A market crash could be caused by one or more of the following factors:
- A sudden geopolitical event
- Rising inflation and interest rates
- Lowering of earnings estimates
- Overvaluation
- An economic crisis
- A bubble in one or more parts of the economy
- An unforeseen disaster
What's really causing the stock market to crash?
While the exact cause of each of these crashes can get a bit complicated, stock market crashes are generally caused by some combination of speculation, leverage, and several other key factors. Here's a rundown of six different stock market crash catalysts that could contribute to the next plunge in the market.
What are the factors affecting a stock market crash?
The effect of firm and stock characteristics on stock returns: Stock market crash analysis
- 1. Introduction. Stock market is important in an economy because of its role in facilitating between surplus fund unit (investors) and deficit fund unit (stock issuers) to trade.
- 3. Data and methodology
- 4. Results and analysis. ...
- 5. Conclusion and managerial implication. ...
- 6. Suggestion for further research. ...
What actually constitutes a stock market "crash"?
United States
- If Threshold Level 1 (a 7% drop) is breached before 3:25pm, trading halts for a minimum of 15 minutes. ...
- If Threshold Level 2 (a 13% drop) is breached before 1 pm, the market closes for two hours. ...
- If Threshold Level 3 (a 20% drop) is breached, the market would close for the day, regardless of the time.
Which stock market crash really was worst?
The Wall Street Crash, or better known as the Great Crash, was the American stock market crash that occurred in 1929. The crash started in September and ended in October when share prices on NYSE collapsed. It was one of the worst stock market crashes in history. The crash followed the London Stock Exchange’s crash of September.

The Stock Market
Since the stock market is the most famous market, and our primary focus at Stockpile, let’s start there.
Examples of Market Crashes
Another way to better understand what causes a market to crash is by looking at crashes in the past. The dotcom bubble is one of the most famous market crashes of our time. In the mid and late 1990s, a company’s value could skyrocket by merely adding a website to their collection of products or services.
Multiple Factors
Several factors can cause a market crash, but the main denominator is always the psychology behind the investors who are buying and selling. To be the most active investor, you have to always look through your available resources to make an educated guess on how you think people will behave collectively.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 followed an epic period of economic growth during what's now known as the Roaring Twenties. The Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJINDICES:^DJI) was at 63 points in August 1921 and increased six-fold over the next eight years, closing at a high of 381.17 points on Sept. 3, 1929. That September day marked the peak of the ...
What happened to the stock market in 1929?
When the stock market crashed in September 1929, all of the entwined investment trusts similarly collapsed. In the wake of the crash, the banks and other lenders that financed the stock-buying spree had little means to collect what they were owed. Their only collateral was stocks for which the amount of debt outstanding exceeded the stocks' worth.
What happens when investment trusts are heavily leveraged?
Some investment trusts, themselves heavily leveraged, also invested in other similarly leveraged investment trusts , which, in turn, invested in other investment trusts employing the same strategy. As a result, each of these trusts became inordinately affected by the movements of others' stock holdings. When the stock market crashed in September ...
What was the total non-corporate debt in 1929?
By September 1929, total noncorporate debt in the U.S. amounted to 40% of the nation's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). At the same time that readily available credit was fueling consumer spending, the buoyant stock market gave rise to many new brokerage houses and investment trusts, which enabled the average person to buy stocks.
What happened after 1929?
The bursting of the stock market's bubble unleashed a cascade of market forces that plagued the U.S. economy for years after 1929 . The economy likely could have recovered more quickly in those ensuing years had the combined effects of excessive borrowing, business closures, and mass layoffs not exacerbated and prolonged the crisis.
What percentage of all consumer purchases were made on installment plans in 1927?
By 1927, 15% of all major consumer purchases were being made on installment plans. People in the 1920s acquired six of every 10 automobiles and eight of every 10 radios on credit.
When did the Dow drop?
By mid-November 1929, the Dow had declined by almost half. It didn't reach its lowest point until midway through 1932, when it closed at 41.22 points -- 89% below its peak. The Dow didn't return to its September 1929 high until November 1954.
Why do stocks crash?
Stock market crashes happen as a result of panic selling of stocks, which could be triggered by the changes in federal regulations, extreme overvaluation of stocks, overinflated economy, natural disasters, sociopolitical events like war or a terrorist attack, and extensive use of margin and leverage by market players.
How did the 1929 stock market crash affect the economy?
Several banks folded, and people lost their life savings. In fact, the 1929 stock market crash heralded the Great Depression — an economic slump that took the US over 12 years to recover.
What was the biggest stock market crash in 1987?
Dubbed the Black Monday, the 1987 stock market crash is the biggest single-day loss in the DJIA history, percentage-wise. The DJIA lost about 23% of its value on a single day — the 19 th of October, 1987. Following the crash in DJIA, other major stock markets around the world began to decline.
How much did the DJIA lose in 2009?
Stock prices fell so badly that by the time the bear market eventually bottomed in 2009, the DJIA had lost about 54% of its pre-crash value. Expectedly, the financial stocks were worst hit, despite the fact that the SEC instituted a temporary restriction on short-selling financial companies.
What was the most famous stock crash in the US?
The 1929 Stock Market Crash. Probably the most famous stock market crash in U.S. history, the 1929 stock market crash brought an end to the market boom of the 1920s. It started on the 24 th of October 1929 — a day, popularly known as the Black Thursday — and lasted till Tuesday, the 29 th of October, 1929 (the Black Tuesday).
How long did it take for the stock market to recover from the DJIA crash?
Following the crash in DJIA, other major stock markets around the world began to decline. Unlike the 1929 crash that took more than 12 years to recover, the 1987 crash started recovering the day after the Black Monday and topped the pre-crash high in less than two years.
What caused the Dot.com bust?
Also known as the Dot.com Bust, this market crash was caused by the proliferation of internet companies. In the 1990s, investors recognized the value of the internet and started acquiring the stocks of dot.com companies with reckless abandon.
How does a stock market crash affect the economy?
Stock market crashes have severe effects on the economy and investors’ behavior. Essentially, the overall economy of a country depends on its stock market. A country’s stock market trend becomes the main focus when investors intend to invest. The most common ways investors are bound to lose their money in the event of a stock market collapse is ...
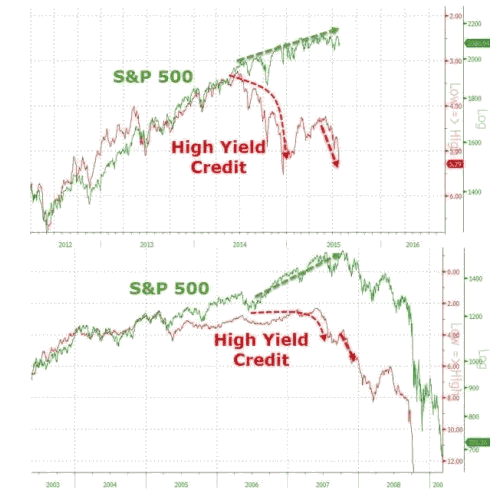
What caused the 2007/08 stock market crash?
The 2007/08 stock market crash was triggered by the collapse of mortgage-backed securities in the housing sector. High frequency of speculative trading caused the securities rise and decline in value as housing prices receded. With most homeowners unable to meet their debt obligations, financial institutions slid into bankruptcy, causing the Great Recession.
What caused the market to collapse in March 2020?
The market collapse in March 2020 was caused by the government’s reaction to the Novel COVID-19 outbreak, a rapidly spreading coronavirus around the world. The pandemic impacted many sectors worldwide, including healthcare, natural gas, food, and software.
What are some examples of stock market crashes?
Historical examples of stock market crashes include the 1929 stock market crash, 1987 October stock market crash, and the 2020 COVID-19 stock market crash.
What was the first major market crash?
The Great Depression Crash of October 1929. This was the first major U.S. market crash, where speculations caused share prices to skyrocket. There was a growing interest in commodities such as autos and homes. Unsophisticated investors flooded the market, driving up prices in a panic buying mode.
What was the 2010 flash crash?
2010 Flash Crash The 2010 Flash Crash is the market crash that occurred on May 6, 2010. During the 2010 crash, leading US stock indices, including the Dow. The Economic Crash of 2020 The economic crash of 2020 was precipitated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
How can turbulence dampen markets?
Turbulent markets can also be dampened by the purchase of massive quantities of stocks by large entities when prices drop. By so doing, established entities hold prices up to prevent individual traders from panic trading. This method is limited in its effectiveness.