The stock market crashed in 1929, plummeting into a correction. Margin buying, lack of legal protections, overpriced stocks and Fed policy contributed to the crash. There are ways to protect investors can protect a portfolio from downturns.
Full Answer
How did the stock market crash of 1929 lead to depression?
The 1929 Stock Market Crash led to the Great Depression, one of the biggest economic crises in American history. En español | Ninety years ago, Wall Street laid an egg. On Oct. 24, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average began a slide that saw a 12.8 percent plunge Oct. 28 and a 11.7 percent decline the next day.
What lessons can we learn from the Great Crash of 1929?
Historians have found plenty of reasons for the Great Crash, ranging from excessive speculation to a slowing global economy to shady investment practices. Even though the world is very different than it was in 1929, we can learn plenty of lessons from the Great Crash and the economic disaster that followed. 1. Diversify.
What should you do after the 1929 stock market crash?
1. Diversify. Even though stocks cratered in the 1929 crash, government bonds were safe havens for investors. A position in bonds probably wouldn't have shielded you completely from stock-market losses, but it certainly would have softened the blow.
What happened to entwined investment trusts after the 1929 stock market crash?
When the stock market crashed in September 1929, all of the entwined investment trusts similarly collapsed. In the wake of the crash, the banks and other lenders that financed the stock-buying spree had little means to collect what they were owed.

What factors led to the stock market crash of 1929?
By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value. Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.
What were three major causes of the crash of 1929?
What were the major causes of the Great Depression? Among the suggested causes of the Great Depression are: the stock market crash of 1929; the collapse of world trade due to the Smoot-Hawley Tariff; government policies; bank failures and panics; and the collapse of the money supply.
What caused the stock market crash of 1929 quizlet?
(1929)The steep fall in the prices of stocks due to widespread financial panic. It was caused by stock brokers who called in the loans they had made to stock investors. This caused stock prices to fall, and many people lost their entire life savings as many financial institutions went bankrupt.
What were the 4 main causes of the Great Depression?
However, many scholars agree that at least the following four factors played a role.The stock market crash of 1929. During the 1920s the U.S. stock market underwent a historic expansion. ... Banking panics and monetary contraction. ... The gold standard. ... Decreased international lending and tariffs.
What was the 1929 stock market crash?
The Wall Street crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, was a sudden and steep decline in stock prices in the United States in late October of that year.
What caused the stock market to go down in 1929?
Other causes included an increase in interest rates by the Federal Reserve in August 1929 and a mild recession earlier that summer, both of which contributed to gradual declines in stock prices in September and October, eventually leading investors to panic. During the mid- to late 1920s, the stock market in the United States underwent rapid ...
What was the Great Depression?
Stock market crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, a sharp decline in U.S. stock market values in 1929 that contributed to the Great Depression of the 1930s. The Great Depression lasted approximately 10 years and affected both industrialized and nonindustrialized countries in many parts of the world. Crowds gathering outside the New York ...
How many points did the Dow close down?
Still, the Dow closed down only six points after a number of major banks and investment companies bought up great blocks of stock in a successful effort to stem the panic that day. Their attempts, however, ultimately failed to shore up the market. The panic began again on Black Monday (October 28), with the market closing down 12.8 percent.
What was the cause of the 1929 Wall Street crash?
The main cause of the Wall Street crash of 1929 was the long period of speculation that preceded it , during which millions of people invested their savings or borrowed money to buy stocks, pushing prices to unsustainable levels. Other causes included an increase in interest rates by the Federal Reserve in August 1929 and a mild recession earlier ...
Why did people sell their Liberty bonds?
People sold their Liberty Bonds and mortgaged their homes to pour their cash into the stock market. In the midsummer of 1929 some 300 million shares of stock were being carried on margin, pushing the Dow Jones Industrial Average to a peak of 381 points in September.
What happened in 1929?
Updated September 02, 2020. The stock market crash of 1929 was a collapse of stock prices that began on Oct. 24, 1929. By Oct. 29, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average had dropped 24.8%, marking one of the worst declines in U.S. history. 1 It destroyed confidence in Wall Street markets and led to the Great Depression .
What happened on September 26th 1929?
September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard. September 29, 1929: The Hatry Case threw British markets into panic. 6. October 3: Great Britain's Chancellor of the Exchequer Phillip Snowden called the U.S. stock market a "speculative orgy.".
How much did the Dow rise in 1933?
On March 15, 1933, the Dow rose 15.34%, a gain of 8.26 points, to close at 62.1. 8. The timeline of the Great Depression tracks critical events leading up to the greatest economic crisis the United States ever had. The Depression devastated the U.S. economy.
What was the Dow down in 1932?
By July 8, 1932, the Dow was down to 41.22. That was an 89.2% loss from its record-high close of 381.17 on September 3, 1929. It was the worst bear market in terms of percentage loss in modern U.S. history. The largest one-day percentage gain also occurred during that time.
Why did banks honor 10 cents for every dollar?
That's because they had used their depositors' savings, without their knowledge, to buy stocks. November 23, 1954: The Dow finally regained its September 3, 1929, high, closing at 382.74. 8.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 followed an epic period of economic growth during what's now known as the Roaring Twenties. The Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJINDICES:^DJI) was at 63 points in August 1921 and increased six-fold over the next eight years, closing at a high of 381.17 points on Sept. 3, 1929. That September day marked the peak of the ...
What happened to the stock market in 1929?
When the stock market crashed in September 1929, all of the entwined investment trusts similarly collapsed. In the wake of the crash, the banks and other lenders that financed the stock-buying spree had little means to collect what they were owed. Their only collateral was stocks for which the amount of debt outstanding exceeded the stocks' worth.
What happened on Oct 29th?
On Monday, Oct. 29, the Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged by nearly 13%. The next day, the index tumbled by almost another 12%. These devastating two days have since become known as Black Monday and Black Tuesday. Over the months and years that followed, the stock market continued to lose value.
What was the total non-corporate debt in 1929?
By September 1929, total noncorporate debt in the U.S. amounted to 40% of the nation's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). At the same time that readily available credit was fueling consumer spending, the buoyant stock market gave rise to many new brokerage houses and investment trusts, which enabled the average person to buy stocks.
How many cars did people buy in the 1920s?
People in the 1920s acquired six of every 10 automobiles and eight of every 10 radios on credit. This debt-fueled buying binge was enabled by thousands of banks and hundreds of new "installment credit" companies, which loaned money to essentially anyone who wanted it.
When did the Dow drop?
By mid-November 1929, the Dow had declined by almost half. It didn't reach its lowest point until midway through 1932, when it closed at 41.22 points -- 89% below its peak. The Dow didn't return to its September 1929 high until November 1954.
What happens when investment trusts are heavily leveraged?
Some investment trusts, themselves heavily leveraged, also invested in other similarly leveraged investment trusts , which, in turn, invested in other investment trusts employing the same strategy. As a result, each of these trusts became inordinately affected by the movements of others' stock holdings. When the stock market crashed in September ...
What happened in 1929?
In October of 1929, the stock market crashed, wiping out billions of dollars of wealth and heralding the Great Depression. Known as Black Thursday, the crash was preceded by a period of phenomenal growth and speculative expansion. A glut of supply and dissipating demand helped lead to the economic downturn as producers could no longer readily sell ...
Why did the economy stumbled in 1929?
In mid-1929, the economy stumbled due to excess production in many industries, creating an oversupply.
How many times did stock prices go up in 1929?
Until the peak in 1929, stock prices went up by nearly 10 times. In the 1920s, investing in the stock market became somewhat of a national pastime for those who could afford it and even those who could not—the latter borrowed from stockbrokers to finance their investments. The economic growth created an environment in which speculating in stocks ...
Why did companies acquire money cheaply?
Essentially, companies could acquire money cheaply due to high share prices and invest in their own production with the requisite optimism. This overproduction eventually led to oversupply in many areas of the market, such as farm crops, steel, and iron.
What was the result of the Great War?
The result was a series of legislative measures by the U.S. Congress to increase tariffs on imports from Europe.
What happens when the stock market falls?
However, when markets are falling, the losses in the stock positions are also magnified. If a portfolio loses value too rapidly, the broker will issue a margin call, which is a notice to deposit more money to cover the decline in the portfolio's value.
What happens if a broker doesn't deposit funds?
If the funds are not deposited, the broker is forced to liquidate the portfolio. When the market crashed in 1929, banks issued margin calls. Due to the massive number of shares bought on margin by the general public and the lack of cash on the sidelines, entire portfolios were liquidated.
What lessons did the Federal Reserve learn from the 1929 stock market crash?
9. First, central banks – like the Federal Reserve – should be careful when acting in response to equity markets. Detecting and deflating financial bubbles is difficult.
What happened in 1929?
Commercial banks continued to loan money to speculators, and other lenders invested increasing sums in loans to brokers. In September 1929, stock prices gyrated, with sudden declines and rapid recoveries.
How much did the Dow drop in 1932?
The slide continued through the summer of 1932, when the Dow closed at 41.22, its lowest value of the twentieth century, 89 percent below its peak.
What happened on Black Monday 1929?
On Black Monday, October 28, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined nearly 13 percent. Federal Reserve leaders differed on how to respond to the event and support the financial system.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average increase?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average increased six-fold from sixty-three in August 1921 to 381 in September 1929 . After prices peaked, economist Irving Fisher proclaimed, “stock prices have reached ‘what looks like a permanently high plateau.’” 2. The epic boom ended in a cataclysmic bust.
Who created the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
Dow Jones Industrial Average (Created by: Sam Marshall, Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond) Enlarge. The financial boom occurred during an era of optimism. Families prospered. Automobiles, telephones, and other new technologies proliferated. Ordinary men and women invested growing sums in stocks and bonds.
Who published a monetary history of the United States in 1963?
Consensus coalesced around the time of the publication of Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz’ s A Monetary History of the United States in 1963.
What caused the 1929 stock market crash?
Copy Link. The stock market crashed in 1929, plummeting into a correction. Margin buying, lack of legal protections, overpriced stocks and Fed policy contributed to the crash. There are ways to protect investors can protect a portfolio from downturns.
How much did stock prices increase in 1929?
However, there is not a lot of evidence to support this. Stocks increased by 120% between 1925 and the third quarter of 1929, an average annual increase of about 22% . This is a big increase but in the context of a period of tremendous economic growth, it is not unreasonable.
How much did stocks return in 1928?
From 1927 to just before the crash, market returns grew exponentially. In 1928, stocks returned a whopping 43.8%. Here’s a look at the Dow Jones Industrial Average from 1927 to 1932: As much as markets fell in the crash, they still had a long way to go before finally bottoming out in 1932.
Why did banks only honor 10 cents on the dollar?
After the crash, banks were only able to honor 10 cents on the dollar because they had used customers’ deposits to purchase stocks without their knowledge. Additionally, investors had no recourse to recover funds if their brokerage firm went out of business. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) were founded in 1933 and 1934, respectively, as part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s efforts to restore confidence in the markets under the New Deal.
What happened to public utilities stocks in 1929?
Public utilities stocks were more than triple their book value in 1929 so these headlines did generate valid concerns. In the run up to Black Thursday, major newspaper headlines continued to focus on market dips, the lack of alarm among Washington officials about these dips, and the rising panic of investors.
What was the total return of a portfolio of 60% stocks and 40% bonds in 1929?
During the period from August 1929 through March 1933, the total return of a portfolio that was 60% stocks and 40% bonds was -50.2%. During that same period, the S&P 500’s total return was -74.6% and the 10-year Treasury’s total return was +15.3%.
What happened on Black Thursday 1929?
By October 23, 1929, the Dow Jones was down nearly 20% from its high and in the last hour of trading that day, stock prices took a sudden plunge. The market closed amidst confusion and concern.
Why did banks lose money in 1929?
In 1929, it was perfectly possible to save prudently in a bank savings account and lose most of your money because bank deposits weren't insured. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. now insures bank deposits up to $250,000 per bank per person and often more depending on how the deposits are titled.
What happened on Oct 24 1929?
On Oct. 24, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average began a slide that saw a 12.8 percent plunge Oct. 28 and a 11.7 percent decline the next day. By the end of the bear market in 1932, the Dow had plummeted 89 percent from its 1929 high, erasing all the gains of the Roaring Twenties, and the nation was in the depths of the Great Depression.
What are some good things to do in the stock market?
4 always-good pieces of advice. 1. Diversify. Even though stocks cratered in the 1929 crash, government bonds were safe havens for investors. A position in bonds probably wouldn't have shielded you completely from stock-market losses, but it certainly would have softened the blow. 2.
What were the causes of the Great Crash?
Historians have found plenty of reasons for the Great Crash, ranging from excessive speculation to a slowing global economy to shady investment practices. Even though the world is very different than it was in 1929, we can learn plenty of lessons from the Great Crash and the economic disaster that followed.
What laws were passed during the Great Depression?
However, some of the laws that came out of the Great Depression have been eased. The portion of the Glass-Steagall Act that required commercial banks and investment banks to be separate entities was repealed in 1999. The 1933 law was passed because banks that speculated on their own accounts collapsed in wake of the Great Crash.
What act required companies to give investors information about their financial condition?
The Securities Act of 1933 cracked down on fraud in the financial services industry and required publicly traded companies to give investors information about their financial condition. And the Investment Company Act of 1940 unified rules for mutual fund companies and limited the purchase of securities on margin.
How to invest when you lose your job?
2. Keep cash in reserve. Your most important investment is you, and if you lose your job, you'll need some savings to enable you and your family to stay afloat. In addition, a cash stash can help you pick up bargains in the aftermath of a market decline.
When did Wall Street collapse?
Front pages of American newspapers dedicated to the collapse of Wall Street in October 1929. DEA Picture Library/Getty Images. Contrary to popular lore, there was no epidemic of suicides—let alone window-jumpings—in the wake of the Stock Market Crash of 1929.
How many people jumped from the roof of the Equitable Building?
There were, in fact, at least two people who jumped to their deaths in Manhattan’s financial district in the weeks following the 1929 Crash. Hulda Borowski, a clerk who had worked for 28 years at a brokerage firm, leapt from the roof of the 40-story Equitable Building on November 7.
How old was George Cutler when he jumped from the seventh floor?
Nine days later, 65-year-old George Cutler, head of a wholesale produce firm and a member of the New York Mercantile Exchange who had sustained heavy losses in the market, jumped from the seventh-floor ledge outside his lawyer’s office and landed on an automobile parked on Wall Street. pinterest-pin-it. An aerial view of the New York Stock Exchange ...
When was the surveyor walking back and forth in New York City?
Down below, however, October 24, 1929 , was no ordinary day.
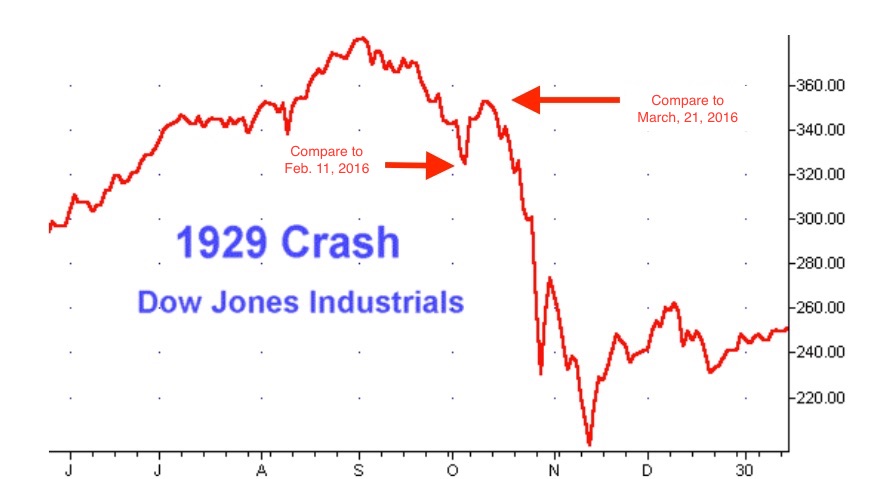
A Timeline of What Happened
Financial Climate Leading Up to The Crash
- Earlier in the week of the stock market crash, the New York Times and other media outlets may have fanned the panic with articles about violent trading periods, short-selling, and the exit of foreign investors; however many reports downplayed the severity of these changes, comparing the market instead to a similar "spring crash" earlier that year, after which the market bounced b…
Effects of The Crash
- The crash wiped many people out. They were forced to sell businesses and cash in their life savings. Brokers called in their loans when the stock market started falling. People scrambled to find enough money to pay for their margins. They lost faith in Wall Street. By July 8, 1932, the Dow was down to 41.22. That was an 89.2% loss from its record-high close of 381.17 on September …
Key Events
- March 1929:The Dow dropped, but bankers reassured investors.
- August 8: The Federal Reserve Bank of New York raised the discount rate to 6%.16
- September 3: The Dow peaked at 381.17. That was a 27% increase over the prior year's peak.1
- September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard.17