
What is the worst stock market crash?
The “Tech bubble”, and resulting stock market crash, which began in 2000 and continued until 2002, is also known as the Dotcom bubble, Dotcom crash, Dotcom boom, internet bubble, and 2000 stock crash. Like all major crashes, prices first rose then fell. Prices were already rising in the mid to late-90’s, but buying accelerated in late 1998.
When will the stock market collapse?
15 rows · Mar 23, 2017 · In an effort to help moderate economic growth, the Fed started to raise interest rates. From 1999 to ...
When will market crash again?
Dot-Com Bubble Set Up Dot-Com Crash of 2000-2002 The Internet commercialized in 1995, creating a speculative bubble from 1997 to 2000. Hype over a …
Did the stock market just crash?
Jun 25, 2019 · What caused the 2000 stock market crash? The 2000 stock market crash was a direct result of the bursting of the dotcom bubble. It popped when a majority of the technology startups that raised money...

What was the main cause of the 2002 stock market crash?
An outbreak of accounting scandals, (Arthur Andersen, Adelphia, Enron, and WorldCom) was also a factor in the speed of the fall, as numerous large corporations were forced to restate earnings (or lack thereof) and investor confidence suffered.
What happened in the stock market in 2000?
In 2000, the stock market experienced a bubble. This period was marked by overvaluations, excess public enthusiasm for stocks, and speculation in the technology sector. When the bubble burst between 2000 and 2002, the technology-centric NASDAQ took a major hit, while the S&P 500 also took a lesser hit.
What were the 4 major causes of the stock market crash?
Among the more prominent causes were the period of rampant speculation (those who had bought stocks on margin not only lost the value of their investment, they also owed money to the entities that had granted the loans for the stock purchases), tightening of credit by the Federal Reserve (in August 1929 the discount ...6 days ago
What was the cause of the stock market crash?
By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value. Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.Apr 27, 2021
What caused the 1999 stock market crash?
Money pouring into tech and internet company start-ups by venture capitalists and other investors was one of the major causes of the dotcom bubble. In addition, cheap funds obtainable through very low interest rates made capital easily accessible.
What caused the stock market crash of 2001?
Key Takeaways. The terrorist attack on Sept. 11, 2001 was marked by a sharp plunge in the stock market, causing a $1.4 trillion loss in market value. The first week of trading after the attacks saw the S&P 500 fall more than 14%, while gold and oil rallied.
Can the Great Depression happen again?
Could a Great Depression happen again? Possibly, but it would take a repeat of the bipartisan and devastatingly foolish policies of the 1920s and ' 30s to bring it about. For the most part, economists now know that the stock market did not cause the 1929 crash.
How long did it take the stock market to recover after the 2008 crash?
The Dow didn't reach its lowest point, which was 54% below its peak, until March 6, 2009. It then took four years for the Dow to fully recover from the crash.Feb 2, 2022
What caused the stock market crash of 2008?
The stock market crash of 2008 was a result of defaults on consolidated mortgage-backed securities. Subprime housing loans comprised most MBS. Banks offered these loans to almost everyone, even those who weren't creditworthy. When the housing market fell, many homeowners defaulted on their loans.
Who made money in 1929 crash?
While most investors watched their fortunes evaporate during the 1929 stock market crash, Kennedy emerged from it wealthier than ever. Believing Wall Street to be overvalued, he sold most of his stock holdings before the crash and made even more money by selling short, betting on stock prices to fall.Apr 28, 2021
What stocks survived the 1929 crash?
Coca-Cola , Archer-Daniels and Deere should like this history lesson.Oct 27, 2008
What caused 1929 Wall Street crash?
The 1929 stock market crash was a result of an unsustainable boom in share prices in the preceding years. The boom in share prices was caused by the irrational exuberance of investors, buying shares on the margin, and over-confidence in the sustainability of economic growth.Jul 5, 2017
What was the growth rate in the 1990s?
In general, the 1990s were one of the best periods of growth in the United States. Gross domestic product (GDP) growth in the 1990s might have averaged just 3.3%, but it was a decade marked by serious expansion. In 1991, U.S. GDP was -0.07 but, by 1999, it was 4.68.
How many companies went public in 1999?
In 1999, 457 companies went public, most of which were Internet stocks. Of those, 117 (25%) doubled in price on the first day of trading. The most infamous Internet IPO of the late 1990s was theglobe.com, inc. (OTCMKTS:TGLO), a primitive social media site company.
When did the tax rate go down?
federal government has to take some of the blame. The Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997 lowered the maximum tax rate on capital gains for individual investors from 28% to 20% for equity held for more than 18 months. The legislation was signed on August 5, 1997, but was retroactive to May 7, 1997. (Source: “ H.R.2014 – Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997 ,” Congress.gov, last accessed March 22, 3017.)
What was the GDP in 1991?
In 1991, U.S. GDP was -0.07 but, by 1999, it was 4.68. As one might expect, the stock market followed a similar trajectory. After all, stocks are a barometer on the health of the U.S. economy, so if the economy is doing well, earnings are up, and so too are stock valuations.
When did the good times end?
The good times ended in May 2003 with the signing of the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003, which set the tax rates for dividends and capital gains to be equal to one another, just like they had been from 1986 to 1997.
What was the NASDAQ in 2000?
On the first day of trading in January 2000, the tech-heavy NASDAQ was at 452. By March 20, 2000, the day the NASDAQ peaked during the dotcom craze, the index had soared 1035% to a record intra-day high of 5132. The S&P 500 had entered 1990 at 353.40 and, by March 10, 2000, it had soared by a more modest 300% to 1413.38.
When did the Fed raise interest rates?
In an effort to help moderate economic growth, the Fed started to raise interest rates. From 1999 to early 2000, the Fed raised its key lending rate six times.
Intro
As per the records of September 1st, 2000 of NASDAQ, the trading was at 4234.33. The fall started after that and by January 2nd, 2001 there was a drop of 45.9% and the NASDAQ was now trading at 2291.86. There was a drop of 78.4% from the 5132.52 of March 2000. In October 2002, the NASDAQ was trading at 1108.49.
Causes of the Crash
The 2000 stock market crash resulted in a loss of almost $8 trillion of wealth. So what must be the reason for the crash? As has been deduced by market experts, the corporate corruption is believed to be a major reason for the crash to occur. Lots of multinational companies had been drawing profits by engaging in illegal means and frauds.
Reforms After the Crash
Now the stock market needed to be revived. And hence lots of fresh reforms were started to stabilize the market once again. As already mentioned one supposed reason for the stock market crash of 2000 was the advent of the internet and online trading in such a huge number.
Aftermath
The stock market crash of 2000 is regarded as one of the biggest crashes in the history of stock trading, the others being in the year 1987 and 1929. All these years the markets incurred heavy losses and the reforms were introduced to once again stabilize the market and restore the losses.
What was the dot com boom?
The dot-com bubble (also known as the dot-com boom, the tech bubble, and the Internet bubble) was a stock market bubble caused by excessive speculation of Internet-related companies in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet. Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Composite stock market index ...
How much did the 3G spectrum auction raise?
In Germany, in August 2000, the auctions raised £30 billion. A 3G spectrum auction in the United States in 1999 had to be re-run when the winners defaulted on their bids of $4 billion. The re-auction netted 10% of the original sales prices.
What was the economic boom of the 1990s?
The 1993 release of Mosaic and subsequent web browsers during the following years gave computer users access to the World Wide Web, popularizing use of the Internet. Internet use increased as a result of the reduction of the " digital divide " and advances in connectivity, uses of the Internet, and computer education.
Why did dot com companies lose money?
Most dot-com companies incurred net operating losses as they spent heavily on advertising and promotions to harness network effects to build market share or mind share as fast as possible, using the mottos "get big fast" and "get large or get lost".
What happened on April 14th 2000?
On Friday, April 14, 2000, the Nasdaq Composite index fell 9%, ending a week in which it fell 25%. Investors were forced to sell stocks ahead of Tax Day, the due date to pay taxes on gains realized in the previous year. By June 2000, dot-com companies were forced to re-evaluate their spending on advertising campaigns.
When did America Online merge with Time Warner?
On January 10, 2000, America Online, led by Steve Case and Ted Leonsis, announced a merger with Time Warner, led by Gerald M. Levin. The merger was the largest to date and was questioned by many analysts.
When did Pets.com go out of business?
By June 2000, dot-com companies were forced to re-evaluate their spending on advertising campaigns. On November 9, 2000, Pets.com, a much-hyped company that had backing from Amazon.com, went out of business only nine months after completing its IPO.
Why did the Internet bubble happen?
The dotcom bubble, also known as the Internet bubble, grew out of a combination of the presence of speculative or fad-based investing, the abundance of venture capital funding for startups, and the failure of dotcoms to turn a profit. Investors poured money into Internet startups during the 1990s hoping they would one day become profitable. Many investors and venture capitalists abandoned a cautious approach for fear of not being able to cash in on the growing use of the Internet.
What was the dotcom bubble?
How the Dotcom Bubble Burst. The 1990s was a period of rapid technological advancement in many areas. But it was the commercialization of the Internet that led to the greatest expansion of capital growth the country ever saw.
How much did the Nasdaq drop in 2000?
The Nasdaq, which rose five-fold between 1995 and 2000, saw an almost 77% drop, resulting in a loss of billions of dollars. The bubble also caused several Internet companies to go bust.
When did the Nasdaq index peak?
The Nasdaq index peaked on March 10, 2000, at 5048 —nearly double over the prior year. Several of the leading high-tech companies, such as Dell and Cisco, placed huge sell orders on their stocks when the market peaked, sparking panic selling among investors. Within a few weeks, the stock market lost 10% of its value. 2.
Who is Adam Hayes?
Adam Hayes is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
How many IPOs were there in 2000?
That year, most of the 457 initial public offerings (IPOs) were related to Internet companies, followed by 91 in the first quarter of 2000 alone. 3 The high-water mark was the AOL Time Warner megamerger in January 2000, which became the biggest merger failure in history. 4.
Why are stocks bearish?
Those of the public who still hold these stocks are potentially bearish factors because, having bought, they must sooner or later sell, and their selling will bring pressure upon the market. This was the case in 1929. The whole market became saturated with stocks held by those who were looking for profit.
What is a stock crash?
Stock Market Crash is a strong price decline across majority of stocks on the market which results in the strong decline over short period on the major market indexes (NYSE Composite, Nasdaq Composite DJIA and S&P 500).
How much wealth was lost in the 1929 stock market crash?
The Crash of 1929. In total, 14 billion dollars of wealth were lost during the market crash. On September 4, 1929, the stock market hit an all-time high. Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks.
When did banks go out of business?
When these banks started to invest heavily in the stock market, the results proved to be devastating, once the market started to crash. By 1932, 40% of all banks in the U.S. had gone out of business.
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low. But by July 1932, the stock market hit a low that made the 1929 crash. By the summer of 1932, the Dow had lost almost 89% of its value and traded more than 50% below the low it had reached on October 29, 1929.
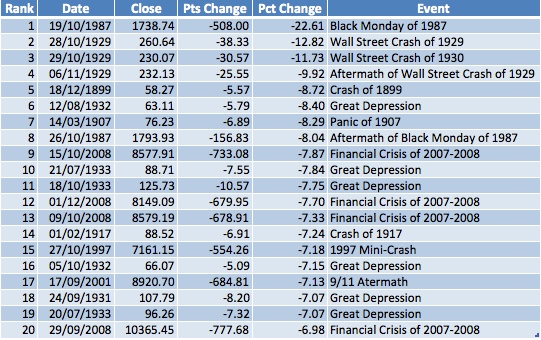
How much did the Dow drop in 1987?
On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
What happened in 1987?
The Crash of 1987. During this crash, 1/2 trillion dollars of wealth were erased. The markets hit a new high on August 25, 1987 when the Dow hit a record 2722.44 points. Then, the Dow started to head down. On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day.
Why did Japan go into recession in the 1990s?
This recession was predicted by economists, because the boom of the 1990s (accompanied by both low inflation and low unemployment) slowed in some parts of East Asia during the 1997 Asian financial crisis.
What was the recession in the 2000s?
Early 2000s recession. The early 2000s recession was a decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The recession affected the European Union during 2000 and 2001 and the United States from March to November 2001. The UK, Canada and Australia avoided the recession, while Russia, a nation that did not experience ...
When did the peak in business activity occur?
The NBER's Business Cycle Dating Committee determined that a peak in business activity occurred in the U.S. economy in March 2001. A peak marks the end of an expansion and the beginning of a recession.
What was the unemployment rate in 1992?
After the relatively mild 1990 recession ended in early 1991, the country hit a belated unemployment rate peak of 7.8% in mid-1992. Job growth was initially muted by large layoffs among defense related industries. However, payrolls accelerated in 1992 and experienced robust growth through 2000.
When did the recession start?
However, in 2008, the NBER confirmed that the recession started in March 2001. From 2000 to 2001, the Federal Reserve, in a move to protect the economy from the overvalued stock market, made successive interest rate increases.
What is recession in economics?
However, economic conditions did not satisfy the common shorthand definition of recession, which is "a fall of a country's real gross domestic product in two or more successive quarters", and has led to some confusion about the procedure for determining the starting and ending dates of a recession.
What was the main problem in Japan in the 2000s?
Japan's recession, which started in the early 1990s, continued into the 2000s, with deflation being the main problem. Deflation began plaguing Japan in the fiscal year ending 1999, and by 2005 the yen had 103% of its 2000 buying power. The Bank of Japan attempted to cultivate inflation with high liquidity and a nominal 0% interest rate on loans. Other aspects of the Japanese economy were good during the early 2000s; unemployment remained relatively low, and China became somewhat dependent on the Japanese exports. The bear market, however, continued in Japan, despite the best efforts of the Bank.
What was the Y2K scare?
The Y2K scare (also known as the Year 2000 scare) may have contributed to the 2001 recession. Computer users and programmers feared that computers would stop working on Dec. 31, 1999. Since many computer codes represented a given year with the last two digits, they believed that these codes would not be able to distinguish between 2000 and 1900.
What was the tax rate in 2001?
9 On June 7, 2001, President Bush signed the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001 (EGTRRA), which gave income tax relief to families retroactive to January of that year. 10 EGTRRA lowed the maximum tax rate of 39.6% to 35% , the 36% rate to 33%, the 31% rate to 28%, the 28% rate to 25%, and some of the 15% tax rate to 10%. 11 EGTRRA also expanded the Earned Income Tax Credit. 12 It also doubled the standard deduction, raised the threshold for the 15% tax bracket for married couples, and doubled the child tax credit from $500 to $1,000. 13
Who is Kimberly Amadeo?
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch.
What was the worst economic event in history?
The stock market crash of 1929 was the worst economic event in world history. What exactly caused the stock market crash, and could it have been prevented?
When did the Dow go up?
The market officially peaked on September 3, 1929, when the Dow shot up to 381.
Who was the bankrupt investor who tried to sell his roadster?
Bankrupt investor Walter Thornton trying to sell his luxury roadster for $100 cash on the streets of New York City following the 1929 stock market crash. (Credit: Bettmann Archive/Getty Images) Bettmann Archive/Getty Images.
What happened in 1929?
In August 1929 – just weeks before the stock market crashed – the Federal Reserve Bank of New York raised the interest rate from 5 percent to 6 percent. Some experts say this steep, sudden hike cooled investor enthusiasm, which affected market stability and sharply reduced economic growth.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
Most economists agree that several, compounding factors led to the stock market crash of 1929. A soaring, overheated economy that was destined to one day fall likely played a large role.
Why did people buy stocks in the 1920s?
During the 1920s, there was a rapid growth in bank credit and easily acquired loans. People encouraged by the market’s stability were unafraid of debt.
Overview
Prelude to the bubble
- The 2000 stock market crash resulted in a loss of almost $8 trillion of wealth. So what must be the reason for the crash? As has been deduced by market experts, the corporate corruption is believed to be a major reason for the crash to occur. Lots of multinational companies had been drawing profits by engaging in illegal means and frauds. The accou...
The bubble
Bursting of the bubble
Aftermath
The dot-com bubble, also known as the dot-com boom, the tech bubble, and the Internet bubble, was a stock market bubble caused by excessive speculation of Internet-related companies in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet.
Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Composite stock marke…
See also
The 1993 release of Mosaic and subsequent web browsers during the following years gave computer users access to the World Wide Web, popularizing use of the Internet. Internet use increased as a result of the reduction of the "digital divide" and advances in connectivity, uses of the Internet, and computer education. Between 1990 and 1997, the percentage of households in the United States owning computers increased from 15% to 35% as computer ownership progre…
Further reading
As a result of these factors, many investors were eager to invest, at any valuation, in any dot-com company, especially if it had one of the Internet-related prefixes or a ".com" suffix in its name. Venture capital was easy to raise. Investment banks, which profited significantly from initial public offerings (IPO), fueled speculation and encouraged investment in technology. A combination of rapidly increasing stock prices in the quaternary sector of the economyand confidence that the c…