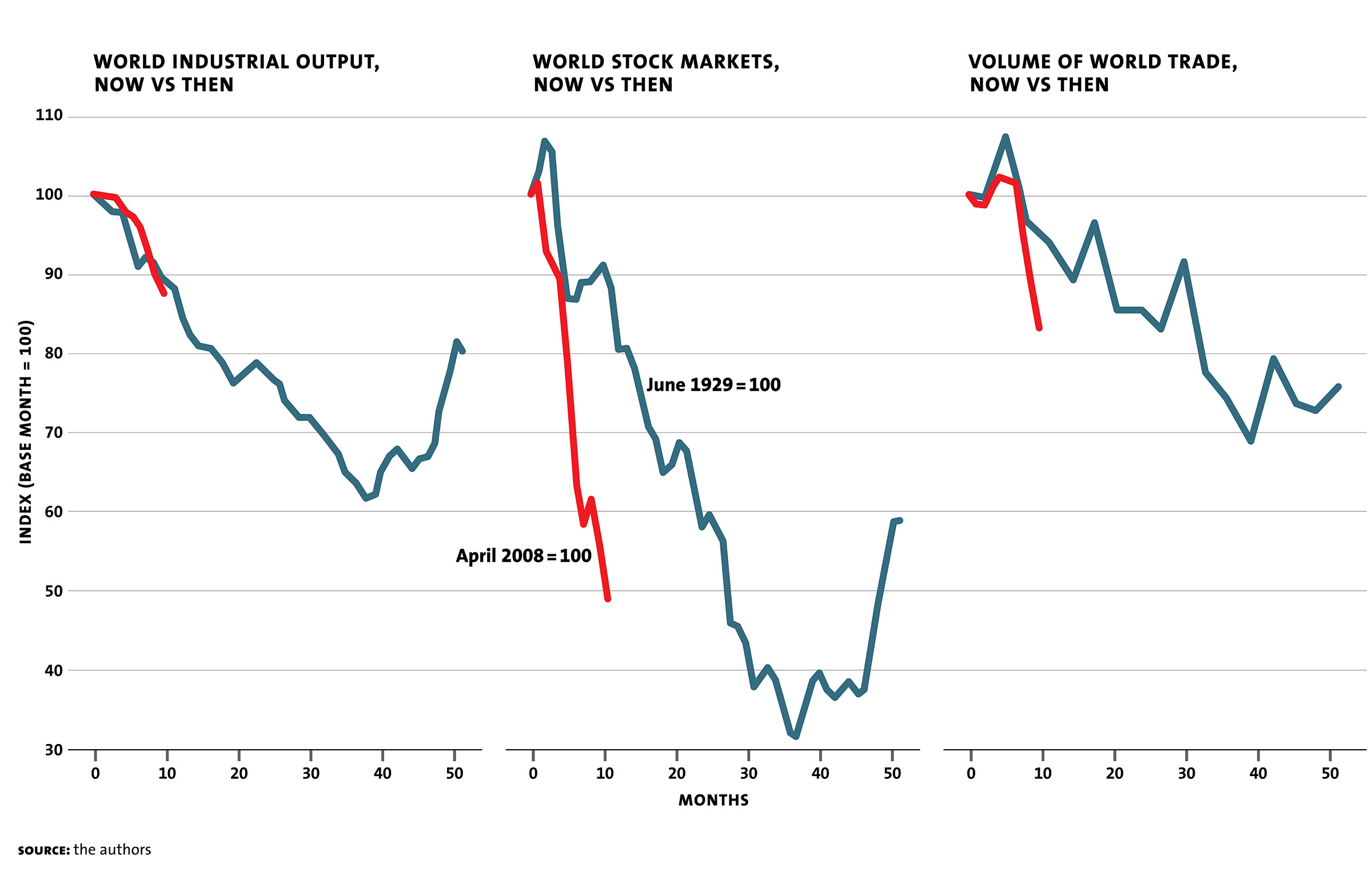
The 2008 stock market crash took place on Sept. 29, 2008, when the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 777.68 points. This was the largest single-day loss in Dow Jones history up to this point. It came on the heels of Congress’ rejection of the bank bailout bill.
Full Answer
When was the last market crash?
Feb 08, 2020 · The stock market crash of 2008 occurred on Sept. 29, 2008. The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 777.68 points in intraday trading. The market crashed because Congress rejected the bank bailout bill.
What is the worst stock market crash?
Nov 03, 2008 · on sept. 6, 2008, with the financial markets down nearly 20% from the oct. 2007 peaks, the government announced its takeover of fannie mae and freddie mac as a result of losses from heavy exposure...
Is the market crashing?
Sep 21, 2021 · The 2008 stock market crash took place on Sept. 29, 2008, when the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 777.68 points. This was the largest single-day loss in Dow Jones history up to this point. It came on the heels of Congress’ rejection of the bank bailout bill.
When was the last financial crisis?
What happened to the stock market in 2008 by Joshua Christoffersen. Prezi. The Science. Conversational Presenting. For Business. For Education. …

What happened in 2008?
By the fall of 2008, borrowers were defaulting on subprime mortgages in high numbers, causing turmoil in the financial markets, the collapse of the stock market, and the ensuing global Great Recession.
How much did the Dow drop in 2008?
The Dow would plummet 3,600 points from its Sept. 19, 2008 intraday high of 11,483 to the Oct. 10, 2008 intraday low of 7,882. The following is a recap of the major U.S. events that unfolded during this historic three-week period.
Why did Bear Stearns fail?
By March 2007, with the failure of Bear Stearns due to huge losses resulting from its underwriting many of the investment vehicles linked to the subprime mortgage market, it became evident that the entire subprime lending market was in trouble.
What is subprime mortgage?
Subprime mortgages are mortgages targeted at borrowers with less-than-perfect credit and less-than-adequate savings. An increase in subprime borrowing began in 1999 as the Federal National Mortgage Association (widely referred to as Fannie Mae) began a concerted effort to make home loans more accessible to those with lower credit and savings than lenders typically required. 1
Which banks are still standing?
Goldman Sachs (GS) and Morgan Stanley (MS), the last two of the major investment banks still standing, convert from investment banks to bank holding companies to gain more flexibility for obtaining bailout funding.
When did the subprime mortgage market start?
Read on to learn how the explosive growth of the subprime mortgage market, which began in 1999, played a significant role in setting the stage for the turmoil that would unfold just nine years later in 2008 when both the stock market and housing market crashed.
What is the role of Fannie and Freddie?
2 . The role of Fannie and Freddie is to repurchase mortgages from the lenders who originated them and make money when mortgage notes are paid. Thus, ever-increasing mortgage default rates led to a crippling decrease in revenue for these two companies.
2008 Market fall
In 2008 Market fell like house of cards! Nifty went from top of 6270 till bottom of 2584 . That’s a 60% fall!This fall was very painful.
2009 Market pullback
Market made a smart come back in 2009. Nifty retest the low of 2500-2600 in March 2009 and then it made a huge come back after the Indian general elections in 2009.
2010 Nifty Pullback
In 2010 there was no looking back for Nifty, after some rounds of consolidation and profit booking Nifty reclaimed the top of 2008 in November 2010. it took almost 4 months for Nifty to go back to top.
What should investors do in recession?
For first time investors who entered into market while there was a bull market, it’s very hard for them to digest a market fall. We have seen many investors trying to catch falling knife and get disappointed with stock price performances.
What happened in 2008 stock market crash – Final thoughts!
Now that you know What happened in 2008 stock market crash; Please keep in mind that this article in no means trying to predict about future, the whole point of article is to inform the investors that What happened in 2008 stock market crash by presenting the data available from nseindia.
What was the financial crisis of 2008?
The 2008 financial crisis had its origins in the housing market, for generations the symbolic cornerstone of American prosperity. Federal policy conspicuously supported the American dream of homeownership since at least the 1930s, when the U.S. government began to back the mortgage market. It went further after WWII, offering veterans cheap home loans through the G.I. Bill. Policymakers reasoned they could avoid a return to prewar slump conditions so long as the undeveloped lands around cities could fill up with new houses, and the new houses with new appliances, and the new driveways with new cars. All this new buying meant new jobs, and security for generations to come.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average fall?
In afternoon trading the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell over 500 points as U.S. stocks suffered a steep loss after news of the financial firm Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection.
Why did the mortgage salesmen make these deals without investigating a borrower's fitness or a property's
The salesmen could make these deals without investigating a borrower's fitness or a property's value because the lenders they represented had no intention of keeping the loans. Lenders would sell these mortgages onward; bankers would bundle them into securities and peddle them to institutional investors eager for the returns the American housing market had yielded so consistently since the 1930s. The ultimate mortgage owners would often be thousands of miles away and unaware of what they had bought. They knew only that the rating agencies said it was as safe as houses always had been, at least since the Depression.
What did the Glass-Steagall Act do?
the Glass-Steagall Act ), they separated these newly secure institutions from the investment banks that engaged in riskier financial endeavors.
When did Bear Stearns go under?
In March 2008, the investment bank Bear Stearns began to go under, so the U.S. treasury and the Federal Reserve system brokered, and partly financed, a deal for its acquisition by JPMorgan Chase.
What was the Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000?
Congress gave them one way to do so in 2000, with the Commodity Futures Modernization Act, deregulating over-the-counter derivatives—securities that were essentially bets that two parties could privately make on the future price of an asset. Like, for example, bundled mortgages.
Who is Eric Rauchway?
Eric Rauchway is the author of several books on US history including Winter War and The Money Makers. He teaches at the University of California, Davis, and you can find him on Twitter @rauchway.
Why did the stock market crash in 2008?
The stock market crashed in 2008 because too many had people had taken on loans they couldn’t afford. Lenders relaxed their strict lending standards to extend credit to people who were less than qualified. This drove up housing prices to levels that many could not otherwise afford.
When did the housing market slow down?
While the housing market slowed down in 2007, many missed the warning bells of the impending recession. The World Bank sounded the alarm in January 2008 when it predicted that global economic growth would slow down as a result of the credit crunch. Few envisioned the severity of the market crash of 2008 or the steep economic decline caused by ...
What happens if a borrower defaults on a mortgage?
If a borrower defaulted, banks could foreclose without taking a loss on the sale. The resulting seller’s market meant that if homeowners couldn’t afford the payments, they could sell the house and the equity would cover the loss. A crisis was virtually inevtiable.
What banks were involved in the bailout?
The build-up of bad debt resulted in a series of government bailouts starting with Bear Stearns, a failing investment bank. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (the nickname given the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation) were next on the government-sponsored bailout train.
What was the unemployment rate in 2007?
The economy continued to lose hundreds of thousands of jobs, and the unemployment rate peaked at 10 percent, double the December 2007 national unemployment rate of 5 percent. Three of the biggest automakers (known as the Big Three) were in trouble and asked the government for help.
What was the stimulus package for the economy?
Only weeks after taking office, President Barack Obama outlined an economic stimulus package to boost consumer spending. Congress passed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 in February as a way to jumpstart the economy and generate jobs.
Why did Lehman Brothers collapse?
In September 2008, investment firm Lehman Brothers collapsed because of its overexposure to subprime mortgages. It was the largest bankruptcy filing in U.S. history up to that point. Later that month, the Federal Reserve announced yet another bailout.

2007
- The Dow opened the year at 12,474.52.2 It rose despite growing concerns about the subprime mortgage crisis. On December 19, 2006, the U.S. Department of Commerce warned that October's new home permits were 28% fewer than the year before.4 But economists didn't think the housin…
2008
- At the end of January, the BEA revised its fourth-quarter 2007 GDP growth estimate down.9 It said growth was only 0.6%. The economy lost 17,000 jobs, the first time since 2004.10 The Dow shrugged off the news and hovered between 12,000 and 13,000 until March.2 On March 17, the Federal Reserve intervened to save the failing investment bank, Bear Stearns. The Dow dropped …
September 2008
- The month started with chilling news. On Monday, September 15, 2008, Lehman Brothers declared bankruptcy. The Dow dropped more than 200 points.2 On Tuesday, September 16, 2008, the Fed announced it was bailing out insurance giant American International Group Inc. It made an $85 billion loan in return for 79.9% equity, effectively taking ownership. AIG had run out of cash. It wa…
October 2008
- Congress finally passed the bailout bill in early October, but the damage had already been done.24 The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a whopping 159,000 jobs in the prior month.25 On Monday, October 6, 2008, the Dow dropped by 800 points, closing below 10,000 for the first time since 2004.26 The Fed tried to prop up banks by lending $540 billion to money mar…
November 2008
- The month began with more bad news. The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a staggering 240,000 jobs in October.34 The AIG bailout grew to $150 billion.35 The Bush administration announced it was using part of the $700 billion bailouts to buy preferred stocks in the nations' banks.36 The Big Three automakers asked for a federal bailout. By November 20, 20…
December 2008
- The Fed dropped the fed funds rate to 0%, its lowest level in history.29 The Dow ended the year at a sickening 8,776.39, down almost 34% for the year.2
2009
- On January 2, 2009, the Dow climbed to 9,034.69.2 Investors believed the new Obama administration could tackle the recession with its team of economic advisers. But the bad economic news continued. On March 5, 2009, the Dow plummeted to its bottom of 6,594.44.37 Soon afterward, President Barack Obama's economic stimulus plan instilled the confidence nee…
Aftermath
- Investors bore the emotional scars from the crash for the next four years. On June 1, 2012, they panicked over a poor May jobs report and the eurozone debt crisis. The Dow dropped 275 points.39 The 10-year benchmark Treasury yield dropped to 1.47.40 This yield was the lowest rate in more than 200 years.41It signaled that the confidence that evaporated during 2008 had not q…