikes make borrowing money more expensive, the cost of doing business rises for public (and private) companies. Over time, higher costs and less business could mean lower revenues and earnings for public firms, potentially impacting their growth rate and their stock values.
What happens when a company's stock price goes up?
A steadily rising share price signals that a company's top brass is steering operations toward profitability. Furthermore, if shareholders are pleased, and the company is tilting towards success, as indicated by a rising share price, C-level executives are likely to retain their positions with the company.
How can you tell if a stock will go up?
We want to know if, from the current price levels, a stock will go up or down. The best indicator of this is stock's fair price. When fair price of a stock is below its current price, the stock has good possibility to go up in times to come.
Why do stock prices change every second?
Stock prices change every second according to market activity. Buyers and sellers cause prices to change and therefore prices change as a result of supply and demand. And these fluctuations, supply, and demand decide between its buyers and sellers how much each share is worth.
What is the relationship between stock prices and interest rates?
Based on historical observation, stock prices and interest rates have generally had an inverse relationship. Said plainly, as interest rates move higher, stock prices tend to move lower.
What happens after Fed rate hike?
If rates rise, it becomes more costly to borrow money. When the Fed boosts its lending rate, consumers and businesses can see increased costs for borrowing, which can discourage spending. Higher costs for credit mean you'll pay more for goods over time and can even discourage you from making certain purchases.
Why might rising interest rates depress stock prices?
Rising interest rates might depress stock prices if investors move their money from stocks to the fixed rate instruments with higher interest rates. This movement reduces the demand for stocks, causing their prices to go down. Consumers usually pay a price for the goods and services they buy.
Does a company make money when stock goes up?
No. Not directly. A company issues stock in order to raise capital for building its business. Once the initial shares are sold to the public, the company doesn't receive additional funds from future transactions of those shares of stock between the public.
What happens if no one sells a stock?
When there are no buyers, you can't sell your shares—you'll be stuck with them until there is some buying interest from other investors. A buyer could pop in a few seconds, or it could take minutes, days, or even weeks in the case of very thinly traded stocks.
Do companies lose money when stocks go down?
Lower demand causes a stock to lose some value—and plummeting demand could cause it to lose all value. Since a stock's price is meant to reflect its future profitability and growth, companies that go bankrupt can become effectively worthless.
Interest rates are going up
Super-easy pandemic monetary policy gave strong support to asset prices. The prices of bonds in the secondary markets increased as new bonds could be issued at lower rates (and thus lower current yields - see example on how interest rates affect bonds).
How do stocks perform when interest rates rise?
Historically, when rates increase it's actually good for stocks overall. Again, the implications are that rates are going up to slow (not stop) the rate of economic growth. A strong economy can be very good for companies.
Diversification, my old friend
The purpose of diversification is because like broad-based market moves, there’s no way to know when certain sectors, styles, or factors are going to outperform or underperform, for how long, and to what extent.