
Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Stock Market Crash of 1929 or the Great Crash, was a major stock market crash that occurred in late October 1929. It started on October 24 and continued until October 29, 1929, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange collapsed.
What exactly caused the stock market to crash in 1929?
Jun 22, 2020 · What happened after the stock market crash of 1929? After October 29, 1929, stock prices had nowhere to go but up, so there was considerable recovery during succeeding weeks. Overall, however, prices continued to drop as the United States slumped into the Great Depression, and by 1932 stocks were worth only about 20 percent of their value in the summer …
Which situation helped cause the stock market crash of 1929?
Oct 25, 2019 · That propped up the market until it finally crashed for good: Plunging 12.8% on Oct. 28, 1929 (Black Monday) and 11.7% on Oct. 29 (Black Tuesday). Those two days of selling still rank as the No. 2...
Why did the New York Stock Exchange crash in 1929?
Nov 22, 2013 · A crowd gathers outside the New York Stock Exchange following the 1929 crash. (Photo: Bettmann/Bettmann/Getty Images) Funds that fled the stock market flowed into New York City’s commercial banks. These banks also assumed millions of dollars in stock-market loans. The sudden surges strained banks.
Why did stock prices decline in 1929?
Mar 06, 2020 · To say that the Stock Market Crash of 1929 devastated the economy is an understatement. Although reports of mass suicides in the aftermath of the crash were most likely exaggerations, many people lost their entire savings. Numerous companies were ruined. Faith in banks was destroyed.
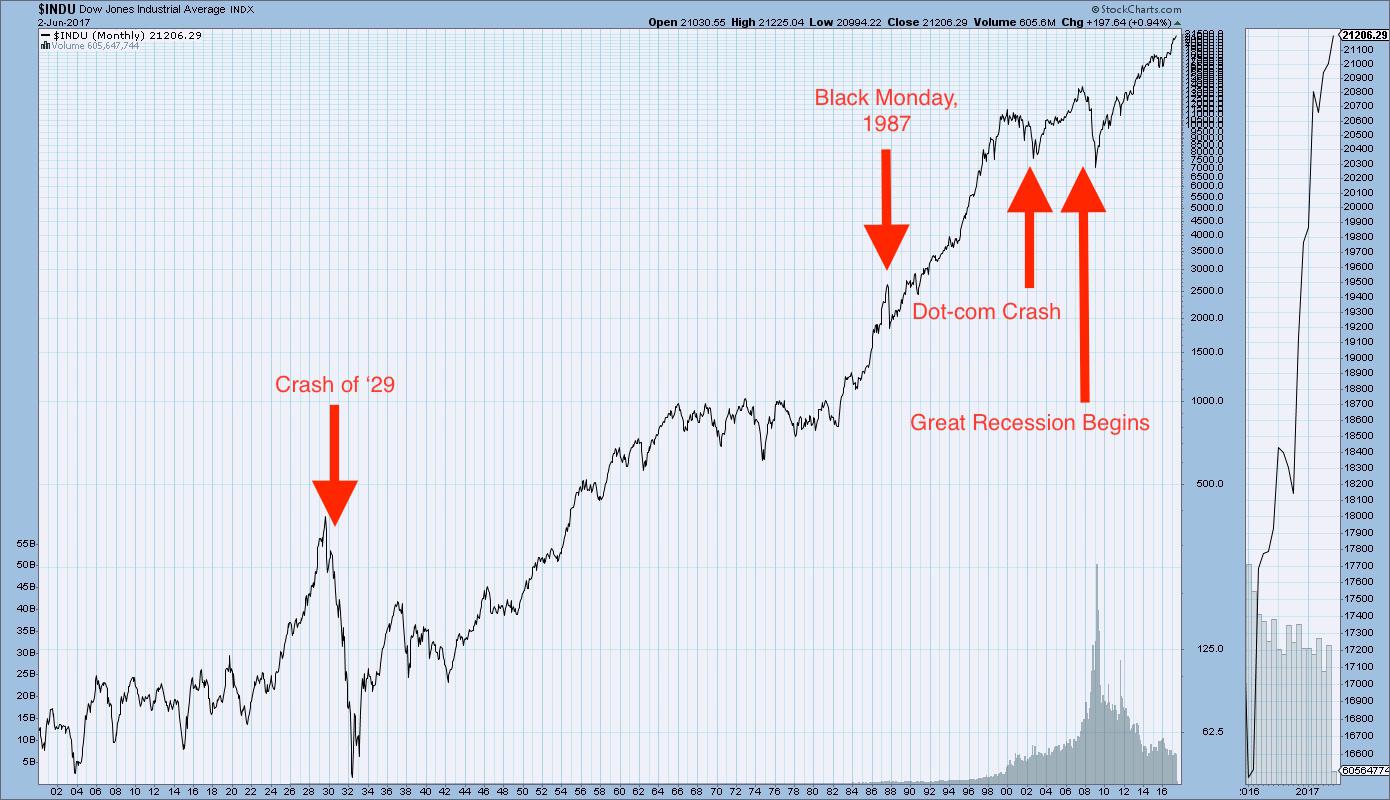
What happened after the stock market crash?
By 1933 the value of stock on the New York Stock Exchange was less than a fifth of what it had been at its peak in 1929. Business houses closed their doors, factories shut down and banks failed. Farm income fell some 50 percent. By 1932 approximately one out of every four Americans was unemployed.
What happened after the Wall Street crash?
Many banks closed, ordinary people lost their savings and people lost all hope for the future. People could no longer buy consumer goods like cars and clothes. As a result, workers were made redundant, other workers' wages were cut and unemployment rose to very high levels.
How did the stock market recover from the 1929 crash?
Though the market did not fully recover in 1930, it did go through a series of rallies and drops as it tried to mount a revival. New York Stock Exchange stocks recovered 73 percent of their losses in 1930.
How long did it take the stock market to recover after the 1929 crash?
25 yearsIt took the DOW 25 years to regain its 1929 highs in nominal terms. Including dividends, which reached a high of 14% at the depths of the crash (when the market was down almost 90%), it took about 10 years for 1929 DOW investors to get their money back.Apr 26, 2009
Who benefited from the stock market crash of 1929?
While most investors watched their fortunes evaporate during the 1929 stock market crash, Kennedy emerged from it wealthier than ever. Believing Wall Street to be overvalued, he sold most of his stock holdings before the crash and made even more money by selling short, betting on stock prices to fall.Apr 28, 2021
What impacts did the stock market crash of 1929 have on the American economy?
What impact did the stock market crash of 1929 have on the American economy? -It led to a widespread panic that deepened the economic crisis. -It drove Americans to place all their available cash in banks to ensure its safety. -It caused the Great Depression.
How long did 1929 depression last?
43The Great Depression / Duration (months)
How long did it take to recover from the 1987 crash?
The market rebounded faster after the 1987 crash than it did in 1929, when the Dow took two decades to fully recover. After 1987, stocks took two years to top the levels seen Oct. 16, 1987 - the last trading session before Black Monday.Oct 9, 2018
What caused the Great Depression of 1929?
What were the major causes of the Great Depression? Among the suggested causes of the Great Depression are: the stock market crash of 1929; the collapse of world trade due to the Smoot-Hawley Tariff; government policies; bank failures and panics; and the collapse of the money supply.
How long did it take the stock market to recover from 2008?
9, 2007 -- but by September of 2008, the major stock indexes had lost nearly 20% of their value. The Dow didn't reach its lowest point, which was 54% below its peak, until March 6, 2009. It then took four years for the Dow to fully recover from the crash.Feb 2, 2022
Do markets always recover?
Market downturns almost always are followed by recoveries, but there are some exceptions worth knowing. A recovery can also depend on your time horizon. The best known example is the Japan bubble.
Will a Great Depression happen again?
Could a Great Depression happen again? Possibly, but it would take a repeat of the bipartisan and devastatingly foolish policies of the 1920s and ' 30s to bring it about. For the most part, economists now know that the stock market did not cause the 1929 crash.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 was not the sole cause of the Great Depression, but it did act to accelerate the global economic collapse ...
What happened to stock market in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929, and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded. Investment companies and leading bankers attempted to stabilize the market by buying up great blocks of stock, producing a moderate rally on Friday. On Monday, however, the storm broke anew, and the market went into free fall. Black Monday was followed by Black Tuesday (October 29, 1929), in which stock prices collapsed completely and 16,410,030 shares were traded on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors, and stock tickers ran hours behind because the machinery could not handle the tremendous volume of trading.
What happened on October 29, 1929?
On October 29, 1929, Black Tuesday hit Wall Street as investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors. In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), ...
What happened after Black Tuesday?
In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), the deepest and longest-lasting economic downturn in the history of the Western industrialized world up to that time .
What were the causes of the 1929 stock market crash?
Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.
When did stock prices drop in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929 , and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded.
When did the stock market peak?
During the 1920s, the U.S. stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929 after a period of wild speculation during the roaring twenties. By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value.
How many points did the Dow drop in 1929?
To put the 1929 stock market crash in perspective, today a two-day, 24.5% drop would take the Dow down 6,576- points. It took 25 years for the Dow "to get back to breakeven from the Crash of 1929," says Sam Stovall, chief investment strategist at CFRA. What can investors learn from the crash?
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average drop?
X. On Oct. 24, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped 11% intraday before bankers stepped in and provided buying support. That propped up the market until it finally crashed for good: Plunging 12.8% on Oct. 28, 1929 (Black Monday) and 11.7% on Oct. 29 (Black Tuesday).
How long does it take for a bear market to break even?
It's only taken 14 months, on average, for investors to break even following the 12 bear markets since 1945, Stovall says, based on the S&P 500. And even following 40% or greater "Mega-Meltdowns," investors got their money back in 58 months, or less than five years.
Which sectors win fans during times of uncertainty?
The consumer staples, health care and utilities sectors win fans during times of uncertainty for a reason. Their more stable earnings give them more ballast during difficult times for the market.
Is October a bad month?
October Gets A Bad Rap. The month of October scares investors as major crashes occurred during the month. But since 1946, October turned into a "bear killer" month, says Stock Trader's Almanac. Buying in October "turned the tide" in 12 bear markets after the second World War.
What happened in 1929?
Commercial banks continued to loan money to speculators, and other lenders invested increasing sums in loans to brokers. In September 1929, stock prices gyrated, with sudden declines and rapid recoveries.
What lessons did the Federal Reserve learn from the 1929 stock market crash?
9. First, central banks – like the Federal Reserve – should be careful when acting in response to equity markets. Detecting and deflating financial bubbles is difficult.
How much did the Dow drop in 1932?
The slide continued through the summer of 1932, when the Dow closed at 41.22, its lowest value of the twentieth century, 89 percent below its peak.
What happened on Black Monday 1929?
On Black Monday, October 28, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined nearly 13 percent. Federal Reserve leaders differed on how to respond to the event and support the financial system.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average increase?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average increased six-fold from sixty-three in August 1921 to 381 in September 1929 . After prices peaked, economist Irving Fisher proclaimed, “stock prices have reached ‘what looks like a permanently high plateau.’” 2. The epic boom ended in a cataclysmic bust.
Who published a monetary history of the United States in 1963?
Consensus coalesced around the time of the publication of Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz’ s A Monetary History of the United States in 1963.
Who created the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
Dow Jones Industrial Average (Created by: Sam Marshall, Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond) Enlarge. The financial boom occurred during an era of optimism. Families prospered. Automobiles, telephones, and other new technologies proliferated. Ordinary men and women invested growing sums in stocks and bonds.
What happened in 1929?
Updated September 02, 2020. The stock market crash of 1929 was a collapse of stock prices that began on Oct. 24, 1929. By Oct. 29, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average had dropped 24.8%, marking one of the worst declines in U.S. history. 1 It destroyed confidence in Wall Street markets and led to the Great Depression .
What happened on September 26th 1929?
September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard. September 29, 1929: The Hatry Case threw British markets into panic. 6. October 3: Great Britain's Chancellor of the Exchequer Phillip Snowden called the U.S. stock market a "speculative orgy.".
How much did the Dow rise in 1933?
On March 15, 1933, the Dow rose 15.34%, a gain of 8.26 points, to close at 62.1. 8. The timeline of the Great Depression tracks critical events leading up to the greatest economic crisis the United States ever had. The Depression devastated the U.S. economy.
What was the Dow down in 1932?
By July 8, 1932, the Dow was down to 41.22. That was an 89.2% loss from its record-high close of 381.17 on September 3, 1929. It was the worst bear market in terms of percentage loss in modern U.S. history. The largest one-day percentage gain also occurred during that time.
Why did banks honor 10 cents for every dollar?
That's because they had used their depositors' savings, without their knowledge, to buy stocks. November 23, 1954: The Dow finally regained its September 3, 1929, high, closing at 382.74. 8.
How did the stock market crash of 1929 affect the economy?
To say that the Stock Market Crash of 1929 devastated the economy is an understatement. Although reports of mass suicides in the aftermath of the crash were most likely exaggerations, many people lost their entire savings. Numerous companies were ruined. Faith in banks was destroyed.
What happened on Oct 24 1929?
On the morning of Thursday, Oct. 24, 1929, stock prices plummeted. Vast numbers of people were selling their stocks. Margin calls were sent out. People across the country watched the ticker as the numbers it spit out spelled their doom.
What was the role of flappers in the 1920s?
In the 1920s, many invested in the stock market.
What was the worst day in the stock market?
Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929. Oct. 29, 1929, became famous as the worst day in stock market history and was called, "Black Tuesday.". There were so many orders to sell that the ticker again quickly fell behind. By the end of close, it was 2 1/2 hours behind real-time stock sales.
What were the signs of trouble in 1929?
Signs of Trouble. By early 1929, people across the United States were scrambling to get into the stock market. The profits seemed so assured that even many companies placed money in the stock market. Even more problematic, some banks placed customers' money in the stock market without their knowledge.
What happened on Black Tuesday 1929?
When the stock market took a dive on Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the country was unprepared. The economic devastation caused by the Stock Market Crash of 1929 was a key factor in the start of the Great Depression .
What was the end of World War I?
The end of World War I in 1919 heralded a new era in the United States. It was an era of enthusiasm, confidence, and optimism, a time when inventions such as the airplane and the radio made anything seem possible. Morals from the 19th century were set aside. Flappers became the model of the new woman, and Prohibition renewed confidence in the productivity of the common man.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
Most economists agree that several, compounding factors led to the stock market crash of 1929. A soaring, overheated economy that was destined to one day fall likely played a large role.
Why did the stock market crash make the situation worse?
Public panic in the days after the stock market crash led to hordes of people rushing to banks to withdraw their funds in a number of “bank runs,” and investors were unable to withdraw their money because bank officials had invested the money in the market.
What was the economic climate in the 1920s?
Additionally, the overall economic climate in the United States was healthy in the 1920s. Unemployment was down, and the automobile industry was booming. While the precise cause of the stock market crash of 1929 is often debated among economists, several widely accepted theories exist. 17. Gallery.
What was the worst economic event in history?
The stock market crash of 1929 was the worst economic event in world history. What exactly caused the stock market crash, and could it have been prevented?
Why did people buy stocks in the 1920s?
During the 1920s, there was a rapid growth in bank credit and easily acquired loans. People encouraged by the market’s stability were unafraid of debt.
When did the Dow go up?
The market officially peaked on September 3, 1929, when the Dow shot up to 381.
Who was the bankrupt investor who tried to sell his roadster?
Bankrupt investor Walter Thornton trying to sell his luxury roadster for $100 cash on the streets of New York City following the 1929 stock market crash. (Credit: Bettmann Archive/Getty Images) Bettmann Archive/Getty Images.
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
Only a few years after the Wall Street stock market crashed in October 1929, America had fallen into the Great Depression - the greatest financial crisis in its history.
Why did the Wall Street crash happen in 1929?
However, whilst people were buying less cars, houses and luxury goods, they still kept buying shares. The Wall Street Crash was also caused by innate weaknesses in the American banking system - in the 1920s America had ...
How did the 1920s affect the economy?
To fund the mass consumption of the 1920s, many consumers used bank credit and loans. People placed so much confidence in the economy that they took out loans they couldn’t pay back. Many used loans to buy shares on the stock market - this was called buying shares on the margin. When confidence started failing in 1929, those people who had borrowed rushed to sell their shares and pay back their debts. This panic selling of shares caused a dramatic fall in the value of the market.
Why did Wall Street crash?
The Wall Street Crash was also caused by innate weaknesses in the American banking system - in the 1920s America had over 30,000 banks; this meant that many were prone to going bankrupt if they run out of funds. On average, more than 600 banks failed each year between 1921 and 1929.
What was the economic situation in the 1920s?
America in the 1920s was generally a place of economic prosperity. Mass production and mass consumption increased the standard of living for many Americans. However, this prosperity was not as widespread as many imagined - 60 per cent of the population still lived below the poverty line. The were many reasons for the Wall Street Crash.
How many banks failed in 1921?
On average, more than 600 banks failed each year between 1921 and 1929. An increase in bank failures at the end of the decade triggered a run on deposits. Confidence in the banking system started to decline, and bank runs became more common.
