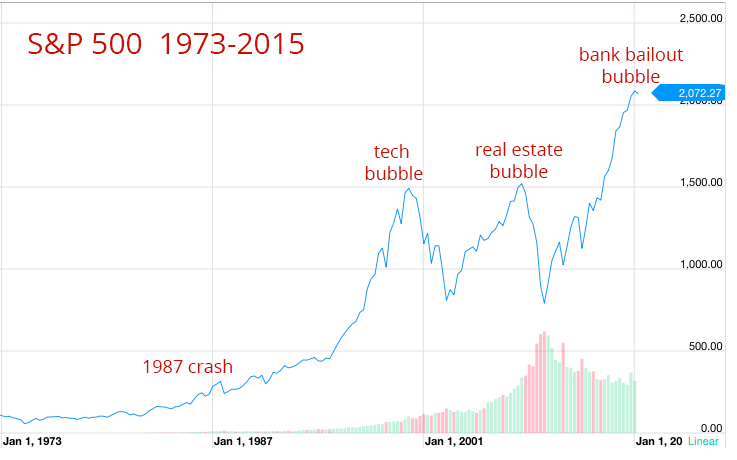
A stock market bubble is a period of growth in stock prices followed by a fall. Typically prices rise quickly and significantly, growing far beyond their previous value in a short period of time. When they fall, they do so quickly and often below the starting value.
What causes stock market bubble?
Jan 23, 2022 · “Stock market bubble” is a term that’s used when the market appears exceptionally overvalued, driven by a combination of heightened enthusiasm, unrealistic expectations, and reckless speculation. The dot-com bubble and housing market bubble are two notable examples of this phenomenon. Understanding what market bubbles are and why they …
What are the consequences of a stock market bubble?
Apr 06, 2021 · – In the economic context, a bubble is when the price for something – a stock, financial asset class or even the entire market is grossly overpriced compared to its fundamental value. – We have four different financial bubbles: stock market bubbles, market bubbles, credit bubbles, and commodity bubbles.
What happens after a stock market bubble?
Mar 03, 2022 · What Does The Stock Market Being In A Bubble Mean? Ultimately, a security’s value will determine its real value – even in short-term fluctuations. During times of excessive price speculation and investor over exuberance, then the market is referred to as “bubble” due to its excess market value.
How to survive a stock market bubble?
Feb 01, 2022 · A market bubble is a rapid rise in the price of stocks or other assets that is not justified by fundamentals and is followed by a sharp fall in prices once investor enthusiasm wanes. Bubbles are...
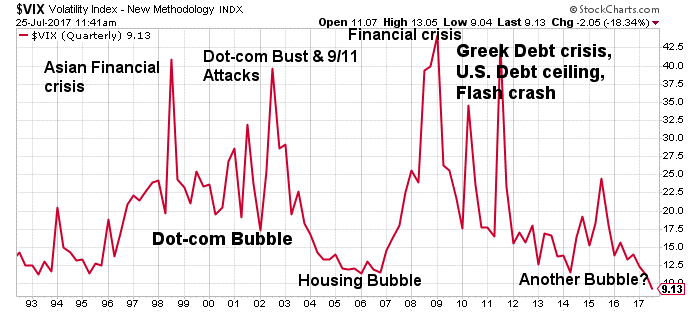
What happens after a stock market bubble?
A range of things can happen when an asset bubble finally bursts, as it always does, eventually. Sometimes the effect can be small, causing losses to only a few, and/or short-lived. At other times, it can trigger a stock market crash, and a general economic recession, or even depression.
Why is a stock market bubble bad?
The expectation of future price appreciation in the bubble assets itself drives buyers to bid prices higher. The resulting flood of investment dollars into the asset pushes the price up to even more inflated levels.
How does a bubble burst?
During a bubble, investors continue to bid up the price of an asset beyond any real, sustainable value. Eventually, the bubble "bursts" when prices crash, demand falls, and the outcome is often reduced business and household spending and a potential decline in the economy.
WILL IT sector bubble burst soon?
Yes, it is a bubble. But it may last some time since it is part of a global bubble blown by major central banks printing money massively to combat the Covid-induced recession. They aim to keep interest rates close to zero. No policy reversal is imminent, so the bubble is not about to burst.Jan 23, 2021
How do investors know when a bubble will pop?
It's very difficult to predict the timing of a bursting bubble. Economist John Maynard Keynes famously said, "Markets can remain irrational longer...
What does it mean for a stock to be overvalued?
Analysts typically use fundamental metrics , such as price-earnings ratio, price-to-sales ratio, price-earnings-to-growth ratio, price-to-free-cas...
How can I avoid losing money when a stock market bubble bursts?
There's no guaranteed way to avoid losses when a bubble bursts, but financial advisors generally recommend maintaining a diversified investment po...
What was the tulip mania?
Bulbs were traded for anything with a store of value, including homes and acreage. At its peak, tulip mania had created such a frenzy that fortunes were made overnight. The creation of a futures exchange, where tulips were bought and sold through contracts with no actual delivery, fueled the speculative pricing.
Why do bubbles happen?
Bubbles are typically attributed to a change in investor behavior, although what causes this change in behavior is debated. Bubbles in equities markets and economies cause resources to be transferred to areas of rapid growth. At the end of a bubble, resources are moved again, causing prices to deflate.
How did the tulip bulb trade start?
The tulip bulb trade initially started by accident. A botanist brought tulip bulbs from Constantinople and planted them for his own scientific research. Neighbors then stole the bulbs and began selling them. The wealthy began to collect some of the rarer varieties as a luxury good. As their demand increased, the prices of bulbs surged. Some rare varieties of tulips commanded astronomical prices.
What was the dot com bubble?
The dot-com bubble was characterized by a rise in equity markets that was fueled by investments in internet and technology-based companies. It grew out of a combination of speculative investing and the overabundance of venture capital going into startup companies. Investors started to pour money into internet startups in the 1990s, with the express hope that they would be profitable.
What are some examples of bubbles?
Examples of Bubbles. Recent history includes two very consequential bubbles: the dot-com bubble of the 1990s and the housing bubble between 2007 and 2008. However, the first recorded speculative bubble, which occurred in Holland from 1634 to 1637, provides an illustrative lesson that applies to the modern-day.
What is bubble economy?
A bubble is an economic cycle that is characterized by the rapid escalation of market value, particularly in the price of assets. This fast inflation is followed by a quick decrease in value, or a contraction, that is sometimes referred to as a "crash" or a "bubble burst.".
What happens at the end of a bubble?
At the end of a bubble, resources are moved again, causing prices to deflate. The Japanese economy experienced a bubble in the 1980s after the country's banks were partially deregulated. This caused a huge surge in the prices of real estate and stock prices.
What is the third stage of the stock market bubble?
The third stage in a stock market bubble is exuberance. Right now, using the bubble model, it appears we are in this stage, maybe even the tail-end. In this stage, there is an unsustainable euphoria. People claim that certain stocks will 10x with no risk.
What is the second stage of the investment boom?
The second stage is take-off. Interest in investing begins to increase as more and more people start to enter the market. Consequently, because of the demand, the price of assets start to gain momentum, setting up the boom.
What is the first stage of a bubble?
The first stage of a bubble is displacement. Displacement occurs when investors and speculators become entranced by new technologies and paradigms. Say, for example, bitcoin or historically low or rock-bottom interest rates we are currently experiencing. In turn, the value of assets starts increasing here as the seeds for the bubble begin to sow.
What is bubble in economics?
– In the economic context, a bubble is when the price for something – a stock, financial asset class or even the entire market is grossly overpriced compared to its fundamental value.
What is a stock market bubble?
What is the Stock Market Bubble? Stock Market Bubble is the phenomena where the prices of the stock of the companies do not reflect the fundamental position of the company and because of this, there is a divide between the real economy and the financial economy caused either due to irrational exuberance of the market participants ...
What happens when the bubble inflates beyond the threshold?
Crash of Market: As explained above, there comes a time when the bubble inflates beyond the threshold, and even a tiny pin poke can burst it, leading to a crash in the market when wealth is eroded completely, stocks lose all their value, and the economy goes into recessions.
Why do stocks bubble?
This is one of the most important reasons that lead to stock market bubbles because this is the reason why the gorge between the financial and real economy widens. When the market participants are not ready to accept the challenges that the real economy is facing and are still buying the stocks of companies that are underperforming in an expectation that they will gain when these companies do well, it leads to inflation in stock prices and creates a bubble.
Why do stock prices get affected?
The prices of securities traded on the stock market get affected by various reasons such as the introduction of a liberal governmental regulation or expansionary measures undertaken by the central bank of the country, such as the reduction in the policy rate by the federal reserve. Such measures encourage people to take out money ...
What was the most popular bubble in the twentieth century?
One of the most popular bubbles in the history of the twentieth century is the crash of Wall Street in 1929, following which the great depression occurred. This was the time when the NYSE stocks crashed, leading to erosion of wealth for scores of investors; this crash followed the crash in London Stock Exchange and led to the starting of the Great Depression.
What are long term instruments?
Long-term instruments include debentures, bonds, GDRs from foreign investors. Short-term instruments include working capital loans, short-term loans. read more. have a higher yield as compared to the long term one, we can say that the economy might be entering into a recession.
What is the Great Financial Crisis of 2007?
, and it implies that the investors are ready to forgo higher interest rates in the future because they want to keep their investments safe, and they have no faith that the economy will do well in the future.
How does a stock market bubble happen?
They typically occur when investors overvalue stocks, either misjudging the value of the underlying companies or trading based on criteria unrelated to that value.
Why do stocks bubble?
As discussed, when a stock market bubble forms it is because investors have bought stocks based on criteria other than the value of the underlying asset. Often this can be as simple as short-term enthusiasm. A category of investment can seem exciting, driving traders to make emotional purchases they otherwise wouldn’t.
What is the difference between a stock market bubble and an economic bubble?
The key difference between a stock market bubble and economic growth is the series of incentives driving prices. In the stock market, growth is marked by trading based on underlying business fundamentals. The price of a stock should approximately reflect the value of owning that particular company.
Why does the market not pop like a bubble?
A growing market will not pop like a bubble because, ultima tely, the assets have inherent value. During a selloff traders have as much incentive to hold on to their stocks as to unload them.
What happens during a selloff?
During a selloff traders have as much incentive to hold on to their stocks as to unload them. This causes selling to hit a natural floor and disrupts the negative feedback loop that characterizes the second stage of a stock market bubble. Bubbles are not the same thing. Essence of a Bubble.
What is a stock market bubble?
A stock market bubble is a period of growth in stock prices followed by a fall. Typically prices rise quickly and significantly, growing far beyond their previous value in a short period of time. When they fall, they do so quickly and often below the starting value.
What was the practice of investing in the 1920s?
In the 1920’s investors engaged heavily in a practice called “speculation.”. This is when an investor will buy stocks with borrowed money, planning to pay off the loan with the profits. When speculation works it can make someone a millionaire overnight. When it fails it can leave them with impossible amounts of debt.
What is a bubble burst in the stock market?
A stock market bubble burst is like a big reset. Stock prices come closer to their real value instead of their perceived value. If there’s enough fear in the markets, they might even end up priced at less than they’re worth. It can take a while for them to recover, though.
What is the indicator of a stock bubble?
Stock market bubble indicators can warn investors when a stock’s price is too high. A popular indicator is the price-to-earnings ratio (P/E). This indicator compares a stock’s current price to the earnings you might expect to get back from it.
What is hopium in stocks?
What’s hopium? It’s the frenzy that occurs when buyers have hope that stocks and the market will keep going up. No matter how high they get, more buyers come in.
What to do if you are a swing trader?
If you’re a swing trader and the uncertainty of a stock market bubble scares you, tighten your stop losses. If you’re a day trader, you can have better luck. A true trader stays in cash most of the time so you’re potentially less exposed to market volatility.
What happens when a stock goes into a bubble?
A stock market bubble happens when a stock costs a lot more than it’s worth or the market in general is overvalued. If you put your money in the market, you want to get back more than you put in. In my trades, I aim to get back three times as much money as I can accept losing.
What happens when the music stops?
When the music stops, you jet back into cash positions before everyone else does. Otherwise, you’re the bag holder with no chair. And that’s not a comfortable position. As a day trader, you won’t have to worry too much about a stock market bubble. Your goal is to be in cash by the end of every trading day.
Does Warren Buffett have a bubble rule?
Warren Buffett has his own stock market bubble rule. If the value of the U.S. stock market exceeds the U.S. gross domestic product (GDP), it’s too expensive for him. Be careful with this one, though. It’s hard for the average trader to time the market.
What is bubble in economics?
The term "bubble," in an economic context, generally refers to a situation where the price for something—an individual stock, a financial asset, or even an entire sector, market, or asset class —exceeds its fundamental value by a large margin. Because speculative demand, rather than intrinsic worth, fuels the inflated prices, ...
What are the hallmarks of a bubble?
"A rapid price rise, high trading volume, and word-of-mouth spread are the hallmarks of typical bubbles," says Timothy R. Burch, an Associate Professor of Finance at the Miami Herbert Business School. "If you learn of an investment opportunity with dreams of unusually high profits from social media or friends, be particularly wary—in most cases, you’ll need uncanny timing to come out ahead."
What is the damage caused by a bubble?
The damage caused by the bursting of a bubble depends on the economic sector (s) involved, whether the extent of participation is widespread or localized, and to what extent debt fueled the investments that inflated the bubble. The term "bubble," in an economic context, generally refers to a situation where the price for something—an individual ...
What are the four types of bubbles?
Financial bubbles, aka asset bubbles or economic bubbles, fit into four basic categories: stock market bubbles, market bubbles, credit bubbles, and commodity bubbles. Bubbles are deceptive and unpredictable, but understanding the five stages they characteristically go through can help investors prepare for them.
What are the steps of the lifecycle of a bubble?
The five steps in the lifecycle of a bubble are displacement, boom, euphoria, profit-taking, and panic. The damage caused by the bursting of a bubble depends on the economic sector (s) involved, whether the extent of participation is widespread or localized, and to what extent debt fueled the investments that inflated the bubble. ...
What happened in 2000?
By March 2000, the panic stage had arrived: eToys had tumbled 81% from its October peak to about $16 on concerns about its spending. The company was spending an extraordinary $2.27 on advertising costs for every dollar of revenue generated. Although the investors were saying that such expenditures were characteristic in the new economy, such a business model simply is not sustainable.
What are some examples of credit bubbles?
Specific examples of assets include corporate bonds or government bonds (like US Treasuries), student loans, or mortgages.