What is preferred stock, and should I buy it?
That means it might be harder to buy or sell your preferred stocks at the prices you seek. Preferred stocks are usually less risky than common dividend stocks, and carry higher yields, but lack the opportunity for price appreciation as the issuing company grows. They also go without voting rights.
What companies have preferred stock?
Preferred Stocks Directory
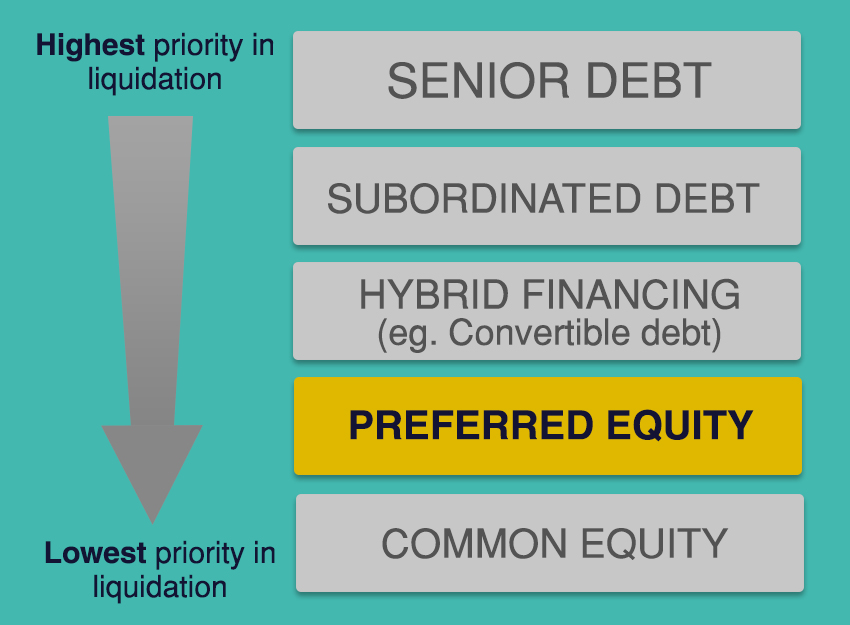
- Preferred shares are shares issued by a corporation as part of its capital structure.
- Preferred stock have a “coupon rate” — the interest rate you will be paid. ...
- Dividends are either cumulative — meaning that dividends continue to accrue if they have been suspended, but they are not paid until the company decides to pay them after suspension ...
What is the difference between preferred stock and common stock?
- Receives a specified dividend that is often higher than common stock dividends
- Less chance of losing value
- Has priority over common stock for payout in a liquidation, as well as for receiving dividends
What are the usual characteristics of preferred stock?
What are some of the major characteristics of common and preferred stock?
- The Voting Rights of Common Stock Holders.
- The Value of Common Stocks.
- Capability of Receiving Periodic Dividends.
- Profit and Risks Relation.
- Tax Exemptions (Indirect)
- Claim on Assets.
- Chances of Losing Everything in the Case of Bankruptcy.
- Right to have Capital Gain.

What is the difference between stock and preferred stock?
The main difference between preferred and common stock is that preferred stock gives no voting rights to shareholders while common stock does. Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders.
Why would you buy a preferred stock?
Preferred stocks do provide more stability and less risk than common stocks, though. While not guaranteed, their dividend payments are prioritized over common stock dividends and may even be back paid if a company can't afford them at any point in time.
How does preferred stock work?
Preferreds are issued with a fixed par value and pay dividends based on a percentage of that par, usually at a fixed rate. Just like bonds, which also make fixed payments, the market value of preferred shares is sensitive to changes in interest rates. If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls.
What is preferred stock in simple words?
Preferred stock is a type of stock that offers different rights to shareholders than common stock. Preferred stock holders receive regular dividends and are repaid first in the event of a bankruptcy or merger.
What is the downside of preferred stock?
Disadvantages of preferred shares include limited upside potential, interest rate sensitivity, lack of dividend growth, dividend income risk, principal risk and lack of voting rights for shareholders.
Are preferred stocks good?
Preferred stocks are usually less risky than common dividend stocks, and carry higher yields, but lack the opportunity for price appreciation as the issuing company grows. They also go without voting rights.
Who buys preferred stock?
InstitutionsInstitutions are usually the most common purchasers of preferred stock. This is due to certain tax advantages that are available to them, but which are not available to individual investors. 3 Because these institutions buy in bulk, preferred issues are a relatively simple way to raise large amounts of capital.
Why would a company issue preferred stock?
Companies issue preferred stock as a way to obtain equity financing without sacrificing voting rights. This can also be a way to avoid a hostile takeover. A preference share is a crossover between bonds and common shares.
Can I sell my preferred stock?
However, more like stocks and unlike bonds, companies may suspend these payments at any time. Preferred stocks oftentimes share another trait with many bonds — the call feature. The company that sold you the preferred stock can usually, but not always, force you to sell the shares back at a predetermined price.
Is preferred stock debt or equity?
equityWhile preferred stock is technically equity, its particular terms may lead it to be treated more like debt for regulatory capital or tax purposes. For example, rating agencies often decline to give full equity credit for preferred stock that is mandatorily redeemable or the dividend obligation of which is cumulative.
How do I invest in preference shares?
How to purchase Preference Share in India? Preference Shares can be purchased through the primary market (in case of an IPO or FPO) or through the secondary market (on the exchange or over the counter) depending on their listing status. For online trading, investors must have a demat account.
Is preferred stock an asset?
Preferred stock is sometimes considered a hybrid of a bond and common stock since the dividends are pre-defined unlike common stock. On a balance sheet, both stock types would be listed under the shareholder equity section of the report. To reiterate, neither one is an asset to the company.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
Why are preferred stocks considered hybrid securities?
Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds. Technically, they are securities, but they share many characteristics with debt instruments . Preferred stocks are sometimes called hybrid securities.
Why are preferred dividends suspended?
Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rates rise?
If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls. If rates decline, the opposite would hold true.
What is preferred stock?
What is a preferred stock? A preferred stock is a share of a company just like a regular (or common) stock, but preferred stocks include some added protections for shareholders. For example, preferred stockholders get priority over common stockholders when it comes to dividend payments.
How do preferred stocks work?
How preferred stocks work 1 Preferred stocks typically pay out fixed dividends on a regular schedule. 2 Similar to other fixed-income securities, which have an inverse relationship with interest rates, preferred stocks may respond to changes in interest rates. 3 Like bonds, preferred stocks have a “par value” they can be redeemed at, typically $25 per share. And both can be repurchased, or “called,” by the issuer after a certain period, often five years.
Why are preferred stocks good investments?
Preferred stocks can make an attractive investment for those seeking steady income with a higher payout than they’d receive from common stock dividends or bonds. But they forgo the uncapped upside potential of common stocks and the safety of bonds.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company usually issues preferred stock for many of the same reasons that it issues a bond, and investors like preferred stocks for similar reasons. For a company, preferred stock and bonds are convenient ways to raise money without issuing more costly common stock. Investors like preferred stock because this type of stock often pays ...
Is preferred stock more risky than common stock?
Thus, preferred stocks are generally considered less risky than common stocks, but more risky than bonds.
Can you postpone a preferred dividend?
Preferred dividends can be postponed (and sometimes skipped entirely) without penalty. This feature is unique to preferred stock, and companies will make use of it if they’re unable to make a dividend payment. Cumulative preferred stocks may postpone the dividend but not skip it entirely — the company must pay the dividend at a later date.
Is preferred stock perpetual?
Preferred stock is often perpetual. Bonds have a defined term from the start, but preferred stock typically does not. Unless the company calls — meaning repurchases — the preferred shares, they can remain outstanding indefinitely. Preferred dividends can be postponed (and sometimes skipped entirely) without penalty.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is a special class of equity that adds debt features. As with common stock, shareholders receive a share of ownership in the company. Preferred stock also receives special rights, including guaranteed dividends that must be paid out before dividends to common shareholders, priority in the event of a liquidation, ...
What is preferred shareholder?
Preferred shareholders also have priority over common shareholders in any remaining equity. The preferred shareholder agreement sets out how remaining equity is divided. Preferred shareholders may receive a fixed amount or a certain ratio versus common shareholders.
What happens to preferred stock when the company goes out of business?
If the company goes out of business and is liquidated, debt holders will be repaid first. Next, preferred shareholders will receive any outstanding dividends.
Why do preferred shares count as equity?
To avoid increasing your debt ratios; preferred shares count as equity on your balance sheet. To pay dividends at your discretion. Because dividend payments are typically smaller than principal plus interest debt payments. Because a call feature can protect against rising interest rates.
Do preferred stock companies pay dividends?
While preferred stock is outstanding, the company must pay dividends. The dividend may be a fixed dollar amount or based on a metric such as profits. Common shareholders may not receive dividends unless preferred dividends have been fully paid. This includes any accumulated dividends.
Do preferred shareholders have voting rights?
Voting: Most preferred shareholders have no voting rights under normal circumstances. Special voting rights may apply when dividends are suspended or the company is in financial distress.
Is a payment to shareholders considered a dividend?
Payments to shareholders and key employees above reasonable salaries may legally be considered dividends. Common shareholders receive lower priority than preferred shareholders in the event of a liquidation. Some states may impose a tax based on the number of authorized or outstanding shares.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock becomes an additional asset on the balance sheet, something that banks need more than oil companies and semiconductor manufacturers do. (For more, see: Preferred Stock Features .)
What are the disadvantages of preferred stock?
Just from the name, you’d figure preferred stockholders would receive, well, preferential treatment. But when a company elects board members, it’s the common stockholders who do the electing while the preferred stockholders sit on the sidelines, disenfranchised. (For more, see: Know Your Rights as a Shareholder .)
Do preferred shareholders receive dividends?
Preferred shareholders indeed receive dividend payments: the dividends are a selling feature, intrinsic to the security. Whereas with common stock, corporations are under no obligation to offer dividends.
Who gets paid first when a company liquidates?
When the company liquidates, the bondholders get paid first. Which makes sense; they’re the creditors, the ones who lent their money to the company to help it stay afloat. Should there be anything left once the bondholders get made whole, the preferred shareholders get paid next.
Do blue chip companies have preferred stock?
In practice, the blue-chip companies that offer dividends on their common stock don’t issue preferred stock, at all. Seldom do the companies that don’t offer dividends on their common stock, either. Preferred stock is a dying class of share. According to some estimates, there’s $80 of common stock circulating in the United States for every dollar of preferred stock. None of the heavyweights – Apple Inc. ( AAPL ), Exxon Mobil Corp. ( XOM ), Microsoft Corp. ( MSFT ), etc., offer preferred stock. Among the 30 largest corporations in America by market capitalization, the only ones that do offer preferred stocks are the Big Four banks – Wells Fargo & Co. ( WFC ), Bank of America Corp. ( BAC ), Citigroup Inc. ( C) and JPMorgan Chase & Co. ( JPM ). In fact, about 88% of preferred stock is issued by banks. As to why, it’s the continuation of the aftermath of the financial crisis and corresponding bailouts of 2008-09. Preferred stock becomes an additional asset on the balance sheet, something that banks need more than oil companies and semiconductor manufacturers do. (For more, see: Preferred Stock Features .)
What is preferred stock?
preferred stock. A security that shows ownership in a corporation and that gives the holder a claim prior to the claim of common stockholders on earnings and also generally on assets in the event of liquidation. Most preferred stock issues pay a fixed dividend set at the time of issuance, stated in a dollar amount or as a percentage of par value.
Do preferred stocks have dividends?
Preferred stocks receive dividends before common shares and sometimes have guaranteed dividends , while common shares only receive the leftovers. Preferred stocks also have a prior claim on capital in the event of liquidation; if the company is liquidated, all preferred shareholders must be paid off before a single common shareholder.
How does preferred stock work?
In fact, preferred stock functions similarly to bonds since with preferred shares, investors are usually guaranteed a fixed dividend in perpetuity. The dividend yield of a preferred stock is calculated as the dollar amount of a dividend divided by the price of the stock.
What is preferred stock in liquidation?
In a liquidation, preferred stockholders have a greater claim to a company's assets and earnings.
What is the difference between common stock and preferred stock?
The main difference is that preferred stock usually does not give shareholders voting rights, while common stock does, usually at one vote per share owned. 1 Many investors know more about common stock than they do about preferred stock.
What is preferred shareholder?
Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders. Common stockholders are last in line when it comes to company assets, which means they will be paid out after creditors, bondholders, and preferred shareholders.
What is common stock?
Common Stock. Common stock represents shares of ownership in a corporation and the type of stock in which most people invest. When people talk about stocks, they are usually referring to common stock. In fact, the great majority of stock is issued in this form.
When are common stockholders last in line?
Common stockholders are last in line for the company's assets. 1 This means that when the company must liquidate and pay all creditors and bondholders, common stockholders will not receive any money until after the preferred shareholders are paid out.
When was the first common stock issued?
But keep in mind, if the company does poorly, the stock's value will also go down. The first common stock ever issued was by the Dutch East India Company in 1602. Preferred shares can be converted to a fixed number of common shares, but common shares don't have this benefit.
What is cumulative preferred stock?
Cumulative preferred stock is a type of preferred stock with a provision that stipulates that if any dividend payments have been missed in the past, the dividends owed must be paid out to cumulative preferred shareholders first.
Is preferred stock a liability?
Preferred stocks are valued similarly to bonds. Bond proceeds are considered to be a liability, while preferred stock proceeds are counted as an asset. Also, bondholders have a priority claim on company assets. Cumulative preferred stock is a type of preferred stock; others include non-cumulative preferred stock, participating preferred stock, ...
Do standard preferred stock shareholders get dividends?
When the company gets through the trouble and starts paying out dividends again, standard preferred stock shareholders possess no rights to receive any missed dividends. These standard preferred shares are sometimes referred to as non-cumulative preferred stock. In contrast, holders of the cumulative preferred stock shares will receive all dividend ...
Do you have to wait until you get your preferred stock dividends?
Essentially, the common stockholders have to wait until all cumulative preferred dividends are paid up before they get any dividend payments again. For this reason, cumulative preferred shares ...
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating preferred stock is a type of preferred stock that gives the holder the right to receive dividends equal to the customarily specified rate that preferred dividends are paid to preferred shareholders, as well as an additional dividend based on some predetermined condition.
Can non-participating preferred stock be issued?
Nonparticipating preferred shareholders, on the other hand, receive their liquidation value and any dividends in arrears if applicable, but they are not entitled to any other consideration. Participating preferred stock is rarely issued, but one way in which it is used is as a poison pill.
