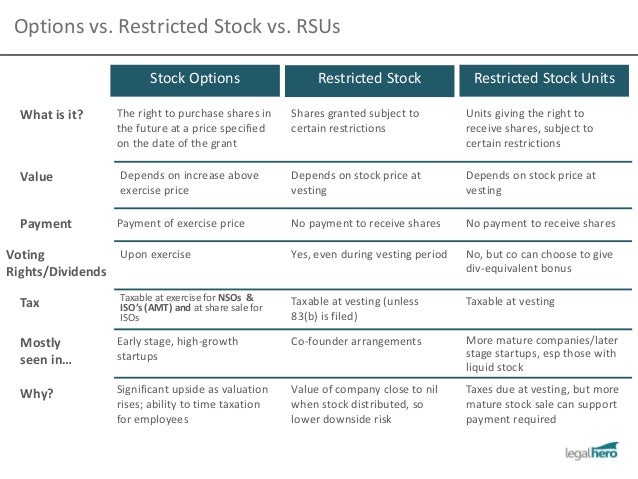
Comparing RSUs to Stock Options
| Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) | Stock Option | |
| Value Over Time | The stock is assigned a fair market valu ... | When the price of stock rises above the ... |
| Vesting | In most cases the vesting schedule is co ... | Stock options do not vest, but instead h ... |
| Term | RSUs are converted to shares once they a ... | Options have a stated expiration date (o ... |
| Taxation | RSUs are taxed as ordinary income at the ... | A stock option is taxed at the time it i ... |
Full Answer
What is restricted stock and how is it taxed?
Jun 22, 2021 · Key Takeaways Restricted shares and stock options are both forms of equity compensation that are awarded to employees. Restricted shares represent actual ownership of stock but come with conditions on the timing of their sale. Stock options are the right to buy a certain number of shares at a ...
How to sell restricted stock?
5 rows · Aug 21, 2020 · Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) Stock Option. Value Over Time. The stock is assigned a fair ...
What to do when your restricted stock units vest?
4 rows · Dec 28, 2021 · Restricted Stock: Stock Options: Restricted stock involves actual shares of stock you ...
What are the tax implications of restricted stock?
Aug 24, 2008 · Restricted stock is, by definition, a stock that has been granted to an executive that is nontransferable and subject to forfeiture under certain conditions, such as termination of employment or...

How does restricted stock option work?
Restricted stock units are a way an employer can grant company shares to employees. The grant is "restricted" because it is subject to a vesting schedule, which can be based on length of employment or on performance goals, and because it is governed by other limits on transfers or sales that your company can impose.
Is it better to take RSU or stock options?
Stock options are only valuable if the market value of the stock is higher than the grant price at some point in the vesting period. Otherwise, you're paying more for the shares than you could in theory sell them for. RSUs, meanwhile, are pure gain, as you don't have to pay for them.Oct 22, 2021
What is the difference between stock options and restricted stock?
Restricted shares represent actual ownership of stock but come with conditions on the timing of their sale. Stock options are the right to buy a certain number of shares at a certain price in the future, with the employee benefiting only if the stock price then exceeds the stock option price.
What is the benefit of restricted stock?
Restricted stock entitles you to receive dividends when they are paid to shareholders. Unlike stock options, which rarely carry dividend equivalent rights, restricted stock typically entitles you to receive dividends when they are paid to shareholders.
Why are RSU taxed so high?
Restricted stock units are equivalent to owning a share in your company's stock. When you receive RSUs as part of your compensation, they are taxed as ordinary income. Think of it like a cash bonus that your company immediately invests into company stock and gives you the stock instead.Feb 26, 2021
Do I get taxed twice on RSU?
Are RSUs taxed twice? No. The value of your shares at vesting is taxed as income, and anything above this amount, if you continue to hold the shares, is taxed at capital gains.Mar 4, 2021
Should I cash out my RSU?
Usually, it is recommended to sell the RSU immediately after the vesting period is complete to avoid any additional taxes. Insiders and employees that hold the RSU, need a RSU selling strategy. But for investors with a different and more diverse portfolio, holding on to the RSU is the choice to make.Jul 29, 2021
Can you sell restricted stock?
Restricted stock units are a form of stock-based employee compensation. RSUs are restricted during a vesting period that may last several years, during which time they cannot be sold. Units are just like any other shares of company stock once they are vested.
Where do RSU shares come from?
What are Restricted Stock Units? Employees granted RSUs have received a deferred and restricted grant which become shares of stock upon vesting. An employer offers Restricted Stock Units to recruit, incentivize, compensate, and retain key employees.Mar 11, 2022
How do I cash out RSU?
An RSU is like a cash bonus that you use right away to buy company stock. It has the same tax treatment as a cash bonus....How do RSUs work?# of Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) that Vest100 shares# of RSU shares sold for taxes (22% x 100 shares)22 shares6 more rows•Jul 25, 2021
Should you sell RSU as soon as they vest?
Given that RSUs are taxed as ordinary income and there is no tax benefit for holding them, I recommend you sell as soon as you vest and use the proceeds to fund your other financial goals.Oct 6, 2020
Can you keep RSU after leaving company?
Whenever you decide to quit, the vested portion of your RSUs will stay yours. Since shares of company stock are released to you upon a vesting date, those RSUs become shares that you own outright. And since you now own company shares outright, your departure from the company has no effect on your ownership.Jan 16, 2022
What is restricted stock unit?
A Restricted Stock Unit ( RSU) refers to a grant of a value equal to an amount of a company’s common stock. It is typically given to employees for employment.7 min read
How long do options last?
Options have a stated expiration date (often, but not always, 10 years from the date they are granted.) Taxation. RSUs are taxed as ordinary income at the time they become vested and liquid. A stock option is taxed at the time it is exercised.
What is an RSU plan?
With an RSU plan, the company offers the employee an economic interest in the company stated as a specific number of shares of company stock. The stock is not immediately given out to the employee, however, but is instead awarded at a future time upon completion of a stated goal or on reaching a stated date.
How long does a RSU vest?
The value of the stock may not be as great as anticipated. RSUs typically do not fully vest for five years, meaning that if you leave the company before that time, you will lose your ability to claim some or all of the stock shares under your RSU plan.
What is graduated vesting?
Graduated vesting refers to vesting schedules under which stock to be awarded as part of an RSU plan vests in stated amounts at stated intervals throughout the vesting period. As an illustration, if an RSU plan calls for the employee to become 100% vested after five years of employment, he or she may become partially vested at stated intervals during the five year period, as laid out in the RSU plan. For example, the RSU plan may call for graduated vesting as follows: 10% after one year; 30% after two years; 50% after three years; 80% after four years; 100% after five years.
What is phantom stock?
Phantom stock is often used as a way to compensate certain individuals with a form of equity participation in a startup in lieu of stock options . For example, the “owner” of phantom shares may receive a predetermined amount of money when the company issuing the phantom shares goes public.
What is stock grant?
Stock grants refer to the issuance of an award, such as a stock option, that is provided to key employees as part of a stock plan. Stock grants allow the employee to purchase a specific number of shares of company stock at a specific price (known as the grant price) as stated in the grant. Restricted stock awarded to employees is a form ...
Restricted Stock Explained
Cameron Williams has nearly a decade of experience working in the financial industry. A former investment advisor, Cameron now writes about investing, banking, insurance, and general personal finance. He studied economics at Utah State University and holds FINRA securities licenses including Series 6, Series 63, and Series 65.
Definition and Examples of Restricted Stock
Restricted stock, also referred to as restricted stock units (RSUs), is a type of equity compensation through which a company pays its employees in shares of stock. The stock is “restricted” because it is often accompanied by a vesting schedule before the employee has full ownership of the stock.
How Restricted Stock Works
Restricted stock plans give employees of a company a personal interest in how well the company does. The vesting schedule of restricted stock units is usually dependent on length of employment or based on performance goals being met. Once you are fully vested, you have voting rights and possibly dividend payments with the shares you are granted.
Types of Restricted Stock
There are two types of restricted stock. They are restricted stock units (RSUs) and restricted stock awards (RSAs). Both are stock compensation plans given to company employees that have certain restrictions to be met before the stock can be delivered to the employee.
Restricted Stock vs. Stock Options
Restricted stock and stock options are some of the more popular equity compensation plans offered by employers. What’s the difference between the two?
What It Means for Individual Investors
How a company compensates its employees is a vital piece of information that can be an indicator of future company success. Restricted stock can be an excellent way for companies to include their employees in the overall ownership of the company and its performance.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted stock is, by definition, a stock that has been granted to an executive that is nontransferable and subject to forfeiture under certain conditions, such as termination of employment or failure to meet either corporate or personal performance benchmarks.
What is Section 83 B?
Section 83 (b) Election. Shareholders of restricted stock are allowed to report the fair market value of their shares as ordinary income on the date that they are granted, instead of when they become vested if they so desire. 2 The capital gains treatment still applies, but it begins at the time of grant.
Is restricted stock taxable?
Those plans generally have tax consequences at the date of exercise or sale, whereas restricted stock usually becomes taxable upon the completion of the vesting schedule.
How are restricted stock shares taxed?
Restricted stockholders pay tax on the capital gain or loss represented by the difference between the stock’s price on the date it vests and the date it is sold. In addition, restricted stock is taxable as ordinary income in the year it vests. This is the opposite of stock options, which are taxed when the employee exercises their option, not when they are vested. 2
When did restricted stock become popular?
The restricted stock units are assigned a fair market value at the time of their vesting. Restricted stock became more popular in the mid-2000s as companies were required to expense stock option grants.
What is restricted share?
Restricted shares provide an employee with a stake in their company, but they have no tangible value before they vest. Vesting gives employees rights to employer-provided assets over time, giving the employees an incentive to perform well and remain with a company.
Do RSUs have voting rights?
Since RSUs are not actually stocks, but only a right to the promised stock, they carry no voting rights. An RSU must be exercised in order to receive the stock. An RSU that is converted to a stock carries the standard voting rights for the class of stock issued. A restricted stock award is similar to an RSU in a number of ways, ...
What is restricted stock forfeiture?
An executive may have to forfeit restricted stock if he leaves the company, fails to meet corporate or personal performance goals, or runs afoul of SEC trading restrictions. The SEC regulations that govern the trading of restricted stock are outlined under SEC Rule 144, which describes the registration and public trading ...
Is restricted stock taxable?
In addition, restricted stock is taxable as ordinary income in the year it vests. This is the opposite of stock options, which are taxed when the employee exercises their option, not when they are vested. 2 .
Who is James Chen?
James Chen, CMT, is the former director of investing and trading content at Investopedia. He is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist. Thomas Brock is a well-rounded financial professional, with over 20 years of experience in investments, corporate finance, and accounting.