The "Black Monday" stock market crash of Oct. 19, 1987, saw U.S. markets fall more than 20% in a single day. It is thought that the cause of the crash was precipitated by computer program-driven trading models that followed a portfolio insurance strategy as well as investor panic.
What caused Black Monday 1987?
The 1987 stock market crash was due to a poor monetary policy. Member commercial bank legal reserves declined at their sharpest rate for both Sept & …
What's really causing the stock market to crash?
It was considered one of the biggest reasons for the crash of 1987. Portfolio Insurance refers to a strategy to hedge or limit losses by buying and selling stocks and futures. People tend to buy in a rising market, which may create a bubble, and sell in …
What is the worst stock market crash?
Nov 22, 2013 · Events Leading Up to the Crash What Caused Black Monday The Fed’s Response The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded in the autumn of 1987 on a day known infamously as “Black Monday.” 1 A chain reaction of market distress sent global stock exchanges plummeting in a matter of hours.
What actually constitutes a stock market "crash"?
The crash Before the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) opened on Black Monday, October 19, 1987, there was pent-up pressure to sell stocks. When the market opened, a large imbalance immediately arose between the volume of sell orders and buy orders, placing considerable downward pressure on stock prices.
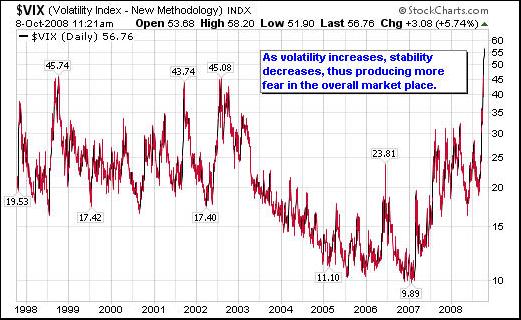
What caused the stock market crash of 1989?
How long did it take for the stock market to recover after 1987?
What are the 3 main causes of the stock market crash?
How long did the stock market crash of 1987 last?
Did Black Monday really happen?
What caused the tech crash in 2000?
How long did it take the stock market to recover after the 1929 crash?
Who profited from the stock market crash of 1929?
Who made money during the Great Depression?
Why did the market crash in 1982?
What caused the stock market crash of 1973?
What happened to the market on October 19 1987?
How long did it take the Dow to recover from the crash?
It took only two years for the Dow to recover completely; by September of 1989, the market had regained all of the value it had lost in the '87 crash. 2. Many feared that the crash would trigger a recession. Instead, the fallout from the crash turned out to be surprisingly small.
Why did the stock market crash in 1987?
The 1987 stock market crash was due to a poor monetary policy. Member commercial bank legal reserves declined at their sharpest rate for both Sept & Oct 87 since the beginning of their series in 1913.
What happened on October 19, 1987?
On October 19, 1987, a date that subsequently became known as"Black Monday," the Dow Jones Industrial Average plummeted 508 points, losing 22.6% of its total value. The S&P 500 dropped 20.4%, falling from 282.7 to 225.06. This was the greatest loss Wall Street had ever suffered on a single day.
What happened to the stock market in 1987?
However, studies show that during the 1987 U.S. Crash, other stock markets which did not use program trading also crashed, some with losses even more severe than the U.S. market. During the Crash, trading mechanisms in financial markets were not able to deal with such a large flow of sell orders.
What was the stock market crash in 1987?
What is the Stock Market Crash in 1987? Stock Market Crash in 1987, also known as Black Monday, was one where DJIA (Dow Jones Industrial Average) fell 22% (508 points) on a single day (19 October 1987) and had a contagious effect in the sense that the fall not only affected the US, but the whole world.
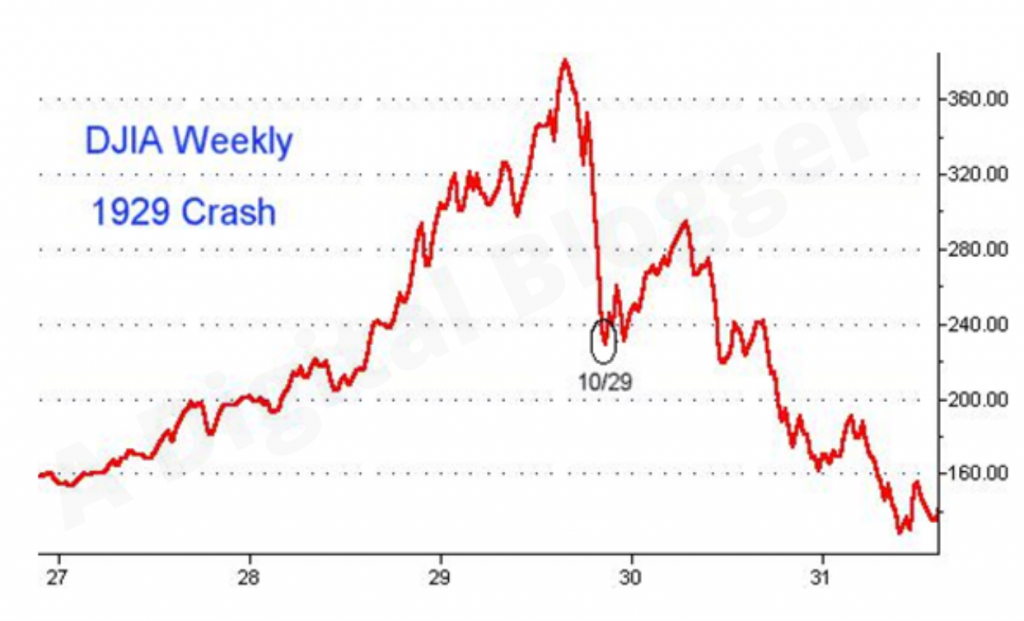
What happened in 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 was a series of the crash that occurred on Thursday (also known as black Thursday) on which the stock market fell by 11%. On Monday, the following Thursday, the market fell another 13%, and then it again fell on Tuesday. Whereas in 1987, the market crashed on a single day.1929 crash led to the great depression, which was the worst ever economic recession the world has seen. Unemployment rose, banks defaulted, companies went bankrupt, and fed didn’t act swiftly to inject money into the system. In 1987, stock markets crashed, but the recession didn’t follow crash due to the money injected into the system by the fed, and also, the reasons were more of technical nature rather than fundamental.
What is a developed economy?
Developed Economies A developed economy is the one that has a high per capita income or per capita GDP, a high degree of industrialization, developed infrastructure, technical advances, and a relatively high rank in human development, health, and education. read more. .
What is a stock exchange?
Stock Exchanges Stock exchange refers to a market that facilitates the buying and selling of listed securities such as public company stocks, exchange-traded funds, debt instruments, options, etc., as per the standard regulations and guidelines—for instance, NYSE and NASDAQ. read more. with growing apprehension and fear.
What is portfolio insurance?
Portfolio Insurance refers to a strategy to hedge or limit losses by buying and selling stocks and futures. People tend to buy in a rising market, which may create a bubble and sell in a falling market, which may lead to a crash, which it did. They short sell.
What is short selling?
They short sell. Short Sell Short Selling is a trading strategy designed to make quick gains by speculating on the falling prices of financial security.
What happened to margin calls in the stock market?
When the market fell, margin calls were triggered, which required futures position holders to deposit a margin, failing, which resulted in the selling future position. Due to large and sudden fall in the stock market, many futures position holders were not able to deposit margin, which led to the liquidation of their holding.
Who was the Chairman of the Federal Reserve in 1987?
The Fed’s Response. In a statement on October 20, 1987, Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan said, “The Federal Reserve, consistent with its responsibilities as the Nation's central bank, affirmed today its readiness to serve as a source of liquidity to support the economic and financial system” (Carlson 2006, 10).
When did the financial crisis start?
The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded on October 19, 1987, a day known as “Black Monday” when the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped 22.6 percent. Composite of newspaper headlines reporting the Stock Market Crash of 1987 (Associated Press)
What caused the Black Monday crisis?
The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded in the autumn of 1987 on a day known infamously as “Black Monday.” 1 A chain reaction of market distress sent global stock exchanges plummeting in a matter of hours.
What was the first crisis in the world?
The Fed’s Response. The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded in the autumn of 1987 on a day known infamously as “Black Monday.” 1 A chain reaction of market distress sent global stock exchanges plummeting in a matter of hours.
What was the first financial crisis?
The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded in the autumn of 1987 on a day known infamously as “Black Monday.” 1 A chain reaction of market distress sent global stock exchanges plummeting in a matter of hours. In the United States, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) dropped 22.6 percent in a single trading session, a loss that remains the largest one-day stock market decline in history. 2 At the time, it also marked the sharpest market downturn in the United States since the Great Depression.
What happened in 1987?
Stock markets raced upward during the first half of 1987. By late August, the DJIA had gained 44 percent in a matter of seven months, stoking concerns of an asset bubble. 4 In mid-October, a storm cloud of news reports undermined investor confidence and led to additional volatility in markets. The federal government disclosed a larger-than-expected trade deficit and the dollar fell in value. The markets began to unravel, foreshadowing the record losses that would develop a week later. Beginning on October 14, a number of markets began incurring large daily losses. On October 16, the rolling sell-offs coincided with an event known as “triple witching,” which describes the circumstances when monthly expirations of options and futures contracts occurred on the same day. By the end of the trading day on October 16, which was a Friday, the DJIA had lost 4.6 percent. 5 The weekend trading break offered only a brief reprieve; Treasury Secretary James Baker on Saturday, October 17, publicly threatened to de-value the US dollar in order to narrow the nation’s widening trade deficit.
What is triple witching?
On October 16, the rolling sell-offs coincided with an event known as “triple witching,” which describes the circumstances when monthly expirations of options and futures contracts occurred on the same day.
What caused the 1929 stock market crash?
Causes of the Crash. One of the many reasons that resulted in the crash of 1929 is the overvaluation of the stocks. The trading of the stocks at that point of time was being carried out at a very high P/E ratio. High P/E ratios do not result in a stock market crash every time.
What happened in 1987?
The 1987 Stock Market Crash was really huge and resulted in millions of people to lose wealth. The reforms that were introduced needed to be strictly followed so that the market could get over the losses soon. To date, the 1987 stock market crash is mentioned to be one of worst crashes in the history of stock trading.
What is Black Monday?
Black Monday (1987) Black Monday is the name commonly attached to the global, sudden, severe, and largely unexpected stock market crash on October 19, 1987. In Australia and New Zealand, the day is also referred to as Black Tuesday because of the time zone difference from other English speaking countries. All of the twenty-three major world markets ...
Why is Black Monday called Black Tuesday?
In Australia and New Zealand, the day is also referred to as Black Tuesday because of the time zone difference from the United States.
What happened on Black Monday 1987?
Before the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) opened on Black Monday, October 19, 1987, there was pent-up pressure to sell stocks. When the market opened, a large imbalance immediately arose between the volume of sell orders and buy orders, placing considerable downward pressure on stock prices. Regulations at the time permitted designated market makers (also known as "specialists") to delay or suspend trading in a stock if the order imbalance exceeded that specialist's ability to fulfill orders in an orderly manner. The order imbalance on the 19th was so large that 95 stocks on the S&P 500 Index (S&P) opened late, as also did 11 of the 30 DJIA stocks. Importantly, however, the futures market opened on time across the board, with heavy selling.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average peak?
Timeline compiled by the Federal Reserve. From August 1982 to its peak in August 1987 , the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) rose from 776 to 2,722, including a 44% year-to-date rise as of August 1987. The rise in market indices for the nineteen largest markets in the world averaged 296% during this period.
How much did the Dow Jones Industrial Average rise in 1987?
From August 1982 to its peak in August 1987, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) rose from 776 to 2,722, including a 44% year-to-date rise as of August 1987. The rise in market indices for the nineteen largest markets in the world averaged 296% during this period.
When was the tax bill introduced?
On the morning of Wednesday, October 14, 1987 , the United States House Committee on Ways and Means introduced a tax bill that would reduce the tax benefits associated with financing mergers and leveraged buyouts.
Is the stock market a single market?
Under normal circumstances the stock market and those of its main derivatives –futures and options–are functionally a single market, given that the price of any particular stock is closely connected to the prices of its counterpart in both the futures and options market. Prices in the derivative markets are typically tightly connected to those of the underlying stock, though they differ somewhat (as for example, prices of futures are typically higher than that of their particular cash stock). During the crisis this link was broken.
What is a market crash?
A market crash denotes a precipitous loss, and the 1987 stock market crash was a stomach-churning example . The event began on Oct. 14, 1987, when markets began to show daily losses, and culminated with Black Monday 2, on Oct. 19, 1987, when the Dow Jones Industrial Average (also known as the Dow) lost a nerve-wracking 508.32 points—which at ...
What is portfolio insurance?
Investment firms had begun offering “portfolio insurance,” which is a strategy of trying to minimize market risk by using financial instruments including options that they would sell short if the market fell. But in hindsight, it may have produced a sense of overconfidence, given the expectation that it would prevent a loss of capital if the market crashed, and may have led to investors taking outsized risks then being forced to sell as the market turned down.
What is Black Monday 2?
Given its moniker, Black Monday 2, that means there was a previous Black Monday. The first Black Monday occurred on Oct. 28, 1929, when the stock market plummeted 13 percent in one day, falling an additional 12 percent the following day. As with the 1987 stock market crash, this drop followed a period of growth, ...
When did Black Monday happen?
The first Black Monday occurred on Oct. 28, 1929, when the stock market plummeted 13 percent in one day, falling an additional 12 percent the following day. As with the 1987 stock market crash, this drop followed a period of growth, along with the hindsight realization that stocks had been overpriced. This 1929 market crash is often considered ...
What was the stock market crash in 2008?
In addition, the 7 percent stock market decline on Sept. 29, 2008 is often considered a stock market crash. That drop was one of many in a falling stock market that ultimately lost half its value before recovering. Combined with the plummeting housing market, it is considered an underlying factor of the Great Recession of 2008.
What is the LSE?
London Stock Exchange (LSE) The London Stock Exchange (LSE), which is based in London, the United Kingdom, is one of the leading stock markets in the world. Owned by the London Stock Exchange Group, the LSE was established in 1571, making it one of the oldest stock exchanges in the world.
How many people died in the 1987 Great Storm?
that, ominously, coincided with the Great Storm of 1987, an unprecedented severe weather phenomenon that produced hurricane-force winds in the English Channel and resulted in nearly two dozen fatalities. On Monday morning, the crash started in Hong Kong.
What was the Black Monday crash?
Summary: “Black Monday” refers to the catastrophic stock market crash that occurred on Monday, October 19, 1987. The crash occurred worldwide, starting in Hong Kong and spreading throughout Asia and Europe before reaching the United States. Two of the major contributing factors to the severity of the Black Monday crash were computerized trading ...
What was the use of computers in the 1980s?
The use of computers enabled brokers to place larger orders and implement trades more quickly. In addition, the software programs developed by banks, brokerages, and other firms were set to automatically execute stop-loss orders.
What was the third factor in the stock market crash?
A third factor in the crash was “portfolio insurance,” which, like computerized trading, was a relatively new phenomenon at the time. Portfolio insurance involved large institutional investors partially hedging their stock portfolios by taking short positions in S&P 500 futures. The portfolio insurance strategies were designed to automatically increase their short futures positions if there was a significant decline in stock prices.
What does it mean when the price level rises?
The rise in the price level signifies that the currency in a given economy loses purchasing power (i.e., less can be bought with the same amount of money). , and trade deficits created warning signs of increased volatility and some occasional severe down days in the market prior to Black Monday in October.
What was the market crash of 1987?
The market crash of 1987 was of a different sort than the stock market crash of 1929 that preceded the Great Depression or the 2008 crash that ushered in a long-term, global recession. The 1987 crash was a significantly shorter-lived phenomenon in the markets.
How long did the oil boom last?
Lasting 23 months, dramatic rise in oil prices, the miners' strike and the downfall of the Heath government.
How long did the Japanese asset bubble last?
1991. Lasting approximately twenty years, through at least the end of 2011, share and property price bubble bursts and turns into a long deflationary recession. Some of the key economic events during the collapse of the Japanese asset price bubble include the 1997 Asian financial crisis and the Dot-com bubble.
What happened on August 24th 2015?
On Monday, August 24, world stock markets were down substantially, wiping out all gains made in 2015, with interlinked drops in commodities such as oil, which hit a six-year price low, copper, and most of Asian currencies, but the Japanese yen, losing value against the United States dollar.