What is the difference between a qualified and non qualified dividend?
There are two types of ordinary dividends: qualified and nonqualified. The most significant difference between the two is that nonqualified dividends are taxed at ordinary income rates, while qualified dividends receive more favorable tax treatment by being taxed at capital gains rates.Nov 12, 2020
What is the difference between dividends and qualified dividends?
Ordinary dividends are taxed as ordinary income, meaning a investor must pay federal taxes on the income at the individual's regular rate. Qualified dividends, on the other hand, are taxed at capital gain rates. Lower-income recipients of qualified dividends may owe no federal tax at all.Jun 29, 2021
What makes a dividend qualified vs ordinary?
Dividends can be classified either as ordinary or qualified. Whereas ordinary dividends are taxable as ordinary income, qualified dividends that meet certain requirements are taxed at lower capital gain rates.Feb 4, 2022
Is qualified dividends included in ordinary dividends?
Qualified dividends are a subset of your ordinary dividends. Qualified dividends are taxed at the same tax rate that applies to net long-term capital gains, while non-qualified dividends are taxed at ordinary income rates. It is possible that all of your ordinary dividends are also qualified dividends.Dec 22, 2021
Are AT&T dividends qualified?
C-Corps and U.S. Mutual Funds Taxes: The Benefits of Qualified Dividends. Let's start with the simplest and most common dividend most investors are faced with, qualified dividends from C-corps such as Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) and AT&T (T). Note that most U.S. mutual fund dividends are also qualified.
Are ETF dividends qualified?
An ETF pays out qualified dividends, which are taxed at the long-term capital gains rate, and non-qualified dividends, which are taxed at the investor's ordinary income tax rate.
How do I report qualified dividends on 1040?
Ordinary dividends are reported on Line 3b of your Form 1040. Qualified dividends are reported on Line 3a of your Form 1040.
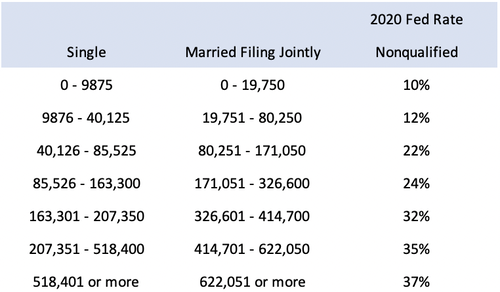
What is the qualified dividend tax rate for 2020?
The dividend tax rate for 2020. Currently, the maximum tax rate for qualified dividends is 20%, 15%, or 0%, depending on your taxable income and tax filing status. For anyone holding nonqualified dividends in 2020, the tax rate is 37%.Nov 12, 2019
Why is dividend income important?
It rewards the patient investor, who's willing and able to buy great companies, then keep holding them while getting paid as those businesses get bigger and stronger, and hopefully grow those dividend payments along the way. Simply put, buying great businesses and then sitting on your hands works great for dividend investing.
What is a qualified dividend?
A qualified dividend is a dividend that meets a series of criteria that result in it being taxed at the lower long-term capital gains tax rate, or for some investors, not taxed at all. Needless to say, the potential tax-saving implications can be enormous.
Do you pay taxes on dividends?
If you receive a dividend, you'll most likely have to pay taxes on it -- but how much you pay will depend on whether or not the payout is a qualified or a nonqualified dividend.
What is the tax rate for dividends?
If you are in the 15% or lower tax bracket, you pay 0% tax on qualified dividends. If your tax bracket is above 15% but below the top 39.6% tax bracket, you pay 15% on qualified dividends. If you are in the top 39.6% tax bracket, you pay 20% on qualified dividends.
What is smart tax planning?
Smart tax planning should play a big role in how you optimize your results. That includes taking advantage of tax-deferred accounts like an IRA, or tax-free accounts like a Roth IRA that can help you avoid almost all taxes, even on most dividend income.
What is qualified dividend?
Qualified dividends are generally dividends from shares in domestic corporations and certain qualified foreign corporations which you have held for at least a specified minimum period of time, known as a holding period.
How long do you have to hold a stock unhedged?
Stock. You must have held those shares of stock unhedged for at least 61 days out of the 121-day period that began 60 days before the ex-dividend date. For certain preferred stock, the security must be held for 91 days out of the 181-day period beginning 90 days before the ex-dividend date.
Do dividends have to be held for tax purposes?
However, not all dividends reported on those lines may have met the holding period requirement. Those non-qualified dividends, as well as other ordinary dividends, may be taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be as high as 37%.
How long do you have to hold a dividend fund?
You must have held the applicable share of the fund for at least 61 days out of the 121-day period that began 60 days before the fund’s ex-dividend date.
What is a qualified dividend?
A qualified dividend is a dividend that is taxed at the long-term capital gains rate rather than the ordinary income rate.
When does ABC pay dividends?
ABC Company pays $1 in dividends per common share once a year and with an ex-dividend date of March 20, 2020. On April 8, 2020, John sold all his shares in ABC Company.
Who pays dividends?
The dividend must be paid by a United States corporation. Corporation A corporation is a legal entity created by individuals, stockholders, or shareholders, with the purpose of operating for profit. Corporations are allowed to enter into contracts, sue and be sued, own assets, remit federal and state taxes, and borrow money from financial ...
What is a foreign corporation?
or by a foreign corporation that meets certain established requirements (incorporated in a U.S. possession, located in a country with an income tax treaty with the U.S., and whose stock is readily tradable on an established U.S. stock market). 2.
What is an ex dividend date?
Ex-Dividend Date The ex-dividend date is an investment term that determines which stockholders are eligible to receive declared dividends. When a company announces a dividend, the board of directors set a record date when only shareholders recorded on the company’s books as ...
What is dividend policy?
Dividend Policy A company’s dividend policy dictates the amount of dividends paid out by the company to its shareholders and the frequency with which the dividends are paid. Important Dividend Dates.
What is dividend in business?
A dividend is a way for a company or fund to distribute payments to their investors. These typically come in the form of cash and on a quarterly basis. However, it is also possible for a corporation to offer other assets, such as stocks, property or even services.
How long do you have to hold on to a dividend?
For a dividend to become qualified, you must hold on to it for more than 60 days. That must take place over a 121-day period beginning 60 days out from the ex-dividend date. This date is the cutoff point for you to purchase a stock and receive a dividend from it.
Is dividend income taxed?
The IRS allows qualified dividends to be taxed at a lower capital gains rate than the higher income tax rate. Here’s a breakdown of the tax requirements, the benefits, how they work and how they differ from ordinary dividends. Consider speaking with a financial advisor before you begin investing or become a shareholder.
What is the tax rate for single filers?
For single filers, you pay a 0% capital gains rate for up to $40,400. After that, you pay a 15% rate if you fall in a tax bracket between $40,401 and $445,850. Anything higher than that results in a 20% rate. Joint filers see the same low rates. They pay a tax rate of 0% on dividend income up to $80,800, 15% on up to $501,600 ...
Do you have to be a shareholder to receive dividends?
Dividends are rewards for corporate or mutual fund investors. So, you have to become a shareholder of a qualifying and domestically based company to earn them. If you are an investor, you will receive a dividend from the company whose shares you own. However, these dividends are designed for long-term stockholders.
What are ordinary dividends?
There are two forms of dividends: ordinary and qualified. Ordinary, or non-qualified, dividends are much more common than their counterpart. Just like qualified dividends, they are paid out from company or corporation’s earnings to its stock holders. These payments tend to come from sources outside of stocks, though. Examples of this include savings accounts, certificates of deposit and REITs. Reporting an ordinary dividend is a little different from a qualified dividend since it is not taxed in the same way.
What is qualified dividend?
The Takeaway. Qualified dividends are a way to reward long-term shareholders. They are taxed at a lower rate than ordinary dividends, giving them a tax benefit status. You can increase your dividend income by putting it in a retirement account for when you’re retired.
Is preferred dividend taxed?
Dividends from preferred issues are treated like dividends from the underlying company. REIT preferred dividends have not been taxed and are ordinary income, for example, while regular corporate preferred dividends have been taxed already and get the qualified treatment.
Who is the number 1 stock analyst in the world?
You can get an edge in individual securities. Joe Springer was the number 1 ranked stock analyst in the world by tipranks.com, and enjoys teaching about the stock market as well as crushing it.
Is it easy to get qualified dividends?
Enviable qualified dividends are not as easy to come by as ordinary dividends, but regional banks, containership preferreds, insurance companies, turnarounds, and companies with over-looked secondary business lines are looking pretty good here. Some have high yields, some have growth, some have a little of both. And their blood-thirst to bring you good income WILL be slaked!
What is the difference between ordinary and qualified dividends?
Dividends paid to investors by corporations come in two kinds – ordinary and qualified – and the difference has a large effect on the taxes that will be owed. Ordinary dividends are taxed as ordinary income, meaning a investor must pay federal taxes on the income at the individual’s regular rate.
Do you pay federal taxes on dividends?
Ordinary dividends are taxed as ordinary income, meaning a investor must pay federal taxes on the income at the individual’s regular rate. Qualified dividends, on the other hand, are taxed at capital gain rates. Lower-income recipients of qualified dividends may owe no federal tax at all.
What is qualified dividend?
Generally speaking, if a stock has been owned for more than a few months , its dividends are likely to be qualified.
Do you have to report dividends to IRS?
It’s not necessary for taxpayers to figure out for themselves which dividend are ordinary and which are qualified. Dividend payers do this for them and report the information to taxpayers as well as the IRS using the 1099-Div form.
What can a financial advisor do?
A financial advisor can help you find an assortment of securities that best meets your needs. Dividends from owning shares of corporations may be classified as qualified dividends and eligible for the lower capital gains rate if the investor has owned them for a minimum period.
How long do you have to hold a stock to pay dividends?
The Internal Revenue Service rule says the shares have to be owned for more than 60 days during the 121-day period that begins 60 days before the ex-dividend date. For preferred shares, the stock must be owned more than 90 days during the 181 days starting 90 days before the ex-dividend date.
What is ex dividend date?
The ex-dividend date is the earliest date after a dividend is declared that a buyer of the won’t be entitled to get the declared dividend. The shares also have to be unhedged during the holding period. This means the investor can’t have used any short sales, puts or calls involving the shares during the holding period.

Qualified Dividends on Your Tax Reporting Statement
- Qualified dividends are reported on Form 1099-DIV in line 1b or column 1b. However, not all dividends reported on those lines may have met the holding period requirement. Those non-qualified dividends, as well as other ordinary dividends, may be taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be as high as 37%. If you neither bought nor sold secu...
Holding Periods
- Although the holding period requirement is the same whether you received a dividend for shares you hold directly or in a mutual fund during the tax year, how you determine the holding period may vary, as outlined below. Note:When counting the number of days the fund was held, include the day the fund was disposed of, but not the day it was acquired.
Example of Determining Holding Period
- Consider this hypothetical situation in which you have dividends reported on Form 1099-DIV as qualified from shares in XYZ fund. You purchased 10,000 shares of XYZ fund on April 27 of the tax year. You sold 2,000 of those shares on June 15, but continue to hold (unhedged at all times) the remaining 8,000 shares. The ex-dividend date for XYZ fund was May 2. Therefore, during the …
Calculating The Amount of Qualified Dividends
- Once you determine the number of shares that meet the holding period requirement, find the portion per share of any qualified dividends. For each qualified dividend, multiply the two amounts to determine the amount of the actual qualified dividend. To continue with the example above, a dividend of $0.18 per share was paid but only 50% of that dividend ($0.09 per share) was report…