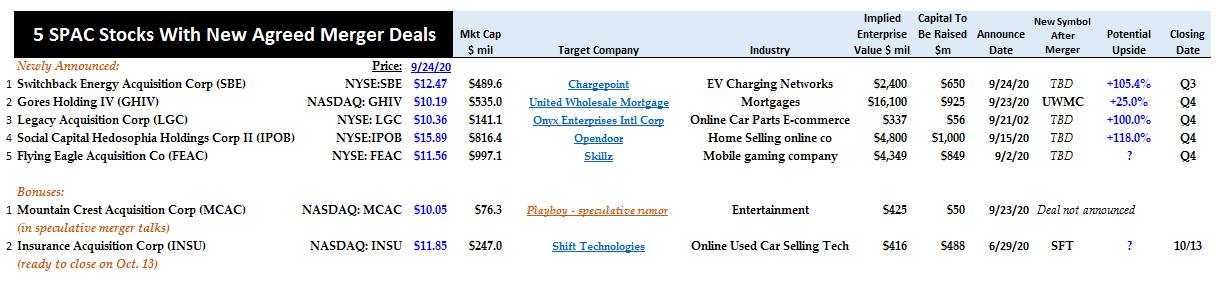
At merger time, SPAC shares maintain their $10 nominal value. But their real value soon drops due to dilution when the merger occurs. For all shareholders, dilution arises from paying the sponsor’s fee in shares (called the “promote,” often about 20% of the equity).
Full Answer
Should you buy a SPAC stock before or after the merger?
If the stock price goes up to $20 after the merger, you can exercise your right to buy it at $12. This gives you an instant gain of $8. Make sure you read the SPAC’s prospectus to understand the rights you have as a SPAC investor.
Why are SPAC sponsors losing money on mergers?
Sponsor incentives are one reason. SPAC sponsors stand to lose millions of dollars if a merger does not close, but make tens of millions of dollars if it does. Sponsor incentives are to close a merger, even on unfavorable terms. To quote Charlie Munger, “Show me the incentives, and I will show you the outcome.”
What happens to the shares of a SPAC when it goes public?
The shares and warrants trade separately. Once public, the SPAC sponsor hunts for a merger partner, which it must find within 18-24 months or the SPAC liquidates and returns all IPO proceeds.
What happens if a SPAC doesn’t merge?
Other options investors have are to: What happens if a SPAC doesn’t merge? SPACs are typically not allowed to use the raised proceeds for any reason other than an acquisition. So, if no acquisition is made within two years, it will take the money from the trust and return it to investors.

How long do you have to wait to sell stock after SPAC merger?
Unlike the traditional IPO process where the lockup period is usually 180 days, after a SPAC merger, employees with stock options may have to wait up to a year to sell shares. Sometimes employees are able to sell a preset number of shares after closing in a tender offer. There have also been instances where exercised options can be sold once the company reaches a target stock price, assuming that happens before the lockup period ends.
What to do after SPAC merger?
Stock option planning after a SPAC merger. Planning to maximize the value of your stock options after your employer goes public via SPAC merger is essential. Much like a typical IPO process, employees will have to make several important decisions after a SPACquisition.
How many SPACs went public in 2009?
According to YCharts, since 2009, 474 SPACs went public and raised capital, but only 188 SPACs mergers were successful. This means about 60% of the time, the target of the SPAC merger doesn’t end up going public, or at least hasn’t already (as of February 2021).
What is SPAC in business?
SPACs are essentially shell companies. Their ‘special purpose’ is to acquire/merge with a private company and take it public. SPACs raise capital through an IPO. When a SPAC goes public, it cannot have a target company already identified. The new capital from the IPO is kept in trust and the SPAC must get shareholder approval ...
What to do if a company doesn't have accelerated vesting?
If the plan doesn’t provide for accelerated vesting, the company could always decide to offer it or amend grant agreements prior to the closing of the deal. A company may do this to retain key employees.
How long does it take to recall a SPAC merger?
Just because your company is the target of a SPAC merger, doesn’t mean it’s going to happen. Recall the deals must usually be complete within 24 months or funds returned to shareholders.
When did SPACs go public?
Although SPACs (special purpose acquisition companies) were first created in 1993, they’ve recently became a very popular way for a company to go public. This happens when a private company merges with or is acquired by the SPAC (which is similar to a blank-check company).
How much is SPAC stock?
SPAC stock will usually be priced at a standard $10 per share. The proceeds will be placed in an interest-bearing trust. The company then has up to two years to find an acquisition. SPAC investing has become popular in the last few years.
What is SPAC in accounting?
A SPAC is a special purpose acquisition company. Also known as blank-check companies, these companies have no business operations. The company is formed to raise funds in an initial public offering (IPO). It then uses the funds to acquire a private company, effectively bringing it to the public market.
How are SPACs formed?
SPACs are usually formed by investors with knowledge and experience in a particular industry or market. Typically, the company intends to pursue an acquisition within that industry. However, although the founders might have a particular company in mind, it isn’t disclosed.
How long does it take to get a SPAC IPO?
As mentioned, the SPAC IPO process is faster and requires fewer steps. Instead of taking six to nine months like a traditional IPO, a SPAC IPO can be accomplished in weeks. It also provides less risk than a traditional IPO. And the acquired company doesn’t need to find investors. SPAC investing provides the money and the investor demand.
What is a SPAC warrant?
A SPAC warrant gives you the right to purchase common stock at a particular price. For example, let’s say you get a warrant for $12 at a 1:1 ratio. That means one warrant equals one share. If the stock price goes up to $20 after the merger, you can exercise your right to buy it at $12.
Is SPAC IPO faster than traditional IPO?
SPAC IPO Process: How and Why. The SPAC IPO process is simpler and faster than the traditional IPO process. A traditional IPO requires a lot of time, money and paperwork. A SPAC still needs to file a prospectus with the SEC. But since a SPAC has no business, there’s little to report.
Is SPAC a popular investment?
SPAC investing is becoming increasingly popular. As more companies choose this method of going public, more investors are curious about investing in SPACs. Let’s take a look at what it is and how SPAC investments work.
How much is the SPAC merger?
Of all 117 SPAC merger deals—with an aggregate value of $99.3 billion —that were announced between Jan. 1, 2019 and Feb. 10, 2021, and for which definitive agreements have been entered into, 39 deals—with an aggregate value of $47.9 billion—have reached completion so far.
When did SPAC merge?
Looking at currently publicly traded companies that went public as a result of a merger with a SPAC announced and completed since Jan. 1, 2019, and for which at least one month of post-merger performance data is available, 14 out of 24 reported a depreciation in value as of one month following the completion of the merger.
What happens to SPAC shareholders after initial business combination?
Once the SPAC has identified an initial business combination opportunity, the shareholders of the SPAC will have the opportunity to redeem their shares and, in many cases, vote on the initial business combination transaction.
What is SPAC investment?
In connection with a business combination, a SPAC provides its investors with the opportunity to redeem their shares rather than become a shareholder of the combined company.
What do you need to know about SPACs?
What You Need to Know About SPACs – Updated Investor Bulletin. The SEC’s Office of Investor Education and Advocacy (OIEA) wants to educate investors about investing in SPACs. You may have heard the term SPAC recently referred to in the financial or other news. This bulletin provides a brief overview for investors of important concepts ...
What is a pro rata share of trust account?
One thing to keep in mind is that if you purchased your shares on the open market, you are only entitled to your pro rata share of the trust account and not the price at which you bought the SPAC shares on the market.
How much is a SPAC IPO?
Trading price. In the IPO, SPACs are typically priced at a nominal $10 per unit. Unlike a traditional IPO of an operating company, the SPAC IPO price is not based on a valuation of an existing business.
How long does a SPAC last?
However, some SPACs have opted for shorter periods, such as 18 months. The SPAC’s governing instruments may permit it to extend that time period.
How long does a SPAC have to complete an initial business combination?
If a SPAC lists its securities on an exchange, it is required to complete an initial business combination within three years of its IPO. IPO proceeds are held in the trust account until a SPAC consummates a business combination or liquidates.
What happens to SPAC sponsors if a merger does not close?
SPAC sponsors stand to lose millions of dollars if a merger does not close, but make tens of millions of dollars if it does. Sponsor incentives are to close a merger, even on unfavorable terms. To quote Charlie Munger, “Show me the incentives, and I will show you the outcome.”. Advertisement.
Why do SPAC shares drop?
At merger time, SPAC shares maintain their $10 nominal value. But their real value soon drops due to dilution when the merger occurs. For all shareholders, dilution arises from paying the sponsor’s fee in shares (called the “promote,” often about 20% of the equity).
How long does QSs hold IPO?
QSs’s ideal holding period is forever, but the SPAC IPO investment is inherently short-term: the vehicle automatically terminates within 18-24 months absent a merger. While SPAC IPO buyers could simply hold through the merger, the shell offers no basis for any substantive investment thesis until then.
When will SPAC IPOs end?
Nearly all IPO-stage shareholders exit before the merger, according to a study covering all SPAC IPOs from 2019 through mid-2020 by Stanford University’s Michael Klausner and New York University’s Michael Ohlrogge.
Is SPAC a bank account?
A SPAC runs this process backwards: It goes public first as a shell — a bank account — created by a sponsoring investor which, within a year or two, merges with a real company that, presto, is public. Examples include Social Capital Hedosophia Holdings IPOE.
Is SPAC cheaper than IPO?
Proponents say the SPAC approach, though convoluted, is cheaper than a traditional IPO. They say it makes the process more orderly, allows forward-looking information on the merger partner that securities laws prohibit for traditional IPOs, and lets ordinary investors in on the ground floor.
Do SPACs have the same results?
Some do; most don’t. All that said, SPACs are not identical. SPACs of high-quality sponsors appear to produce better results, either due to less dilutive terms such as lower promotes or no warrants, or superior post-merger performance, from staying involved to nurture the business.