
On the ex-date, investors may drive down the stock price by the amount of the dividend to account for the fact that new investors are not eligible to receive dividends and are therefore unwilling to pay a premium. 2 However, if the market is particularly optimistic about the stock leading up to the ex-dividend date, the price increase this creates may be larger than the actual dividend amount, resulting in a net increase despite the automatic reduction.
Full Answer
What is a large stock dividend?
A stock dividend is considered a large stock dividend if the number of shares being issued is greater than 25%. For example, assume a company owns 5,000 common shares outstanding and declares a 50% common stock dividend.
What happens when a stock goes ex-dividend?
After a stock goes ex-dividend, the share price typically drops by the amount of the dividend paid to reflect the fact that new shareholders are not entitled to that payment. Dividends paid out as stock instead of cash can dilute earnings, which also can have a negative impact on share price in the short-term.
What is a stock dividend and how does it work?
As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
Is a dividend stock worth more than a non-dividend stock?
At the end of the year we would expect the share price of the dividend stock to be 2% lower than the non-dividend stock. And an equal investment in both stocks would yield exactly the same amount of money.
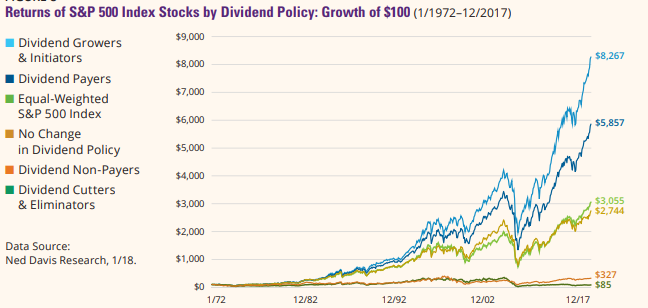
Can dividend be higher than stock price?
Though stock dividends do not result in any actual increase in value for investors at the time of issuance, they affect stock price similar to that of cash dividends. After the declaration of a stock dividend, the stock's price often increases.
What is the largest dividend?
Highest current dividend yieldsCompanyTickerCurrent annual dividend rateAltria Group Inc.MO$3.60Simon Property Group Inc.SPG$6.80Vornado Realty TrustVNO$2.12ONEOK Inc.OKE$3.7412 more rows•May 25, 2022
What stock has been paying dividends the longest?
Stanley Black & Decker: 146 years of consecutive payouts Among publicly traded industrial stocks, none has a longer streak of paying consecutive dividends, with Stanley Black & Decker doling out payouts to investors since 1876.
Do stock prices go up before dividend?
Dividends can be a sign that a company is doing well. That's why a stock's price may rise immediately after a dividend is announced. However, on the ex-dividend date, the stock's value will inevitably fall. The value of the stock will fall by an amount roughly corresponding to the total amount paid in dividends.
How much does Warren Buffett make from dividends?
Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.B) famously doesn't pay dividends – it has better things to do with its shareholders' cash – but Chairman and CEO Warren Buffett sure loves collecting them. In 2018 alone, Berkshire raked in $3.8 billion in dividends – “a sum that will increase in 2019,” Buffett said in the annual letter.
Do you pay taxes on dividends?
Yes – the IRS considers dividends to be income, so you usually need to pay taxes on them. Even if you reinvest all of your dividends directly back into the same company or fund that paid you the dividends, you will pay taxes as they technically still passed through your hands.
What companies have never missed a dividend payment?
15 Companies That Have Paid Dividends For More Than 100 YearsE I Du Pont De Nemours And Co (DD) — NO.General Mills, Inc. (GIS) — YES.Edison International (EIX) — NO.Johnson Controls Inc. (JCI) — YES.Church & Dwight Co., Inc. ... Stanley Black & Decker, Inc. ... Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM) — NO.Eli Lilly and Co (LLY) — YES.More items...
Is Walmart a good dividend stock?
Walmart has a track record of increasing its annual dividend every year since it started paying a dividend in 1974, and its dividend yield is roughly 1.55%, as of Dec. 2021.
Will Pfizer raise its dividend?
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)-- Pfizer Inc. (NYSE: PFE) today announced that its board of directors declared a $0.40 second-quarter 2022 dividend on the company's common stock, payable June 10, 2022, to holders of the Common Stock of record at the close of business on May 13, 2022.
What is a good dividend yield?
2% to 4%What is a good dividend yield? In general, dividend yields of 2% to 4% are considered strong, and anything above 4% can be a great buy—but also a risky one. When comparing stocks, it's important to look at more than just the dividend yield.
Should I sell stock before or after dividend?
You must have acquired your shares before the ex-dividend date in order to receive a dividend. If you acquired your shares on or after the ex-dividend date, the previous owner will receive the dividend. Sell your shares on or after the Ex-Dividend Date and you'll receive the dividend.
How many dividend stocks should I own?
By owning fewer than 25 stocks, investment risk increases significantly. But, by owning more than 25 stocks, there are diminishing benefits from diversification. Especially when additional stocks are added to a portfolio beyond 30. So, 25 stocks should be plenty.
Can I live off of dividends?
Depending on how much money you have in those stocks or funds, their growth over time, and how much you reinvest your dividends, you could be generating enough money to live off of each year, without having any other retirement plan.
Does Disney pay dividends?
Disney is one of just three Dow stocks that does not pay a dividend.
Does the S&P 500 pay dividends?
S&P Global has paid a dividend each year since 1937. The current annualized rate is $3.08 per share and was declared on January 27, 2022.
Do Tesla pay dividends?
Plus, Tesla does not pay a dividend to shareholders, which is also an important factor for income investors to consider.
Why are dividend stocks attractive?
Income-oriented investors find such stocks attractive because the dividend yield relative to their purchase price rises over time.
What is a common stock dividend?
They provide current income to investors and help stabilize the stock price. Common stock dividends are optional and can change over time. A corporation fixes preferred stock dividends at the time it issues the stock.
How do corporations pay dividends?
Corporations pay dividends out of retained earnings -- the accumulated profits of the company. Dividends are normally paid every quarter. The dividend yield is the annual payout divided by the current stock price. Dividends change when stock prices rise and fall. A corporation may also change the size of a dividend. Corporations do not need to change dividend amounts when the common stock price changes. However, a corporation committed to a particular dividend yield will need to increase the payout if the common stock price rises. When a stock price rises because of increased profits, the corporation might decide to boost dividends to “share the wealth” with stockholders, but it’s optional.
When do dividends change?
Dividends change when stock prices rise and fall. A corporation may also change the size of a dividend. Corporations do not need to change dividend amounts when the common stock price changes. However, a corporation committed to a particular dividend yield will need to increase the payout if the common stock price rises.
Do preferred shares have to be paid before common stock dividends?
“Cumulative” preferred shares also require that any missed dividends be paid before common stock dividends may be paid.
Can a missed dividend be a default?
A missed interest payment can throw a company into default and bankruptcy, but a cut or missed dividend payment does not result in default. For this reason, when a corporation's board of directors evaluates its response to low cash reserves, it will suspend the dividend rather than default on an interest payment. 00:00.
Does preferred stock change over time?
Preferred Stock. The dividends on preferred stock do not change over time. This has the effect of divorcing the value of preferred shares from the growth of the company.Traders price preferred shares based on their dividend yield relative to prevailing interest rates. If interest rates rise, preferred share prices fall and the dividend yield rises, ...
What is stock dividend?
A stock dividend, a method used by companies to distribute wealth to shareholders, is a dividend payment made in the form of shares rather than cash. Stock dividends are primarily issued in lieu of cash dividends when the company is low on liquid cash on hand. The board of directors. Board of Directors A board of directors is a panel ...
Why do stock dividends depress the market?
The market may perceive a stock dividend as a shortage of cash, signaling financial problems. Market participants may believe the company is financially distressed, as they do not know the actual reason for management issuing a stock dividend. This can put selling pressure on the stock and depress its price.
How many shares are in a small dividend?
A stock dividend is considered a small stock dividend if the number of shares being issued is less than 25%. For example, assume a company holds 5,000 common shares outstanding and declares a 5% common stock dividend. In addition, the par value per stock is $1, and the market value is $10 on the declaration date. In this scenario, 5,000 x 5% = 250 new common shares will be issued. The following entries are made:
How many shares does Colin own?
Colin is a shareholder of ABC Company and owns 1,000 shares. The board of directors of ABC Company recently announced a 10% stock dividend. Assuming that the current stock price is $10 and there are 100,000 total shares outstanding, what is the effect of a 10% stock dividend on Colin’s 1,000 shares?
How does a dividend affect a company's stock?
Maintaining an “investable” price range. As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
Why do companies issue dividends instead of cash?
Issuing a stock dividend instead of a cash dividend may signal that the company is using its cash to invest in risky projects. The practice can cast doubt on the company’s management and subsequently depress its stock price.
Why does the price per share decrease?
Although it increases the number of shares outstanding for a company , the price per share must decrease accordingly. An understanding that the market capitalization of a company remains the same explains why share price must decrease if more shares are issued.
Why are dividend stocks so popular?
Dividend stocks have become popular partially due to the fact that they are viewed as safe investments. Unfortunately in investing, there is always some risk involved. Although many investors have been very successful with dividend stocks, others have lost money when share prices drop or dividends are cut.
What are some myths about dividends?
Be sure to also read the Top 10 Myths About Dividend Investing. 1. General Motors (GM) The General Motors Company is an American multinational corporation founded in 1908, and the largest automaker in the United States. GM paid reliable, consistent dividends for several decades during its glory days.
How much did Citigroup pay in dividends in 2003?
By May 2003, the company’s dividend had increased to 23 cents, and then increased again three months later to 35 cents. In 2007, dividend payments for Citigroup were at an all-time high of 54 cents.
When did JCP increase dividends?
In 2006, JCP increased its dividend from 12.5 cents to 18 cents. Although JCP’s share price began to sink in 2007, the company boosted its dividend again to 20 cents per share. During this time, its share price tumbled, and JCP’s share price continued to fall 80% over the next two years.
Why did Kodak cut dividends?
Kodak reported that the drastic cut in dividends was due to a new company strategy that included increased investment in newer technology. The news brought Kodak’s stock down 18% in a single day. Finally, in April 2009, Kodak announced that it would no longer pay dividends on its stock as a result of declining sales.
When did GM cut its dividend?
In February 2006, GM cut its dividend in half to 25 cents per share. On May 15, 2008, the company paid its last 25 cent dividend. GM promptly suspended its dividend altogether, sold $4 to $7 billion in assets, and cut 20% of its salary costs to save billions of dollars. And still, some investors held on.
When did GM go bankrupt?
In 2009, GM declared bankruptcy. The stock price went to zero. Thankfully for its employees, the company was subsequently bailed out by the U.S. government. GM later became public once again in October 2011 on the NYSE, and on January 15, 2014 the company announced it would re-instate its dividend.
How much did Dr Pepper Snapple invest in Keurig?
Instead, they proposed making an equity investment of $9 billion in Dr Pepper Snapple. But that wouldn't have been enough to give Keurig the commanding stake in the combined company that it wanted, so in addition, the merger agreement called for Dr Pepper Snapple investors to get a special dividend.
Why do you have to declare a special dividend?
It's always worth keeping your eyes open when a stock you own declares a special dividend, because it can represent a big inflow of cash that you'll need to decide how to reinvest. Whether you put that money back into additional shares of that stock or use it to pay living expenses, special dividends can provide a healthy chunk of liquidity to give you more flexibility in your financial decision making than you typically have with regular dividends.
Does Dr Pepper pay dividends?
Keurig investors got their liquidity, and Dr Pepper shareholders got their payday. Going forward, dividend investors will still be pretty happy with Keurig Dr Pepper. The drink giant has said that it will pay roughly $0.60 per share in annual dividends going forward, giving shareholders a nearly 3% dividend yield.
Is Dr Pepper Snapple publicly traded?
In January 2018, beverage company Dr Pepper Snapple got an interesting, unexpected offer. Keurig Green Mountain, which had previously been a publicly traded company but which went private in a buyout led by private equity investor JAB Holding Company in 2016, offered to merge with Dr Pepper Snapple. Under the terms of the deal, the surviving entity would be called Keurig Dr Pepper ( NYSE:DPS) and combine the cold-beverage sodas and still drinks of Dr Pepper, Snapple, and their other brands with the coffee specialist's prowess in both home-brewing and retail partnership operations.
Is Keurig publicly traded?
Yet rather than going to the expense of doing an IPO of Keurig by itself, the merger with already publicly traded Dr Pepper Snapple allowed the private equity investors to translate their stake in privately held Keurig into an equivalent publicly traded stake in the combined company. Keurig investors got their liquidity, and Dr Pepper shareholders got their payday.
Do dividends make you happy?
For most investors, the more dividends they get, the happier they are about it. Most dividend stocks make predictable, regular payments of income, often on a quarterly basis. But every so often, some stocks make truly massive dividend payments that can provide a nice windfall for investors.
Who is Dan Caplinger?
Dan Caplinger has been a contract writer for the Motley Fool since 2006. As the Fool's Director of Investment Planning, Dan oversees much of the personal-finance and investment-planning content published daily on Fool.com.
What is dividend screener?
The dividend screener can help to research sectors and industries offering attractive dividend yields and investors can research more than 15 parameters, as well as download data for their own custom analysis.
Why do companies pay dividends?
Finally, companies that pay attractive dividends out to investors tend to have lower price volatility. A company that can safely pay a $1 per share dividend to investors has a floor under its price that a non-dividend paying firm lacks. Dividends ensure that shareholders always get some return, which in turn helps to bolster the stock price.
What is the P/E ratio?
Essentially, the P/E ratio is simply the price of a stock by its earnings per share. There are some small variations here – many investors use the last 12 months of GAAP earnings, while others will focus on earnings from the last calendar year, or on non- GAAP earnings. Regardless of the specifics, the P/E ratio is a widely used – though imperfect – tool for evaluating stock investments.
What is the alternative to P/E ratio?
An alternative to the P/E ratio is to use a metric that accounts for cash flows , and one good option is to compute the Price to Dividend Per Share ratio, or P/ DPS ratio.
What is the P/E ratio of a company with earnings per share of $4?
If Company A has earnings per share of $4, then its P/E ratio is $40/$4 or 10X. If Company B has earnings per share of $1, then its P/E ratio is 20X ($20/$1). In this case, relative valuation would suggest that Company A offers a better opportunity as it costs less to generate a profit of $1, all else being equal.
What does smart investing focus on?
When smart investors go looking for stocks, they do not focus on the price of the stock. A stock that is trading for $100 a share can easily be a better deal than a stock trading for $10 a share. Rather than focus on price, clever investors focus on valuation – specifically, the relative valuation of a stock’s price compared to how much cash it ...
Is P/E ratio effective?
Overall, the P/E ratio is a widely used metric, but it is not as useful or effective as the P/ DPS ratio . Investors might start by using a simple P/E ratio, but it generally makes sense to go beyond that before investing.
What would happen if dividends were pointless?
If dividends were pointless then the following scenario would be true: Let's assume, hypothetically, two identical stocks, only one of which pays a 2% annual dividend quarterly. At the end of the year we would expect the share price of the dividend stock to be 2% lower than the non-dividend stock. And an equal investment in both stocks would yield exactly the same amount of money.
How much money do you get from buying stocks?
You buy stocks for dividends over the long term. If a share of stock pays $1.00 in dividends every quarter, that's four dollars a year. If you bought it for $40, it pays out $4 in a year, and it's still worth roughly $40 at the end of the year, you're $4 richer. People will often invest large amounts of money in stable stocks not planning to sell it, but only collect the dividends which are either re-invested or pulled out as income.
How to create a dividend if a stock does not pay dividends?
If a stock does not pay a dividend, you can synthetically create a dividend by periodically selling shares.
Why are dividends important?
Regular dividends can produce a regular source of income to retirees and help supplement the income of those still working. Stocks with high dividends attract demand from investors thus potentially adding to the increase of the stock price over time.
What is the smartest way to invest in dividends?
Best as I can tell, the simple answer is: the smartest approach to investing for dividends is to pick a company that is, has, and will continue to make a solid profits. There are lots of them out there. Specifically, companies with no debt, a history of long-term and steady growth and a stable market share will, almost always recoup any drop in stock valuation due to a dividend payout...and usually in short order. This is why dividends were created...as a mechanism for distributing profits back to investor without diminishing their stake in the company. The trick then, is to find such companies with the best ratio between stock price and dividend payout. And again, there are a lot of good options out there.
How does a stock price go down?
You are right in the sense that in theory a stock's price will go down in value by the amount of the dividend. As the amount of dividend was adding to the value of the company, but now has been paid out to shareholder, so now the company is worth less by the value of the dividend. However, in real life this may or may not happen. Sometimes the price will drop by less than the value of the dividend. Sometimes the price will drop by more than the dividend. And other times the price will go up even though the stock has gone ex-dividend.
What would happen if you bought a stock the day before the dividend?
So if you bought the stock the day before the dividend, the next day you would immediately receive $1. If without the dividend the stock is worth $10, then the day before the dividend the stock is worth $11 because you know that the next day you will get a $1 "refund".
