
What financial ratios determine a stock's value?
No single financial ratio can determine whether a stock is a value or not. It's best to combine several ratios to form a more comprehensive view of a company's financials, it's earnings, and its stock's valuation.
What are investor ratios?
Investor ratios are usually used in comparing to the prior period or other company in the same industry in order to evaluate the company’s ability and its performance in generating the return back to investors. The commonly seen investor ratios include earnings per share (EPS), price-earnings ratio (P/E ratio), dividend cover and dividend yield.
What are the 8 key financial ratios that value investors absolutely must know?
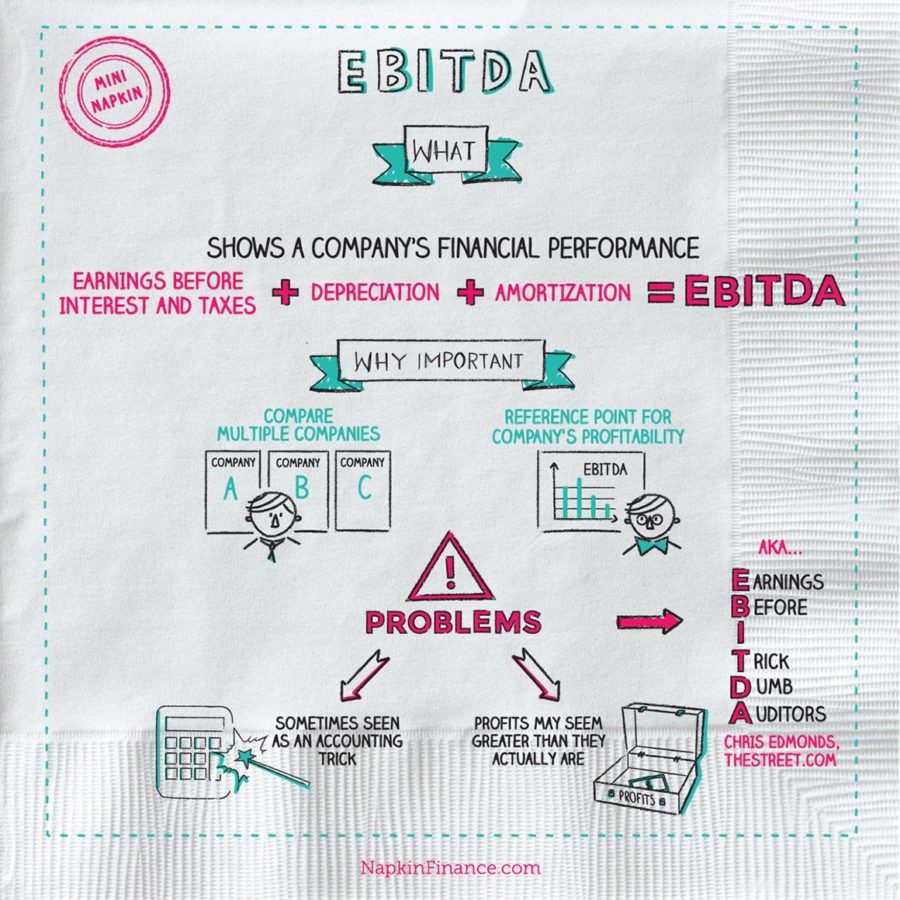
8 Key Financial Ratios That Value Investors Absolutely Must Know #1 – Price-Earnings #2 – Price / Free Cash Flow(FCF) #3 – Price Earnings Growth Rate (PEG) #4 – Price-to-Book or Price-to-Net Asset Value #5 – Debt-to-Asset or Debt-to-Equity #6 – Current Ratio or Quick Ratio #7 – Payout Ratio #8 – Management Ownership Percentage
What are the five basic ratios used to pick stocks?
There are five basic ratios that are often used to pick stocks for investment portfolios. These include price-earnings (P/E), earnings per share, debt-to-equity and return on equity (ROE).
What is stock value ratio?
The price-to-book ratio or P/B ratio measures whether a stock is over or undervalued by comparing the net value (assets - liabilities) of a company to its market capitalization. Essentially, the P/B ratio divides a stock's share price by its book value per share (BVPS).
Which ratio is used by investors?
There are six basic ratios that are often used to pick stocks for investment portfolios. These include the working capital ratio, the quick ratio, earnings per share (EPS), price-earnings (P/E), debt-to-equity, and return on equity (ROE).
What is investment to value ratio?
Essentially, this is the ratio of leverage to equity on each of the re-performing mortgage notes that we purchase. You may recall from our previous posts that our fund operates and produces income for our investors by purchasing and managing re-performing mortgage notes.
How do you determine the value of a stock?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
Why do investors use current ratio?
The current ratio helps investors understand more about a company's ability to cover its short-term debt with its current assets and make apples-to-apples comparisons with its competitors and peers.
What are the 4 types of ratios?
Typically, financial ratios are organized into four categories:Profitability ratios.Liquidity ratios.Solvency ratios.Valuation ratios or multiples.
How do you use PEG ratio?
How to Calculate the PEG Ratio. The math behind the PEG ratio is straightforward. One simply divides a company's P/E ratio by its expected rate of growth. A company with a P/E ratio of 20 and an expected growth rate of 10%, for example, would have a PEG ratio of 2 (20 / 10).
What does LTV stand for?
loan-to-valueThe loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is a measure comparing the amount of your mortgage with the appraised value of the property. The higher your down payment, the lower your LTV ratio.
How is LTV ratio calculated?
To figure out your LTV ratio, divide your current loan balance (you can find this number on your monthly statement or online account) by your home's appraised value. Multiply by 100 to convert this number to a percentage. Caroline's loan-to-value ratio is 35%.
What is Graham ratio?
The Formula for Graham Number Book value per share (BVPS) is the ratio of equity available to common shareholders divided by the number of outstanding shares. This figure represents the minimum value of a company's equity and measures the book value of a firm on a per-share basis.
What is market book ratio?
The book-to-market ratio compares a company's book value to its market value. The book value is the value of assets minus the value of the liabilities. The market value of a company is the market price of one of its shares multiplied by the number of shares outstanding.
What do valuation ratios tell you?
A valuation ratio shows the relationship between the market value of a company or its equity and some fundamental financial metric (e.g., earnings). The point of a valuation ratio is to show the price you are paying for some stream of earnings, revenue, or cash flow (or other financial metric).
Why do we use investor ratios?
Investor ratios are usually used in comparing to the prior period or other company in the same industry in order to evaluate the company’s ability and its performance in generating the return back to investors.
Why is a higher dividend cover ratio better for shareholders?
In general, the higher the dividend cover ratio is the better it is for the shareholders, as it indicates the lower risk that they will not receive dividends in the future.
How to calculate dividend cover?
Dividend Cover Formula. Dividend cover can be calculated by comparing the net income after tax to the dividends declared or paid. Dividend cover can also be calculated by comparing the earnings per shares (EPS) to the dividend per (ordinary) share.
How to calculate earnings per share?
Earnings per share can be calculated by comparing the net income after tax and preferred dividends during the period to the total ordinary shares at the end of the period.
What is P/E ratio?
P/E ratio is the financial ratio that looks at how much it costs to own a share in the company compared with the benefits or earnings generated from that share. Likewise, it shows the relationship between the company’s share price and its earnings per share (EPS).
Why do investors use dividend yield?
Dividend yield is one of important factors that is commonly used by investors to make a decision in buying or selling shares in the capital market. In a similar way, investors usually use the dividend yield to assess the relative benefits of different investment opportunities in the capital market.
Why do investors use earnings per share?
Investors usually use earnings per share as an indication of the company’s performance. In general, the higher earnings per share is the better the company’s performance is. The trend in earnings per share over time can be helpful for investors to make a decision whether to buy share of the company in the capital market.
What is the purpose of ratios in financial analysis?
Ratios—one variable divided by another—are used widely in financial analysis to understand how companies are doing internally and relative to one another. Financial ratios can be computed using data found in financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, and form the basis of fundamental analysis.
Why do we use valuation ratios?
Valuation ratios are some of the most commonly quoted and easily used ratios for analyzing the attractiveness of an investment in a company. These measures primarily integrate a company’s publicly traded stock price to give investors an understanding of how inexpensive or expensive the company is in the market.
What are the four types of financial ratios?
Financial ratios are typically cast into four categories: Profitability ratios. Liquidity ratios. Solvency ratios. Valuation ratios or multiples.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is one of the most well-known valuation ratios . It compares a company's stock price to its earnings on a per-share basis. Like other valuation ratio analyses, the price to earnings shows the premium that the market is willing to pay.
What is a solvency ratio?
Solvency ratios, also known as leverage ratios, are used by investors to get a picture of how well a company can deal with its long-term financial obligations. As you might expect, a company weighed down with debt is probably a less favorable investment than one with a minimal amount of debt on its books.
Why is it important to understand the variables driving ratios?
In most cases, it is also important to understand the variables driving ratios as management has the flexibility to, at times, alter its strategy to make the company's stock and ratios more attractive. Generally, ratios are typically not used in isolation but rather in combination with other ratios.
What does a 100% profit margin mean?
In general, the higher a company's profit margin, the better. A net profit margin of 1, or 100%, means a company is converting all of its revenue to net income. Profit margin levels vary across industries and time periods as this ratio can be affected by several factors.
Why do value investors like to seek out companies with a market value less than its book value?
Value investors often like to seek out companies with a market value less than its book value in hopes that the market perception turns out to be wrong. By understanding the differences between market value and book value, investors can help pinpoint investment opportunities.
What is value investing?
The basic premise of value investing is to purchase quality companies at a good price and hold onto these stocks for the long-term. Many value investors believe they can do just that by combining several ratios to form a more comprehensive view of a company's financials, its earnings, and its stock valuation.
What is debt to equity ratio?
The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is a stock metric that helps investors determine how a company finances its assets. The ratio shows the proportion of equity to debt a company is using to finance its assets.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio) is a metric that helps investors determine the market value of a stock compared to the company's earnings. In short, the P/E ratio shows what the market is willing to pay today for a stock based on its past or future earnings.
What does a P/B ratio of 0.95 mean?
A P/B ratio of 0.95, 1, or 1.1 means the underlying stock is trading at nearly book value.
Why is a P/B ratio of 0.5 attractive?
To a value-seeking investor, a company that trades for a P/B ratio of 0.5 is attractive because it implies that the market value is one-half of the company's stated book value.
Who is the most well known value investor?
Berkshire Hathaway leader Warren Buffett is perhaps the most well-known value investor. Value investors use financial ratios such as price-to-earnings, price-to-book, debt-to-equity, and price/earnings-to-growth to discover undervalued stocks. Free cash flow is a stock metric showing how much cash a company has after deducting operating expenses ...
What is the PE ratio?
PE ratio is the most common financial ratio to investors. The numerator is the price of the stocks while the denominator is the earnings of the company. This means that how many times of earnings are you paying for the stocks. For example, if the PE is 10, it means that you are paying 10 years worth of earnings. The lower the PE, the better. Let’s use an example to illustrate this. You saw a house selling for $1m and the owner said it is tenanted. The owner tells you the rental is worth $5k a month. After you have factored all the costs in owning and maintaining the house, your net profit is $2k a month or $24k a year. So the PE ratio for the house will be about 42. It will take 42 years for you to get back the worth of the house through a positive cashflow of $2k per month.
Why is there no point listening to too many opinions or over-analysed a company?
There is no point listening to too many opinions or over-analyse a company and end up taking no action because the signals are contradicting one another. To help you, I have list down 8 key financial ratios that you, as a value investor, must know.
Is value investing fanciful?
Value Investing is nothing fanciful. The problem is that there are too many financial ratios to confuse the investors. The key is to look at the right ones. Study enough to make an informed decision to buy and sell. There is no point listening to too many opinions or over-analyse a company and end up taking no action because ...
Is PE a favourite ratio?
Although PE is a favourite ratio, it is ever changing. Firstly, price can change. No one can predict how high the stock prices can go and although the PE can be high in your opinion, it can continue to go higher beyond your imagination.
Is a PEG ratio less than 1 undervalued?
In general, PEG ratio less than 1 is deem as undervalued. However, it is important to understand that we are ASSUMING the company would continue to grow at this rate. No one can forecast earnings accurately. Warren Buffett is smart in this area because he buys into companies with competitive advantage.
Why is a lower ratio important?
A lower ratio indicates a company may be undervalued, while a higher ratio may signal overvaluation. Valuation ratios are important, but so are quality measures, such as debt and liquidity metrics. Divide a company's total liabilities by its shareholder equity to compute the debt-equity ratio.
What does a lower ratio mean?
A lower ratio indicates a company may be undervalued, while a higher ratio may signal overvaluation. Debit-equity ratio. Valuation ratios are important, but so are quality measures, such as debt and liquidity metrics. Divide a company's total liabilities by its shareholder equity to compute the debt-equity ratio.
How to calculate P/E ratio?
Divide a company's share price by its annual earnings per share to calculate the P/E ratio. This ratio shows how much investors are willing to pay for $1 of a company's earnings. "It is probably the best way of comparing assets in different sectors and of finding true bargains," says Steven Jon Kaplan, CEO of True Contrarian Investments. Higher P/E ratios suggest a company's future earnings are expected to grow and may appear overvalued compared with companies with lower P/Es. That said, a high or low P/E doesn't necessarily indicate a good or bad investment; it offers a snapshot that begs additional inquiry. Given the uncertainty of future cash flows, it can be helpful for investors to rely on historical P/Es and use a mix of other ratios to evaluate and pick stocks.
Why are lower P/S stocks better?
Industry consensus says lower P/S stocks have better value because investors are paying less for every dollar of a company's revenues. P/S ratio values can vary across sectors, so to best assess a company's P/S, compare it with industry peers. Profit margin ratio.
Why do investors use the PEG ratio?
Because the P/E ratio isn't enough in and of itself, many investors use the price to earnings growth (PEG) ratio. Instead of merely looking at the price and earnings, the PEG ratio incorporates the historical growth rate of the company's earnings. This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock.
Why do stocks have high P/E?
The reason stocks tend to have high P/E ratios is that investors try to predict which stocks will enjoy progressively larger earnings. An investor may buy a stock with a P/E ratio of 30 if they think it will double its earnings every year (shortening the payoff period significantly).
Why are dividend stocks attractive?
It's always nice to have a back-up when a stock's growth falters. This is why dividend-paying stocks are attractive to many investors—even when prices drop, you get a paycheck. The dividend yield shows how much of a payday you're getting for your money. By dividing the stock's annual dividend by the stock's price, you get a percentage. You can think of that percentage as the interest on your money, with the additional chance at growth through the appreciation of the stock.
What does a PEG ratio mean?
A PEG of 1 means you're breaking even if growth continues as it has in the past.
Why is a low P/B ratio good?
In either case, a low P/B ratio can protect you— but only if it's accurate. This means an investor has to look deeper into the actual assets making up the ratio.
What is book value?
The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds. With purely financial firms, the book value can fluctuate with the market as these stocks tend to have a portfolio of assets that goes up and down in value.
What is the P/B ratio?
Made for glass-half-empty people, the price-to-book (P/B) ratio represents the value of the company if it is torn up and sold today. This is useful to know because many companies in mature industries falter in terms of growth, but they can still be a good value based on their assets. The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds.
How can market value ratios be used to enhance stock research?
Market value ratios can be a great way to enhance stock research by using mathematical formulas for publicly traded companies. Stock traders use these financial metrics to analyse stocks and provide potential investment ideas. This article will give more colour to market value ratios and how they can be used to implement investment strategies.
What does it mean when a stock ratio is greater than one?
A ratio greater than one suggests that the stock price of a company is trading at value more than the worth of its equity.
What is dividend yield ratio?
This ratio shows the proportion of dividends that a company pays out in comparison to the market price of its stock. It is important to note that many companies do not pay dividends which excludes this ratio.
What are the different ratios?
Different ratios provide different types of feedback to the investor. Relying on one specific ratio is never wise as a single data point may only give one perspective while other ratios could obviate this singular view with an opposing indication. That is, a broader outlook (multiple ratios) give rise to more informed investment decisions. Below is a list of important market value ratios to keep in mind when analysing stocks: 1 P/E Ratio 2 Dividend Yield Ratio 3 Market Capitalization 4 Book Value Per Share 5 Price-to-Book Ratio
What is the P/E ratio?
The P/E ratio also knows as the price/earnings multiple is one of the most popular ratios used by investors to determine the value of a share. This ratio measures the current share price against the earnings per share (EPS). The P/E ratio simply indicates the amount an investor would pay for $1 of a company’s earnings.
Why are market value ratios important?
These ratios are important because they give insight into different aspects of a company which is why investors do not usually rely on only one ratio. Market value ratios are like pieces of a puzzle. These pieces need to be individually analysed to compile an overall picture for informed investment decisions.
What is market value ratio?
Market value ratios are formulas that are used to provide insights into a company’s share price. There are many formulas that are used in various combinations for different analytical techniques. One thing is for sure, market value ratios give equity analysts a basic framework of a company and can possibly help to identify undervalued ...
Working Capital Ratio
Quick Ratio
- Also called the acid test, the quick ratio is another measure of liquidity. It represents a company's ability to pay current liabilities with assets that can be converted to cash quickly. The calculation for the quick ratio is current assets minus inventory minus prepaid expenses divided by current liabilities. The formula removes inventory because it can take time to sell and convert inventory i…
Earnings Per Share
- When buying a stock, you participate in the future earnings (or risk of loss) of the company. Earnings per share (EPS)is a measure of the profitability of a company. Investors use it to gain an understanding of company value. The company's analysts calculate EPS by dividing net income by the weighted averagenumber of common shares outstanding during the year. If a company has …
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- What if your prospective investment target is borrowing too much? This can increase fixed charges, reduce earnings available for dividends, and pose a risk to shareholders. The debt-to-equity (D/E)ratio measures how much a company is funding its operations using borrowed money. It can indicate whether shareholder equity can cover all debts, if needed. Investors often …
Return on Equity
- Return on equity(ROE) measures profitability and how effectively a company uses shareholder money to make a profit. For common stock shareholders, ROE (which is expressed as a percentage) is calculated by taking net income (income less expenses and taxes) figured before paying common share dividends and after paying preferred share dividends, and dividing the res…
The Bottom Line
- Financial ratios can help you pick the best stocks for your portfolio and build your wealth. Dozens of financial ratios are used in fundamental analysis. We've briefly highlighted six of the most common and easiest to calculate. Remember that a company cannot be properly evaluated using one ratio in isolation. So be sure to put a variety of ratios to use for more confident investment d…
Profitability Ratios
Liquidity Ratios
- Liquidityrelates to how quickly a company can repay its debts. It indicates how well company assets cover expenses. Liquidity ratios give investors an idea of a company’s operational efficiency. They also show how quickly and easily a company can generate cash to purchase additional assets or to repay creditors. This need can arise in an emergency situation or in the n…
Solvency Ratios
- Solvency ratios, also known as leverage ratios, are used by investors to see how well a company can deal with its long-term financial obligations. As you might expect, a company weighed down with debt is probably a less favorable investment than one with a minimal amount of debt. Some of the most popular solvency ratios include: 1. Debt-to-total-assets 2. Debt-to-equity 3. Time inte…
valuation Ratios
- Valuation ratios are often referred to by the media. They're easy to use to analyze the attractiveness of an investment in a company. These metrics primarily incorporate the price of a company's publicly traded stock. They can give investors an understanding of how inexpensive or expensive the stock is relative to the market. In general, the lower ...
The Bottom Line
- Financial ratios can be used to compare companies. They can help investors evaluate stocks within an industry. Moreover, they can provide a measure of a company today that can be compared to its historical data. The information you need to calculate ratios is easy to come by. Every figure can be found in a company's financial statements. Once you have the raw data, you …
Price-To-Earnings Ratio
Price-to-Book Ratio
- The price-to-book ratio or P/B ratio measures whether a stock is over or undervalued by comparing the net value (assets - liabilities) of a company to its market capitalization. Essentially, the P/B ratio divides a stock's share price by its book value per share(BVPS). The P/B ratio is a good indication of what investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company's net value. T…
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- The debt-to-equity ratio(D/E) is a stock metric that helps investors determine how a company finances its assets. The ratio shows the proportion of equity to debt a company is using to finance its assets. A low debt-to-equity ratio means the company uses alower amount of debt for financing versus shareholder equity. A high debt-equity ratio means the company derives more o…
Free Cash Flow
- Free cash flow (FCF) is the cash produced by a company through its operations, minus the cost of expenditures. In other words, free cash flow is the cash left over after a company pays for its operating expenses and capital expenditures(CapEx). Free cash flow shows how efficient a company is at generating cash and is an important metric in determining whether a company ha…
Peg Ratio
- The price/earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratiois a modified version of the P/E ratio that also takes earnings growth into account. The P/E ratio doesn't always tell you whether or not the ratio is appropriate for the company's forecasted growth rate. The PEG ratio measures the relationship between the price/earnings ratio and earnings growth. The PEG ratio provides a more complete …
The Bottom Line
- No single stock metric can determine with 100% certainty whether a stock is a value or not. The basic premise of value investing is to purchase quality companies at a good price and hold onto these stocks for the long-term. Many value investors believe they can do just that by combining several ratios to form a more comprehensive view of a company's financials, its earnings, and it…
Price-Earnings
Price / Free Cash Flow
- There is a belief that while it is possible to fake the income statement, it is harder to fake cash flow. Hence, besides looking at the PE ratio, you can examine the P/FCF Ratio. FCF is calculated based on the values from the cash flow statement, which shows the movement of money in and out of the company. FCF is defined as, Cash Flow from Operations – Capital Expenditures. If th…
Price Earnings Growth Rate
- We recognise the deficiency of PE ratio which is that it only reflects historical performance. Is there a better way to look into the future to get a sense if the company is a good buy? In the house example above, I assumed that the rental does not grow over time. But you and I know that it is not totally true. Rental may go up due to inflation. Likewise, growing companies are likely to incr…
Price-to-Book (Pb) Or Price-To-Net Asset Value
- PB ratio is the second most common ratio. Some people call it price to net asset value (NAV) instead. Net asset is the difference between the value of the TANGIBLE assets the company possessed and the liability the company assumed (intangible assets like goodwill which should be excluded). Let’s revisit the house example. Your house is worth $1m dollars and you owe the …
Debt-to-Asset Or Debt-to-Equity
- Initially, I wondered if I should be looking at Debt-to-Asset (D/A) or Debt-to-Equity (D/E) ratios. After a while, I realised either one of them is fine because both are just trying to measure the debt level of the company. Most importantly, use the same metricto make comparisons. Do not compare a stock’s D/A with another stocks’s D/E! Let’s go back to the example of your $1m hous…
Current Ratio Or Quick Ratio
- Long term debts usually take up the majority of the total liabilities. Although the company may have a manageable long-term debt level, it may not have sufficient liquidity to meet short term debts. This is important as cash in the short term is the lifeline of a business. One way to assess this is to look at the Current Ratio or Quick Ratio. Again, it does not really matter which one you a…
Payout Ratio
- A company can do two things to their earnings: 1. distribute dividends to shareholders and/or 2. retain earnings for company’s usage. Payout ratio is to measure the percentage of earnings given out as dividends. You will understand how much the company is keeping the earnings and you should ask the management what do they intend to do with the money. 1. Are they expanding th…
Management Ownership Percentage
- This is not a financial ratio per se but it is important to look at. It is unlikely for the CEO or Chairman of a large corporation to own more than 50%. Hence, this is more applicable to small companies. But, I like to buy into small and profitable companies where their CEO/Chairman is a majority shareholder. This helps me to ensure that his interests are aligned with the shareholder…
Where to Find These Ratios?
- You do not need to calculate all these values yourself! There are websites which have done the service for us. Some are free and some are paid. My advice is to try the free ones first and if they are not sufficient, then pay for more information.