
A stock market crash is a noticeably rapid decline in share prices. Stocks normally fluctuate, even within the same day. There could even be identifiable patterns, like the market rising on a few percentage points one week, then falling a few the next.
Full Answer
What is a stock market crash?
Nov 25, 2006 · A stock market crash occurs when a market index drops severely in a day, or a few days, of trading. The main indexes in the United States are the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S&P 500, and the Nasdaq. A crash is more sudden than a stock market correction, which occurs when the market falls 10% from its 52-week high over days, weeks, or even ...
Should you sell during a stock market crash?
Feb 19, 2022 · A crash is usually defined as a rapid drop of 20% or more. But not all crashes are the same. Short-term panic selling often gets reversed in a few days making the crash sort of a minor footnote. In...
What happens to gold after a stock market crash?
A stock market crash is a very infrequent occurrence, happening about every 10 years. This is a massive correction that far exceeds the 20% dip that indicates a bear market. A crash is a drop of 40% or more. For example, the crash of 2007 to 2009 resulted in a 54% drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
What is a stock market crash and a correction?
Apr 12, 2022 · Stocks Could Crash at Any Time. Here's How. T he start of 2022 has been interesting, to say the least, from a stock market perspective. Stocks slumped for much of January and February before ...
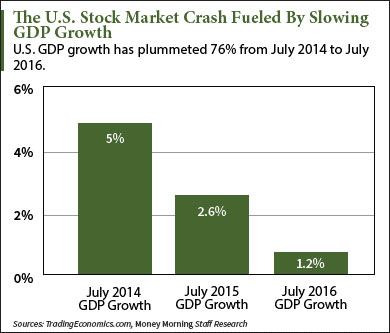
What are the signs of stock market crash?
Indicators That Help in Predicting Stock Market CrashesRampant Speculation: The first step towards the downfall is when speculation becomes rampant. ... Low Growth Rates: A slowdown in the overall economic growth is a significant indicator that the stock market is going to crash.More items...
What happens in a stock market crash?
Stock market crashes wipe out equity-investment values and are most harmful to those who rely on investment returns for retirement. Although the collapse of equity prices can occur over a day or a year, crashes are often followed by a recession or depression.
How much does the stock market have to drop to be a crash?
While there is no official threshold for what qualifies as a stock market crash, a common standard is a rapid double-digit percentage decline in a stock index, such as the Standard & Poor's 500 Index or Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), over a couple days.Feb 28, 2022
How long does a stock market crash usually last?
There have been 26 bear markets in the S&P 500 Index since 1928. However, there have also been 27 bull markets—and stocks have risen significantly over the long term. Bear markets tend to be short-lived. The average length of a bear market is 289 days, or about 9.6 months.
Where should I put my money before the market crashes?
Where to Put Your Money Before a Market CrashReduce Risk: Diversify Your Portfolio. ... Bet on Basics: Consumer cyclicals and essentials. ... Boost Your Wealth's Stability: Cash and Equivalents. ... Go for Safety: Government Bonds. ... Go for Gold, or Other Precious Metals. ... Lock in Guaranteed Returns. ... Invest in Real Estate.More items...•Feb 16, 2022
Where does the money go when the stock market crashes?
Key Takeaways. When a stock tumbles and an investor loses money, the money doesn't get redistributed to someone else. Essentially, it has disappeared into thin air, reflecting dwindling investor interest and a decline in investor perception of the stock.
Should I pull out of the stock market?
If you pull your money out now and prices surge, you'll miss out on those gains. If you reinvest later, you could end up paying even more if prices have continued to increase. On the other hand, if you wait too long to sell, you could lose money if prices have dropped substantially.Feb 24, 2022
Do you lose all your money if the stock market crashes?
Sometimes, however, the economy turns or an asset bubble pops—in which case, markets crash. Investors who experience a crash can lose money if they sell their positions, instead of waiting it out for a rise. Those who have purchased stock on margin may be forced to liquidate at a loss due to margin calls.
How long did it take the stock market crash 2008?
9, 2007 -- but by September of 2008, the major stock indexes had lost nearly 20% of their value. The Dow didn't reach its lowest point, which was 54% below its peak, until March 6, 2009. It then took four years for the Dow to fully recover from the crash.Feb 2, 2022
Should I sell my stocks before a crash?
The answer is simple: Don't panic. Panic selling is often people's gut reaction when stocks are plunging and there's a drastic drop in the value of their portfolios. That's why it's important to know beforehand your risk tolerance and how price fluctuations—or volatility—will affect you.
Who benefited from stock market crash?
As and when the stock market crashes, there are certain sectors that benefit. These are – utilities, consumer staples and the healthcare sectors. This is because all three sectors are necessary to run our daily lives.Oct 21, 2021
How do you survive a stock market crash?
5 Key Tips to Survive a Market CrashTake a long-term approach. Everything starts with embracing a long-term mindset to your investments. ... Use dollar-cost averaging. ... Avoid margin debt. ... Diversify your portfolio. ... Keep funding your account.Feb 4, 2022
What is a stock crash?
Stock Market Crash is a strong price decline across majority of stocks on the market which results in the strong decline over short period on the major market indexes (NYSE Composite, Nasdaq Composite DJIA and S&P 500).
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low. But by July 1932, the stock market hit a low that made the 1929 crash. By the summer of 1932, the Dow had lost almost 89% of its value and traded more than 50% below the low it had reached on October 29, 1929.
How much wealth was lost in the 2000 crash?
The Crash of 2000. A total of 8 trillion dollars of wealth was lost in the crash of 2000. From 1992-2000, the markets and the economy experienced a period of record expansion. On September 1, 2000, the NASDAQ traded at 4234.33. From September 2000 to January 2, 2001, the NASDAQ dropped 45.9%.
What happened in 1987?
The Crash of 1987. During this crash, 1/2 trillion dollars of wealth were erased. The markets hit a new high on August 25, 1987 when the Dow hit a record 2722.44 points. Then, the Dow started to head down. On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day.
How much did the Dow drop in 1987?
On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
What is a weak technical position on the bull side?
"A market (or a stock) is said to be in a weak technical position on the bull side when the buying power has been exhausted, either in a small or a large way. A campaign of distribution exhausts buying power in a large way because much of the floating supply of stocks is then in the hands of traders and the public. Sponsors and large operators have sold. Those of the public who still hold these stocks are potentially bearish factors because, having bought, they must sooner or later sell, and their selling will bring pressure upon the market.
Why did large institutional investment companies use computers?
Large institutional investment companies used computers to execute large stock trades automatically when certain market conditions prevailed. Some analysts claim that the program trading of index futures and derivatives securities was also to blame.
Doug Kass, Hedge Fund Manager Who Writes the Daily Daily on Real Money Pro
Crashes, or greater than 20% declines in the market averages, are a rare occurrence.
Will There Be a Market Crash in 2022?
With interest rates and prices/costs rising into a slowing economy, we believe investors face a number of dilemmas and that any strength in the U.S. stock market may be short-lived.
Bob Lang: Options Expert and Co-Portfolio Manager, Action Alerts PLUS
The stock market already crashed in 2022. Did you miss it? Maybe the headlines did not creep into media and we did not see a ‘markets in turmoil’ special on CNBC, but the market was in a slow-motion crash of sorts in January. Now, my definition of a ‘crash’ is very different than others.
Bob Byrne, Real Money Contributor
If a stock market correction is a decline of more than 10%, and a bear market is a decline of greater than 20%, what’s a stock market crash? In my view, a crash is a decline of 20% or more over a short period, like one to five days.
What Is a Stock Market Crash?
The words crash, correction, and bear market are often used interchangeably. It is important to understand the difference between these.
What Is a Bubble?
A bubble forms when hoards of people begin to invest in a particular asset. As more people invest, the market value, or what people are willing to pay, drifts further and further away from the intrinsic value, or the actual underlying value of the asset.
What to Do Before a Crash
If you believe that a market is becoming overvalued and you want to take some precautionary steps, here are a few that you could do. Again, we reemphasize that no person or institution can see the future and know when a stock market crash will occur.
What to Do During a Crash
If you believe you are currently invested in a market that is experiencing a crash, here are a few things you could consider doing:
What to Do After a Crash
If you believe the stock market has crashed and you are ready to take advantage of the opportunities, here are a few steps you could follow:
What Tools to Use to Prepare for a Crash
One of these precautionary steps is to get registered with Front. Much like your credit score indicates your level of risk to a lender or bank, your Front score can indicate the same thing about your portfolio. By using this new app, you can link all of your investment accounts to see where your portfolio stacks up in the face of adversity.
What To Do Before, During and After a Stock Market Crash: Final Thoughts
While you may be thinking that these suggestions might be overly simplistic, remember that sometimes inaction is the best action in the stock market. This is counterintuitive and goes against your emotions, but often, it's the best thing to do. We are all irrational individuals that make decisions based on limited information.
What not to do
First, though, let's get one thing straight upfront: You can't avoid the next stock market crash. The costs of missing out on the stock market's long-term gains are too great to risk missing out based on predictions that a crash will happen at any specific time.
The 1 question to ask yourself
If you can't avoid the next stock market crash, then what should you do? The answer is simple: Ask yourself whether you own any stocks that you won't want to own if they fall 50%.
A smart rebalancing
What you'll probably find when you go through this exercise is that there are some stocks you feel more confident about than others. If that's the case, you might want to sell your lower-conviction picks in favor of reinvesting in those higher-conviction stocks.
The Motley Fool
Founded in 1993 in Alexandria, VA., by brothers David and Tom Gardner, The Motley Fool is a multimedia financial-services company dedicated to building the world's greatest investment community.
S&P 500 Price to Earnings
Price to earnings (P/E) is the most often used method to value stocks. It’s common for investors to use the trailing 12 months (ttm) of earnings in the P/E denominator, as shown in the first graph.
Price To Sales
The benefit of using the ratio price to sales (P/S) versus P/E is that sales, or revenue, are not easy to manipulate by executives.
More Valuation Metrics
The following graph is purportedly Warren Buffet’s favorite valuation technique. The measure compares the inflation-adjusted market cap of the S&P 500 as a ratio to the economy. Given that earnings and economic growth correlate well over time, the ratio effectively points out valuation extremes.
Compared to What?
Conservatively speaking, current valuations are on par or greater than those in 1999 and any other period. Such a statement is statistically factual, but it ignores the economic environments of both periods.
The Fed is the Fundamentals
The bottom line is investors are paying more and getting less compared to 1999. The graph below shows numerous measures of valuations are at extremes except three. Those three in green shading use comparisons of stock prices to interest rates. They are “fairly valued.”
Statistics Warn of 2650
The graph below shows the strong correlation between CAPE valuations and future 20-year returns. At current levels, highlighted in yellow, we should expect annualized returns ranging from 2-4% for the next 20 years.
Summary
Every era of speculation brings forth a crop of theories designed to justify the speculation, and the speculative slogans are easily seized upon. The term “new era” was the slogan for the 1927-1929 period. We were in a new era in which old economic laws were suspended .” -Dr. Benjamin Anderson – Economics and the Public Welfare
What were the early warning signs of the 2008 financial crisis?
The early warning signs of the 2008 Financial Crisis were rapidly falling housing prices and increasing mortgage defaults in 2006. 16 Left untended, the resulting subprime mortgage crisis, which panicked investors and led to massive bank withdrawals, spread like wildfire across the financial community. 17 The U.S. government had no choice but to bail out “too big to fail” banks and insurance companies, like Bear Stearns and AIG, or face both national and global financial catastrophes. 18
How did the gold standard affect inflation?
The OPEC oil embargo and President Richard Nixon’s abolishment of the gold standard triggered double-digit inflation. The government responded to this economic downturn by freezing wages and labor rates to curb inflation. 7 The result was a high unemployment rate. Businesses, hampered by low prices, could not afford to keep workers at unprofitable wage rates. 8
How much will the global economy cost in 2020?
According to the United Nations’ Conference on Trade and Development, the global economic hit could reduce global growth rates to 0.5% and cost the global economy as much as $2 trillion for 2020. 19 .
What is the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation?
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insures banks, so there is little chance of a banking collapse similar to that in the 1930s. The president can release Strategic Oil Reserves to offset an oil embargo. Homeland Security can address a cyber threat.
How much did the 2001 terrorist attacks cost the United States?
14 The United States’ response, the War on Terror, has cost the nation $6.4 trillion, and counting. 15
How much would a 4 degree Celsius increase cost the US economy?
One study estimates that a global average temperature increase of 4 degrees celsius would cost the U.S. economy 2% of GDP annually by 2080. (For reference, 5% of GDP is about $1 trillion.) The more the temperature rises, the higher the costs climb.
How many people left the Dust Bowl?
Thousands of farmers and other unemployed workers moved to California and elsewhere in search of work. Two-and-a-half million people left the Midwestern Dust Bowl states. 6 The Dow Jones Industrial Average didn't rebound to its pre-Crash level until 1954.