The first major bear market after World War II occurred when OPEC imposed its oil embargo on the world in 1973. Stock market speculation on the “Nifty Fifty” and other high-flying stocks drove up stock prices in the early 1970s, but 1973 saw numerous economic problems which drove the market down over 40% producing the worst bear market since the Great Depression.
How did the stock market react to WW2?
However, from the beginning of the war in 1939 to its eventual end in 1945, the Dow Jones gained almost 50 percent. U.S. stock markets bottomed in April 1942 and then they were in a general uptrend. As the Allied forces continued to build their lead, stock markets reacted positively.
How much did the Dow Jones increase during World War II?
However, from the beginning of the war in 1939 to its eventual end in 1945, the Dow Jones gained almost 50 percent. U.S. stock markets bottomed in April 1942 and then they were in a general uptrend.
Why do stocks increase after a war breaks out?
However, in cases when a war starts as a surprise, the outbreak of a war decreases stock prices. They called this phenomena "the war puzzle" and said there is no clear explanation why stocks increase significantly once war breaks out after a prelude.
How did the bull market start after WW2?
Bull Market Began In Darkest Days Of World War II. That was the beginning of a bull market that carried the Dow up 130% in four years. At the end of the war in 1945, the Federal Reserve began to raise interest rates, and the market slumped into a correction. But the great postwar boom was on.

What stocks did well during WW2?
"In occupied Europe during World War II, all things considered, gold was the best asset to hide in, preserve wealth, and maintain some liquidity. Stocks, land, real estate, and businesses worked only if you had a very long-tern horizon. The black market was the most lucrative profession."
What happens to stock market after war?
Though war and defense spending can amount to a sizable portion of the U.S. GDP, wars often have little sustained impact on stock markets or economic growth at home. Markets largely have ignored recent conflicts related to the Middle East and Iran.
How did World War I affect the stock market?
The outbreak of World War I in Europe forced the NYSE to shut its doors on July 31, 1914, after large numbers of foreign investors began selling their holdings in hopes of raising money for the war effort. All of the world's financial markets followed suit and closed their doors by August 1.
How much did the stock market drop during WW2?
April 8th, 1940 – The Dow Jones Industrial Average closes at 151.29, which would come to represent the market's peak prior to World War 2. The Dow Jones Industrial Average would hit a WW2 low of 92.92 on April 28th 1942. The Dow would not close above 151.29 until December 29th 1944.
Should you buy stocks during war?
1. Stocks will stay resilient amid the war. Steiner said past precedent shows stocks can maintain value during major conflicts. "If we take a historical view looking at the geopolitical lens, most portfolios heavily weighted in equities tend to be pretty resilient."
Do stocks drop during war?
Yes, during the pre-war phase, stock prices decline due to uncertainty, but once war begins, the stock market goes up. Most of the pre-war volatility subsides, and investors enjoy relative stability.
Was the stock market closed during ww2?
When World War II began, the London Stock Exchange closed for only a week, and the New York Stock Exchange never closed during World War II, save for August 15-16, 1945 when the NYSE closed to recognize V-J Day and the end of WWII.
Who profited from the stock market crash of 1929?
The classic way to profit in a declining market is via a short sale — selling stock you've borrowed (e.g., from a broker) in hopes the price will drop, enabling you to buy cheaper shares to pay off the loan. One famous character who made money this way in the 1929 crash was speculator Jesse Lauriston Livermore.
Do oil stocks go up during war?
So far, oil stocks are outperforming the market, with the Energy Select SPDR Fund (NYSE: XLE) up 15% since the start of the war. Nonetheless, buying oil stocks during war is proving to be an excellent hedge. See which companies are wining with higher oil prices below.
What did stock market do during World War 2?
During World War II from Sept. 1, 1939 to Aug. 31, 1945, the Dow Jones Industrial Average gained 50%, or roughly a 7% annual return.
How Did The Stock Market Perform During WWII?
T he stock market is a strange and amorphous thing. If people could understand it better they could be rich. Indeed, even today there are entire businesses set up to try and get people to buy the secret to understanding the stock market.
American stock market
The Great Depression ruined the stock market and caused a banking crash that is still talked about today. After the initial crash in 1929, the market went through a horrible three year period in the depths of the Great Depression that saw the market bottom out.
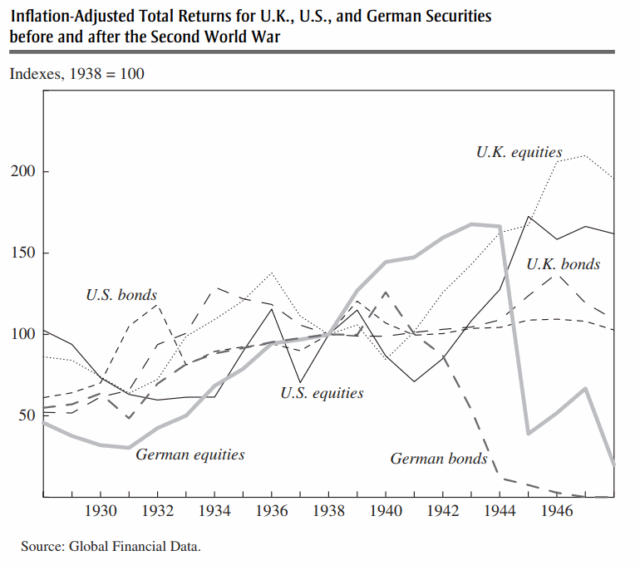
German stock market
The German stock market followed a much more interesting trend than the American markets. Stocks plummeted after the rise of Adolf Hitler in response to poor economic outlooks and a volatile political scene. However, in 1933, as Hitler begins to consolidate his power and put in place his economic reforms the German markets begin a massive bull run.
Conclusion
When you train your eye, you can clearly see World War II in the stock market charts but their beats are not necessarily exactly the ones you would expect. You can see where the world was anxious before the war, where the Allies faltered in the early years and how they bounced back and won the war. It is all reflected in the numbers.
What was the worst economic downturn in the 20th century?
The U.S. had just gone through the Great Depression , the worst and longest economic downturn of the 20th century. The stock market crashed Oct. 29, 1929, as the Dow Jones industrial average lost nearly half its value in a few weeks and continued sinking for months. By 1933, the unemployment rate stood at nearly 25%.
What happened on May 7, 1942?
was fully mobilizing for war and would eventually win. The Federal Reserve dropped interest rates to nearly zero. On May 7, 1942, the Dow rose 1.06 to 97.77, a gain of 1.1%, in volume greater than the day before.
When did Germany invade Poland?
Germany invaded Poland on Sept. 1, 1939, launching WWII in Europe. At first, the Dow didn't react much. Many people expected the U.S. to stay out. But when Hitler invaded France in May 1940, the market got hammered (1). Over an eight-day period, it fell 23%.
What was the first bear market after World War II?
The first major bear market after World War II occurred when OPEC imposed its oil embargo on the world in 1973. Stock market speculation on the “Nifty Fifty” and other high-flying stocks drove up stock prices in the early 1970s, but 1973 saw numerous economic problems which drove the market down over 40% producing the worst bear market since the Great Depression. Between the collapse of Bretton Woods, Watergate, the Yom Kippur War, the OPEC Oil Embargo, the quadrupling of oil prices, inflation, an increase in the prime rate to 11.5% and the recession that followed, stock prices collapsed.
When did the bear market end?
The 1968-1970 bear market did not occur outside of the United States, and the 1989 bear market lasted until April 1992 outside of the United States rather than ending in September 1990. Figure 1 compares the behavior of the S&P 500 and GFD’s World Stock Index.
What happened on October 19 1987?
The October 19, 1987 stock market crash was as unexpected as it was dramatic. The S&P 500 declined 20.5% in one day and the DJIA fell 508 points, a decline of 22.6%. At the time, analysts compared the 1987 crash with the decline in 1929 and many feared that there would be another Great Depression. Every stock market in the world except Japan followed up on the Wall Street crash with similar declines. The Hang Seng Index in Hong Kong declined 52%, France fell 45% and Germany 46%. The Crash began in the Far East on the morning of October 19, accelerated in Europe and finally collapsed in New York. There was no better illustration of how integrated stock markets had become in the age of financial globalization.
How many bear markets were there in the 1800s?
The 1800s, on the other hand, was a century of peace, with numerous panics, but only one global bear market which occurred in the 1840s. There were no global bear markets between 1848 and 1912, a 64-year stretch of peace and economic growth. War hit the world in 1914 when World War I began. Four bear markets occurred between 1912 and 1949.
How many stock markets are there in the world?
Today there are over 100 stock markets throughout the world with about 25 developed markets, 25 emerging markets and 50 frontier markets. The 1700s was a century of war during which there were five bear markets, each driven directly or indirectly by a European war. The 1800s, on the other hand, was a century of peace, with numerous panics, ...
What happened to Bear Stearns?
The collapse of Bear Stearns, Indy Mac, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, Lehman Brothers, Washington Mutual, and other financial companies led to a 50% decline in U.S. stock markets. The $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) was introduced to prevent the financial system from collapsing.
Why did bear markets happen?
With the world generally at peace after World War II, recessions, sometimes driven by financial panics, were the main cause of bear markets. This certainly was the case of the two bear markets that have occurred in the twenty-first century. Over time, bear markets have become more frequent, more integrated, but shorter in duration.
How long does it take for stocks to bottom after a shock?
In fact, on a median basis, shocks normally cause stocks to bottom out six days after the shock hits, with a total drop of 5.3%.
Which shocks caused bigger one day drops than the Kennedy assassination?
In contrast, shocks that caused bigger one-day drops than the Kennedy assassination included the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, the 9/11 terror attacks back in 2001 and the Lehman Bros. bankruptcy in the fall of 2008. The stock market tends to be resilient.
Does the stock market rebound after a shock?
In general, the stock market tends to rebound quickly following shocks, once it is determined that the economy won't be irreparably harmed by the event, says Stovall. And despite the tragedy of JFK's death, the market quickly realized that it was an emotional event, not an economic event.
What happens when the stock market falls?
However, when markets are falling, the losses in the stock positions are also magnified. If a portfolio loses value too rapidly, the broker will issue a margin call, which is a notice to deposit more money to cover the decline in the portfolio's value.
How many times did stock prices go up in 1929?
Until the peak in 1929, stock prices went up by nearly 10 times. In the 1920s, investing in the stock market became somewhat of a national pastime for those who could afford it and even those who could not—the latter borrowed from stockbrokers to finance their investments. The economic growth created an environment in which speculating in stocks ...
Why did companies acquire money cheaply?
Essentially, companies could acquire money cheaply due to high share prices and invest in their own production with the requisite optimism. This overproduction eventually led to oversupply in many areas of the market, such as farm crops, steel, and iron.
What was the result of the Great War?
The result was a series of legislative measures by the U.S. Congress to increase tariffs on imports from Europe.
Why did the economy stumbled in 1929?
In mid-1929, the economy stumbled due to excess production in many industries, creating an oversupply.
What happens if a broker doesn't deposit funds?
If the funds are not deposited, the broker is forced to liquidate the portfolio. When the market crashed in 1929, banks issued margin calls. Due to the massive number of shares bought on margin by the general public and the lack of cash on the sidelines, entire portfolios were liquidated.
What was the era of the Roaring Twenties?
Excess Debt. The Aftermath of the Crash. The decade, known as the "Roaring Twenties," was a period of exuberant economic and social growth within the United States. However, the era came to a dramatic and abrupt end in October 1929 when the stock market crashed, paving the way into America's Great Depression of the 1930s.
How long did it take for the stock market to recover from the bear market?
According to the Wall Street Journal, taking into account all U.S. bear markets since the mid-1920s, it took an average of 3.1 years for the broad market to recover from where it stood before the bear market began on a dividend and inflation-adjusted basis.
How long did it take for the S&P 500 to fall?
As you’ve likely heard by now, the U.S. has fallen into the fastest bear market in history: it took only 16 trading days for the S&P 500 to fall over 20% from the high on February 19. March 2020 also made history as the most volatile month for the S&P on record . MORE FROM FORBES ADVISOR.
How long does a recession last?
By definition, a recession must last at least six months, where a bull or bear market could last a matter of days in theory. In fact, after 11 trading days, the Dow Jones managed to climb out of bear market territory at the end of March. Historically, the stock market has bottomed out long before the worst of the economic data unfolded, ...
Is the S&P 500 down in 2020?
While this may be welcome news, it’s still important to keep in mind the impact that volatility and the sequence of returns can have on a portfolio, particularly for individuals late in their career or recently retired. For example, on March 12, 2020 the S&P 500 was down -9.5% only to return following day up 9.3%.
Is a bear market the same as a recession?
As you know, a bear market (generally thought of as a decline of 20% or more from recent highs) is not the same as a recession (broadly defined as two or more consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth). On average, the S&P 500 has been up over 15% in the year following a recession. In fact, the index even averaged nearly 4% during the recessions.
