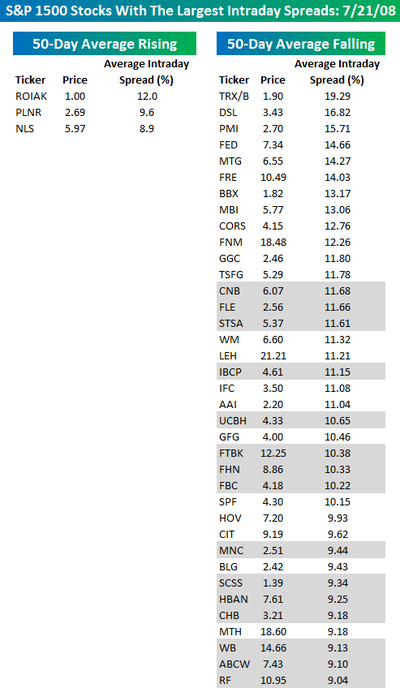
A volatile stock market is one in which there is a fair amount of liquidity and price valuation. Not all markets are volatile, or not all markets are volatile at all times. There are variations in volatility that are seasonal, news, or event-specific, or even based on broader trends like election years and the general direction of fiscal policy.
What makes stock prices volatile?
Volatility is simply a statistical value that measures the range of returns for a given security or market index. It measures this dispersion through standard deviation or variance between returns. A stock’s volatility is equal to the amount that particular stock will separate from the original price at which it was traded. When volatility is high, the dispersion will be wider as well …
What is the definition of volatile stock?
· Stock market volatility is a measure of how much the stock market's overall value fluctuates up and down. Beyond the market as a whole, individual stocks can be considered volatile as well. More...
What is the most volatile stock?
At its most basic, stock volatility is the extent to which share prices increase and decrease. It measures how fast those movements are, how often they occur, and how big they are.
What does high volatility mean in stocks?
· Stock volatility is when stock dramatically increases or decreases within a period of time. Stock volatility refers to the potential for a given stock to experience a drastic decrease or increase in value within a predetermined period of time.
What is volatility in the stock market?
In the securities markets, volatility is often associated with big swings in either direction. For example, when the stock market rises and falls more than one percent over a sustained period of time, it is called a "volatile" market. An asset's volatility is a key factor when pricing options contracts.
What is volatility in securities?
Volatility is often measured as either the standard deviation or variance between returns from that same security or market index. In the securities markets, volatility is often associated with big swings in either direction.
What is volatility in financials?
Volatility often refers to the amount of uncertainty or risk related to the size of changes in a security's value. A higher volatility means that a security's value can potentially be spread out over a larger range of values.
What does lower volatility mean?
A lower volatility means that a security's value does not fluctuate dramatically, and tends to be more steady. One way to measure an asset's variation is to quantify the daily returns (percent move on a daily basis) of the asset.
What is implied volatility?
Implied volatility (IV), also known as projected volatility, is one of the most important metrics for options traders. As the name suggests, it allows them to make a determination of just how volatile the market will be going forward. This concept also gives traders a way to calculate probability.
What is the beta of a stock?
One measure of the relative volatility of a particular stock to the market is its beta (β). A beta approximates the overall volatility of a security's returns against the returns of a relevant benchmark (usually the S&P 500 is used). For example, a stock with a beta value of 1.1 has historically moved 110% for every 100% move in the benchmark, based on price level. Conversely, a stock with a beta of .9 has historically moved 90% for every 100% move in the underlying index.
What is volatility in the stock market?
What is stock market volatility? Stock market volatility is a measure of how much the stock market's overall value fluctuates up and down. Beyond the market as a whole, individual stocks can be considered volatile as well. More specifically, you can calculate volatility by looking at how much an asset's price varies from its average price.
Is volatility the same as risk?
It's important to note, though, that volatility and risk are not the same thing. For stock traders who look to buy low and sell high every trading day, volatility and risk are deeply intertwined. Volatility also matters for those who may need to sell their stocks soon, such as those close to retirement.
Is blue chip stock volatile?
That blue-chip stock is considered to have low volatility, while the tech stock has high volatility. Medium volatility is somewhere in between.
What is the beta of a stock?
For individual stocks, volatility is often encapsulated in a metric called beta. Beta measures a stock's historical volatility relative to the S&P 500 index. A beta of more than one indicates that a stock has historically moved more than the S&P 500.
What is medium volatility?
Medium volatility is somewhere in between. An individual stock can also become more volatile around key events like quarterly earnings reports. Volatility is often associated with fear, which tends to rise during bear markets, stock market crashes, and other big downward moves.
Is the VIX a fear gauge?
The number itself isn't terribly important, and the actual calculation of the VIX is quite complex. However, it's important for investors to know that the VIX is often referred to as the market 's "fear gauge.". If the VIX rises significantly, investors could be worried about massive stock price movements in the days and weeks ahead.
What does a negative beta mean?
And, finally, a negative beta (which is quite rare) tells investors that a stock tends to move in the opposite direction from the S&P 500.
What is volatility in stock market?
At its most basic, stock volatility is the extent to which share prices increase and decrease. It measures how fast those movements are, how often they occur, and how big they are.
What is historical volatility?
As the name implies, historical volatility is a look back at a stock’s volatility in the preceding 12-month period. High levels of volatility correspond to higher risk. For some investors, that can mean higher reward.
Is there a science to investing in the stock market?
Stock Volatility Explained: There is a science to investing in the stock market. Collecting and analyzing financial and economic data can lead to smart trading decisions. However, when it comes to buying and selling securities, science will only get you so far. To date, there is no formula that delivers perfect results with every trade.
Why is the VIX a fear index?
The VIX is also known as the “ fear index ”, because it is essentially a measure of how investors are feeling. Higher volatility indicates greater uncertainty among investors, and an upswing in the VIX often indicates a coming drop in stock prices.
Why do share prices go up?
As a general rule, share prices tend to move up or down dramatically when there is an imbalance in trading activity – for example, many more buyers than sellers, or vice versa. When demand is high, share prices go up, and when demand is low , share prices go down.
Is volatility good or bad?
The question of whether stock volatility is good or bad doesn’t have a simple answer. Instead, it’s a matter of degree, as well as whether and how varying levels of volatility fit into your specific investment strategy. An asset that has zero volatility would never increase in value, which presents a number of issues.
Is the S&P 500 more volatile than the S&P 500?
Yes. No. If the specific stock’s movement corresponds perfectly with the S&P 500 Index, it has a beta of 1.0. If the given stock has a beta greater than 1.0, it is more volatile than the S&P 500 Index. Conversely, if the beta is less than 1.0, the stock is less volatile than the S&P 500.
What is stock volatility?
Seconds. Stock volatility is when stock dramatically increases or decreases within a period of time. Investors should be aware of the stock volatility associated with any given stock. Market volatility can take place when consumers begin to lose confidence in the economy.
What are the factors that affect stock volatility?
There are number of factors that can impact stock volatility. One of the major concerns is the stability of the underlying assets supporting the stock issue. For example, if public confidence in a corporation should suddenly decrease, there is a good chance that the stock issue will also experience a significant drop.
What is volatility in the market?
Market volatility is the frequency and magnitude of price movements, up or down. The bigger and more frequent the price swings, the more volatile the market is said to be.
Is volatility a part of investing?
It can be scary to see large—or even small—losses on paper. But in the end, you must remember that market volatility is a typical part of investing, and the companies you invest in will respond to a crisis.
What is the VIX index?
Casual market watchers are probably most familiar with that last method, which is used by the Chicago Board Options Exchange’s Volatility Index, commonly referred to as the VIX.
Is the stock market calm?
Most of the time, the stock market is fairly calm, interspersed with briefer periods of above-average market volatility . Stock prices aren’t generally bouncing around constantly—there are long periods of not much excitement, followed by short periods with big moves up or down.
Is investing a long haul game?
Investing is a long-haul game, and a well-balanced, diversified portfolio was actually built with periods like this in mind. If you need your funds in the near future, they shouldn’t be in the market, where volatility can affect your ability to get them out in a hurry.
What is the difference between bullish and bearish?
In general, bullish (upward-trending ) markets tend to be associated with low volatility, and bearish (downward-trending) markets usually come with unpredictable price swings, which are typically downward. “This is how it works,” Lineberger says.
What is volatility?
A more specific definition of the word volatility when it comes to the stock market is how large the price movements of a stock or index have been (or are expected to be).
Why is knowing volatility important?
To be clear, this isn't an exhaustive discussion of all of the volatility terms that exist in the investing world, but they are perhaps the most important volatility-related concepts for everyday (nonprofessional) investors to know and understand.
Your relationship with volatility
The past several months have offered an opportunity for investors to reevaluate their risk tolerance. One way to assess your willingness to withstand risk is to reflect on your emotional reactions to the recent swings. If they kept you from sleeping and caused churning in your stomach, it might mean your portfolio is too aggressive.
What is a highly volatile stock?
A stock with a price that fluctuates wildly—hits new highs and lows or moves erratically—is considered highly volatile. A stock that maintains a relatively stable price has low volatility. A highly volatile stock is inherently riskier, but that risk cuts both ways. When investing in a volatile security, the chance for success is increased as much ...
What is volatility in investing?
The most simple definition of volatility is a reflection of the degree to which price moves. A stock with a price that fluctuates wildly—hits new highs and lows or moves erratically—is considered highly volatile.
What is the measure of volatility?
This metric reflects the average amount a stock's price has differed from the mean over a period of time. It is calculated by determining the mean price for the established period and then subtracting this figure from each price point. The differences are then squared, summed, and averaged to produce the variance .
What are Bollinger bands?
Bollinger Bands are comprised of three lines: the simple moving average (SMA) and two bands placed one standard deviation above and below the SMA. The SMA is a smoothed out version of the stock's price history, but it is slower to respond to changes.
What does a beta of 1 mean?
A beta of 1 means the security has volatility that mirrors the degree and direction of the market as a whole. If the S&P 500 takes a sharp dip, the stock in question is likely to follow suit and fall by a similar amount.
What is maximum drawdown?
Maximum drawdown is another way to measure stock price volatility, and it is used by speculators, asset allocators, and growth investors to limit their losses. Beta measures volatility relative to the stock market, and it can be used to evaluate the relative risks of stocks or determine the diversification benefits of other asset classes.
What is a volatile stock market?
A volatile stock market is one in which there is a fair amount of liquidity and price valuation. Not all markets are volatile, or not all markets are volatile at all times. There are variations in volatility that are seasonal, news, or event-specific, or even based on broader trends like election years and the general direction of fiscal policy.
What does volatility mean in stocks?
Updated Jun 25, 2019. Volatility refers to the upward and downward movement of price. The more prices fluctuate, the more volatile the stock market is, and vice versa. A higher level of volatility means that prices can change dramatically over a short time period in either direction.
Is short term volatility good?
In some cases, short-term volatility is seen as a good thing, especially for active traders. The reason for this is that active traders look to profit from short-term movements in the market and individual securities—the greater the movement or volatility, the greater the potential for quick gains. Of course, there is the real possibility ...
Who is Brian Beers?
Brian Beers is a digital editor, writer, Emmy-nominated producer, and content expert with 15+ years of experience writing about corporate finance & accounting, fundamental analysis, and investing. Volatility refers to the upward and downward movement of price. The more prices fluctuate, the more volatile the stock market is, and vice versa.
What is the relationship between portfolio returns and risk?
One examination of the relationship between portfolio returns and risk is the efficient frontier, a curve that is a part of the modern portfolio theory. The curve forms from a graph plotting return and risk indicated by volatility, which is represented by the standard deviation. According to the modern portfolio theory, funds lying on the curve are yielding the maximum return possible, given the amount of volatility.
What is standard deviation in investing?
The standard deviation essentially reports a fund's volatility, which indicates the tendency of the returns to rise or fall drastically in a short period of time. A volatile security is also considered a higher risk because its performance may change quickly in either direction at any moment.
What is the difference between standard deviation and beta?
Beta. While standard deviation determines the volatility of a fund according to the disparity of its returns over a period of time, beta, another useful statistical measure, compares the volatility (or risk) of a fund to its index or benchmark. A fund with a beta very close to one means the fund's performance closely matches the index or benchmark.
What does R squared mean in mutual funds?
The R-squared of a fund shows investors if the beta of a mutual fund is measured against an appropriate benchmark. Measuring the correlation of a fund's movements to that of an index, R-squared describes the level of association between the fund's volatility and market risk, or, more specifically, the degree to which a fund's volatility is a result of the day-to-day fluctuations experienced by the overall market.
What is the difference between beta and alpha?
Beta, another useful statistical measure, compares the volatility (or risk) of a fund to its index or benchmark . The R-squared of a fund shows investors if the beta of a mutual fund is measured against an appropriate benchmark. Alpha measures how much , if any , extra risk helped the fund outperform its corresponding benchmark.