
What exactly caused the stock market to crash in 1929?
Nov 22, 2013 · A crowd gathers outside the New York Stock Exchange following the 1929 crash. (Photo: Bettmann/Bettmann/Getty Images) Funds that fled the stock market flowed into New York City’s commercial banks. These banks also assumed millions of dollars in stock-market loans. The sudden surges strained banks.
Which situation helped cause the stock market crash of 1929?
Lacking up-to-date market data in 1929, investors spread stories about the likelihood of a stock market crash even before it actually happened, Robert Shiller, professor of …
Why did the New York Stock Exchange crash in 1929?
Apr 13, 2018 · Panic Made the Situation Worse. Public panic in the days after the stock market crash led to hordes of people rushing to banks to withdraw their funds in a number of “bank runs,” and investors ...
Why did stock prices decline in 1929?
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 brought the prosperity of the 1920s to an abrupt end. Only a few years after the Wall Street stock market crashed in October 1929, America had fallen into the Great Depression - the greatest financial crisis in its history. America in the 1920s was generally a place of economic prosperity.

What was the aftermath of the stock market crash in 1929?
What happened immediately after the stock market crash?
This meant that much of the money the clients was trying to withdraw was already gone. As the reality of the crash set in, many realized they had lost their complete life savings with no way to get the money back. Meanwhile, countless banks went belly up.
How long did it take the stock market to recover after the 1929 crash?
What happened after the Wall Street crash?
Who made money in 1929 crash?
How does a stock market crash affect me?
How did the Great Depression end?
What should I invest in before a market crash?
Investors can buy and hold physical precious metals, but then you may have to pay for storage and insurance. Other investment options include precious metal funds and ETFs, options, futures and mining companies.Feb 16, 2022
What caused the 1928 stock market crash?
What were the social consequences of the crash?
What happened in 1929?
Commercial banks continued to loan money to speculators, and other lenders invested increasing sums in loans to brokers. In September 1929, stock prices gyrated, with sudden declines and rapid recoveries.
What lessons did the Federal Reserve learn from the 1929 stock market crash?
9. First, central banks – like the Federal Reserve – should be careful when acting in response to equity markets. Detecting and deflating financial bubbles is difficult.
What happened on Black Monday 1929?
On Black Monday, October 28, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined nearly 13 percent. Federal Reserve leaders differed on how to respond to the event and support the financial system.
How did the stock market crash affect the economy?
While New York’s actions protected commercial banks, the stock-market crash still harmed commerce and manufacturing. The crash frightened investors and consumers. Men and women lost their life savings, feared for their jobs, and worried whether they could pay their bills. Fear and uncertainty reduced purchases of big ticket items, like automobiles, that people bought with credit. Firms – like Ford Motors – saw demand decline, so they slowed production and furloughed workers. Unemployment rose, and the contraction that had begun in the summer of 1929 deepened (Romer 1990; Calomiris 1993). 7
How did the Fed help the banks during the financial crisis?
It assured commercial banks that it would supply the reserves they needed. These actions increased total reserves in the banking system, relaxed the reserve constraint faced by banks in New York City, and enabled financial institutions to remain open for business and satisfy their customers’ demands during the crisis. The actions also kept short term interest rates from rising to disruptive levels, which frequently occurred during financial crises.
What was the financial boom?
The financial boom occurred during an era of optimism. Families prospered. Automobiles, telephones, and other new technologies proliferated. Ordinary men and women invested growing sums in stocks and bonds. A new industry of brokerage houses, investment trusts, and margin accounts enabled ordinary people to purchase corporate equities with borrowed funds. Purchasers put down a fraction of the price, typically 10 percent, and borrowed the rest. The stocks that they bought served as collateral for the loan. Borrowed money poured into equity markets, and stock prices soared.
When did the Dow drop?
The epic boom ended in a cataclysmic bust. On Black Monday, October 28, 1929, the Dow declined nearly 13 percent. On the following day, Black Tuesday, the market dropped nearly 12 percent. By mid-November, the Dow had lost almost half of its value. The slide continued through the summer of 1932, when the Dow closed at 41.22, its lowest value of the twentieth century, 89 percent below its peak. The Dow did not return to its pre-crash heights until November 1954.
What happened in 1929?
Updated September 02, 2020. The stock market crash of 1929 was a collapse of stock prices that began on Oct. 24, 1929. By Oct. 29, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average had dropped 24.8%, marking one of the worst declines in U.S. history. 1 It destroyed confidence in Wall Street markets and led to the Great Depression .
What happened on September 26th 1929?
September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard. September 29, 1929: The Hatry Case threw British markets into panic. 6. October 3: Great Britain's Chancellor of the Exchequer Phillip Snowden called the U.S. stock market a "speculative orgy.".
What were the three key trading dates of the Dow crash?
The three key trading dates of the crash were Black Thursday, Black Monday, and Black Tuesday. The latter two days were among the four worst days the Dow has ever seen, by percentage decline.
How did the stock market crash affect people?
The crash wiped people out. They were forced to sell businesses and cash in their life savings. Brokers called in their loans when the stock market started falling. People scrambled to find enough money to pay for their margins. They lost faith in Wall Street.
How much did the Dow rise in 1933?
On March 15, 1933, the Dow rose 15.34%, a gain of 8.26 points, to close at 62.1. 8. The timeline of the Great Depression tracks critical events leading up to the greatest economic crisis the United States ever had. The Depression devastated the U.S. economy.
What was the financial invention that allowed people to borrow money from their broker to buy stocks?
Everyone invested, thanks to a financial invention called buying "on margin." It allowed people to borrow money from their broker to buy stocks. They only needed to put down 10%. 7 Investing this way contributed to the irrational exuberance of the Roaring Twenties.
What happened overnight during the Great Depression?
Overnight, many people lost their businesses and life savings, setting the stage for the Great Depression.
What happened on Oct 24 1929?
On Oct. 24, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped 11% intraday before bankers stepped in and provided buying support. That propped up the market until it finally crashed for good: Plunging 12.8% on Oct. 28, 1929 (Black Monday) and 11.7% on Oct. 29 (Black Tuesday). Those two days of selling still rank as the No. 2 and No. 3 worst percentage drops in Dow Jones Industrial Average history (the 22.6% drop on Oct. 19, 1987 is the worst).
How many points did the Dow drop in 1929?
To put the 1929 stock market crash in perspective, today a two-day, 24.5% drop would take the Dow down 6,576- points. It took 25 years for the Dow "to get back to breakeven from the Crash of 1929," says Sam Stovall, chief investment strategist at CFRA. What can investors learn from the crash?
What stocks outpaced the market in the bear market since 1946?
Such behavior is predictable from looking at past periods of weakness. Consumer staples, health care and utilities stocks outpaced the market in 83% of bear markets since 1946.
Which sectors win fans during times of uncertainty?
The consumer staples, health care and utilities sectors win fans during times of uncertainty for a reason. Their more stable earnings give them more ballast during difficult times for the market.
Is October a bad month?
October Gets A Bad Rap. The month of October scares investors as major crashes occurred during the month. But since 1946, October turned into a "bear killer" month, says Stock Trader's Almanac. Buying in October "turned the tide" in 12 bear markets after the second World War.
Is October the worst month in the world?
It's not even the worst month anymore ( it ranks seventh). Big October gains followed "atrocious Septembers" from 1999 to 2003.
Is it good to wait to get money back after a meltdown?
That's good news for investors who don't have time or patience to wait nearly three decades to get their money back after a meltdown. It's also help for investors to mentally and financially prepare for what to expect when the market sells off.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
Most economists agree that several, compounding factors led to the stock market crash of 1929. A soaring, overheated economy that was destined to one day fall likely played a large role.
What happened to stocks during the stock market crash?
Some experts argue that at the time of the crash, stocks were wildly overpriced and that a collapse was imminent.
What was the economic climate in the 1920s?
Additionally, the overall economic climate in the United States was healthy in the 1920s. Unemployment was down, and the automobile industry was booming. While the precise cause of the stock market crash of 1929 is often debated among economists, several widely accepted theories exist. 17. Gallery.
Why did the stock market crash make the situation worse?
Public panic in the days after the stock market crash led to hordes of people rushing to banks to withdraw their funds in a number of “bank runs,” and investors were unable to withdraw their money because bank officials had invested the money in the market.
What was the worst economic event in history?
The stock market crash of 1929 was the worst economic event in world history. What exactly caused the stock market crash, and could it have been prevented?
What happened on October 28th?
On October 28, dubbed “Black Monday,” the Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged nearly 13 percent. The market fell another 12 percent the next day, “ Black Tuesday .” While the crisis send shock waves across the financial world, there were numerous signs that a stock market crash was coming. What exactly caused the crash—and could it have been prevented?
Why did people buy stocks in the 1920s?
During the 1920s, there was a rapid growth in bank credit and easily acquired loans. People encouraged by the market’s stability were unafraid of debt.
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
Only a few years after the Wall Street stock market crashed in October 1929, America had fallen into the Great Depression - the greatest financial crisis in its history.
Why did the Wall Street crash happen in 1929?
However, whilst people were buying less cars, houses and luxury goods, they still kept buying shares. The Wall Street Crash was also caused by innate weaknesses in the American banking system - in the 1920s America had ...
How did the 1920s affect the economy?
To fund the mass consumption of the 1920s, many consumers used bank credit and loans. People placed so much confidence in the economy that they took out loans they couldn’t pay back. Many used loans to buy shares on the stock market - this was called buying shares on the margin. When confidence started failing in 1929, those people who had borrowed rushed to sell their shares and pay back their debts. This panic selling of shares caused a dramatic fall in the value of the market.
Why did Wall Street crash?
The Wall Street Crash was also caused by innate weaknesses in the American banking system - in the 1920s America had over 30,000 banks; this meant that many were prone to going bankrupt if they run out of funds. On average, more than 600 banks failed each year between 1921 and 1929.
What was the economic situation in the 1920s?
America in the 1920s was generally a place of economic prosperity. Mass production and mass consumption increased the standard of living for many Americans. However, this prosperity was not as widespread as many imagined - 60 per cent of the population still lived below the poverty line. The were many reasons for the Wall Street Crash.
How many banks failed in 1921?
On average, more than 600 banks failed each year between 1921 and 1929. An increase in bank failures at the end of the decade triggered a run on deposits. Confidence in the banking system started to decline, and bank runs became more common.
Why did easy access to credit affect stock market?
Easy access to credit gave people too much confidence in the stock market, leading to more people buying shares. This meant that stock prices became divorced from the real value of the shares.
How to protect yourself from the 1929 stock market crash?
1. Diversify. Even though stocks cratered in the 1929 crash, government bonds were safe havens for investors. A position in bonds probably wouldn't have shielded you completely from stock-market losses, but it certainly would have softened the blow.
Why did banks lose money in 1929?
In 1929, it was perfectly possible to save prudently in a bank savings account and lose most of your money because bank deposits weren't insured. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. now insures bank deposits up to $250,000 per bank per person and often more depending on how the deposits are titled.
What was the cause of the Great Depression?
The 1929 Stock Market Crash led to the Great Depression, one of the biggest economic crises in American history.
What were the causes of the Great Crash?
Historians have found plenty of reasons for the Great Crash, ranging from excessive speculation to a slowing global economy to shady investment practices. Even though the world is very different than it was in 1929, we can learn plenty of lessons from the Great Crash and the economic disaster that followed.
What laws were passed during the Great Depression?
However, some of the laws that came out of the Great Depression have been eased. The portion of the Glass-Steagall Act that required commercial banks and investment banks to be separate entities was repealed in 1999. The 1933 law was passed because banks that speculated on their own accounts collapsed in wake of the Great Crash.
What act required companies to give investors information about their financial condition?
The Securities Act of 1933 cracked down on fraud in the financial services industry and required publicly traded companies to give investors information about their financial condition. And the Investment Company Act of 1940 unified rules for mutual fund companies and limited the purchase of securities on margin.
How long did the bear market last?
The most recent bear market, which lasted from 2007 to 2009, clawed the S&P 500 for more than 50 percent of its value and saw millions of people default on their mortgage loans. Only immediate government action kept many major banks from failing.
What happened before 1929?
Prior to the events of 1929 – 1932 businesses and financial markets were largely unregulated. The unbridled capitalism at the turn of the century resulted in monopolies, stock manipulation, and other abuses – all of it legal – finally ending in the excessive speculation that drove stock prices to unsupportable heights in the twenties.
What were the major changes in the financial system prior to the 1929 crash?
Prior to the events of 1929 – 1932 businesses and financial markets were largely unregulated. The unbridled capitalism at the turn of the century resulted in monopolies, stock manipulation, and other abuses – all of it legal – finally ending in the excessive speculation that drove stock prices to unsupportable heights in the twenties. The social, political, economic and technological changes that erupted out of the turbulence of the four decades spanning 1910 to 1950 were many and profound. Here’s a brief summary of legislative changes, first changes that were instituted prior to the 1929-1932 crash but that were motivated by several debilitating recessions:
How does a crash in the stock market affect the economy?
Whether you have savings, or are invested or not, having roads that are paved, bridges that don't fall down and a police force can be useful for the average citizen.
What happened to the people after Roosevelt stole gold?
People could be sent to prison just for keeping their own hard earned money if it was a gold coin. After Roosevelt ripped off people by stealing their gold he raised the price of gold.
How does the stock market benefit society?
The Society as a whole benefits when there is a balanced allocation of time between Labor, Leisure and Charity. A well functioning Stock Market provides capital for growth and jobs (labor) and earnings for consumption and leisure pursuits and the ability to direct excess capital to the Charitable interests of your own choosing.
Why did Ford crush Model T cars?
Ford, for instance, crushed thousands of Model T cars as a result of overproduction, and they were hardly alone. Overproduction led to needing fewer workers, and fewer workers, who had no unemployment insurance, meant less consumer spending. This was the beginning of a downward-spiralling cycle.
What was the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938?
- The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938, which set a minimum wage and outlawed child labor. 2.8K views. ·.
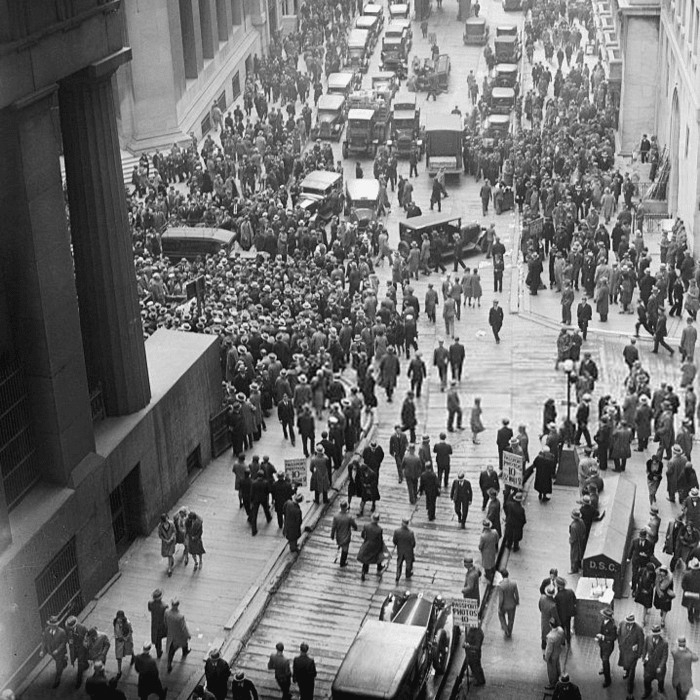
A Timeline of What Happened
Financial Climate Leading Up to The Crash
- Earlier in the week of the stock market crash, the New York Times and other media outlets may have fanned the panic with articles about violent trading periods, short-selling, and the exit of foreign investors; however many reports downplayed the severity of these changes, comparing the market instead to a similar "spring crash" earlier that year, after which the market bounced b…
Effects of The Crash
- The crash wiped many people out. They were forced to sell businesses and cash in their life savings. Brokers called in their loans when the stock market started falling. People scrambled to find enough money to pay for their margins. They lost faith in Wall Street. By July 8, 1932, the Dow was down to 41.22. That was an 89.2% loss from its record-h...
Key Events
- March 1929:The Dow dropped, but bankers reassured investors.
- August 8: The Federal Reserve Bank of New York raised the discount rate to 6%.16
- September 3: The Dow peaked at 381.17. That was a 27% increase over the prior year's peak.1
- September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard.17
Introduction : Stock Market Crash of 1929
Before The Crash: A Period of Phenomenal Growth
The Great Crash
What Was The Crash?
Causes of The Stock Market Crash of 1929
in The Aftermath of The Crash
- After the crash, Hoover announced that the economy was “fundamentally sound.” On the last day of trading in 1929, the New York Stock Exchange held its annual wild and lavish party, complete with confetti, musicians, and illegal alcohol. The U.S. Department of Labor predicted that 1930 would be “a splendid employment year.” These sentiments were not...
Conclusion