
As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
Full Answer
How do stock dividends affect the price of a stock?
Maintaining an “investable” price range As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
Does a stock dividend increase the market capitalization of a company?
A stock dividend does not increase the market capitalization of a company. The market capitalization of ABC Company remains $1,000,000. With 110,000 total shares outstanding, the stock price of ABC Company would be $1,000,000 / 110,000 = $9.09. The following diagram illustrates the impact of a stock dividend on Colin:
What does it mean when a dividend is increased?
Dividends represent company profits that are paid to shareholders. When a dividend increase is the result of improved cash flows, it is often a positive indicator of company performance. Another reason for a dividend hike is a shift in company strategy away from investing in growth and expansion.
Do dividends go up when stock price goes down?
But there's no direct connection between a company's dividend and its stock price. Just because a stock price falls doesn't mean the company will take a meat cleaver to the dividend.
Do dividends increase when stock price increases?
Stock Dividends After the declaration of a stock dividend, the stock's price often increases. However, because a stock dividend increases the number of shares outstanding while the value of the company remains stable, it dilutes the book value per common share, and the stock price is reduced accordingly.
Do stock dividends change with stock price?
The dividend yield is the annual payout divided by the current stock price. Dividends change when stock prices rise and fall. A corporation may also change the size of a dividend. Corporations do not need to change dividend amounts when the common stock price changes.
What happens when dividend increases?
Dividend Increases The first is simply an increase in the company's net profits out of which dividends are paid. If the company is performing well and cash flows are improving, there is more room to pay shareholders higher dividends. In this context, a dividend hike is a positive indicator of company performance.
What causes dividend yield to decrease?
Companies usually make drastic dividend cuts because of financial challenges like declining earnings or mounting debts. Sometimes companies may cut dividend payments for more positive reasons, like preparing for a major acquisition or a stock buyback.
How do dividends increase income?
How to Increase Your Dividend Income Without Lifting a FingerDividend stocks are a simple way to grow your wealth over time.You can invest in dividend growth stocks if you want to earn more income every year.These stocks can help you automate your income and make money while you sleep.
Are dividends based on purchase price?
Many investors don't realize that a company's dividend is not based on its current share price. Dividends in their most basic form are payments made to shareholders based on company profits. Companies can either retain their earnings and plow them back into operations or give a portion of them to shareholders.
What does an increase in dividend yield mean?
If a company's dividend yield has been steadily increasing, this could be because they are increasing their dividend, because their share price is declining, or both. Depending on the circumstances, this may be seen as either a positive or a negative sign by investors.
How do dividends Work?
If dividends are paid, a company will declare the amount of the dividend, and all holders of the stock (by the ex-date) will be paid accordingly on the subsequent payment date. Investors who receive dividends may decide to keep them as cash or reinvest them in order to accumulate more shares.
Do stock prices rise before ex dividend date?
Because investors know they will receive a dividend if they purchase a stock before its ex-dividend date, they are often willing to buy it at a premium. This often causes the price of a stock to increase in the days leading up to its ex-dividend date.
Do share prices go up before ex-dividend date?
Because investors know they will receive a dividend if they purchase a stock before its ex-dividend date, they are often willing to buy it at a premium. This often causes the price of a stock to increase in the days leading up to its ex-dividend date.
How much do dividends increase over time?
This translates to about an average 7.2% annual dividend growth rate, Quinlan says, putting it well above the average annual inflation rate of 3.8%. A stock with a dividend that outpaces inflation can be like a "pension with a cost-of-living adjustment," McMahon says.
Does the dividend yield change?
While a stock's dividend may hold steady quarter-after-quarter, its dividend yield can change daily, because it is linked to the stock's price. As the stock rises, the yield drops, and vice versa.
How long do you have to hold a stock to get the dividend?
Briefly, in order to be eligible for payment of stock dividends, you must buy the stock (or already own it) at least two days before the date of record and still own the shares at the close of trading one business day before the ex-date.
How to anticipate dividend changes?
You can anticipate changes in dividends by going on the company's website, reading the annual report, participating in quarterly calls and paying close attention to any press releases issued by the company regarding dividend changes. The stock price will react before the actual dividend change based on company news.
What is the total return on dividends?
Your total return from dividend stocks consists of the rise in your stock prices plus the corporate profits companies pay out as dividends on your shares of their stocks. You profit when stock prices rise and dividends remain steady.
Why do dividends go up?
When dividends go up, the stock becomes more attractive to buyers. That increased demand will cause sellers to raise the price to gain more profits. If you hold this dividend stock, the share price will go up as the dividend rises. Investors generally consider rising dividends a sign of a company's good health.
How does the stock price react to dividends?
The stock price will react before the actual dividend change based on company news. Your stock price will also rise or fall based on profit and sales projections, because these tend to be leading indicators of a coming change in dividends.
What happens when a company reduces its dividend?
If a company reduces the dividend it pays on its stock, the stock becomes less attractive to investors. That means that the price of the stock will drop. If you own this stock, you will not only receive a lower dividend, but you will also watch your share prices fall. The market reacts very quickly to dividend changes, so even a hint of a dividend reduction can cause your stock to go down in price.
Who is Kevin Johnston?
He has written about business, marketing, finance, sales and investing for publications such as "The New York Daily News," "Business Age" and "Nation's Business." He is an instructional designer with credits for companies such as ADP, Standard and Poor's and Bank of America.
How are Dividends Paid?
Not every company pays dividends, but those that do typically pay them as a way to thank shareholders for their investments and to encourage further investment. There is a lot of variation in how dividends are paid out by different companies, or even by the same company over time. For example, while most dividends are paid in cash, they can also be paid in stock. In addition, dividend amounts are not fixed – companies may decide to raise or lower their dividends at any time, depending on their recent profits and whether they want to use excess profits to fund a dividend or to fund other projects. Some companies that pay dividends also do so irregularly, while others do so on a set monthly or quarterly schedule.
What is dividend discount?
The dividend discount model, or Gordon growth model, is popular among long-term value investors as a way to determine the fair share price of a company based on its dividends. According to this conservative valuation model, stocks are essentially worth what they will pay out to investors over their lifetime. Thus, the dividend discount model is extremely dependent on assumptions about the rate of future dividend increases, future interest rates, and a company’s growth. Note also that the dividend discount model does not take into account the value of an increase in the stock’s price over time relative to what it was purchased for.
What does dividend per share mean?
Dividends per share indicates the actual value that a company is paying out in dividends each year. Changes in the dividend per share are typically what investors look at to determine whether a company is performing well or poorly based on its dividends.
How to calculate dividends per share?
Dividends per Share = (Total Dividends – Special Dividends) / Shares Outstanding. The dividends per share can thus be used to track changes in a company’s dividends over time and can be used in combination with dividend payout to determine how what fraction of the company’s earnings per share is paid out to investors in dividends.
How does dividends affect stock?
One of the benefits and perils of a company issuing dividends is that dividends can have a significant effect on investor sentiment about that company. A company that is known for issuing consistent dividends over many years is likely to appeal to long-term value investors and to be seen as a steady, mature, and profitable company by investors, which can help drive up the share price over time. Investor sentiment may be even more favorable, increasing demand for the stock, if the company is known for consistently increasing its dividend payouts and day traders can potentially profit off of dividend increase announcements.
What is dividend yield?
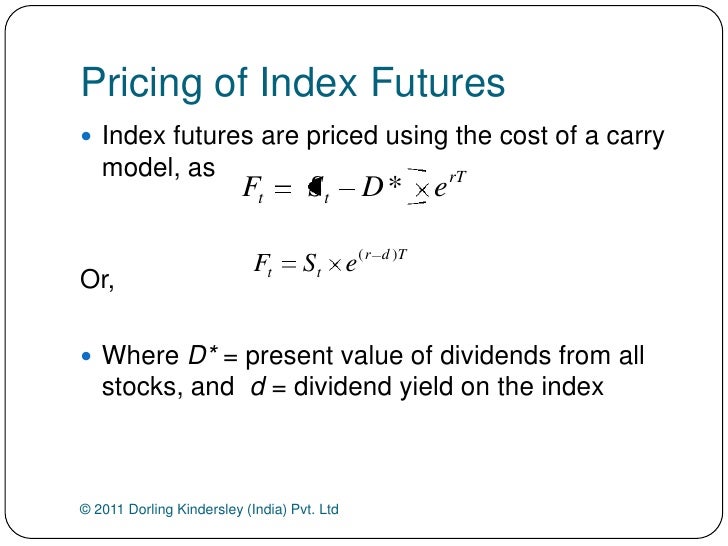
The dividend yield and dividend payout ratio are two metrics used to evaluate the value of anticipated dividends from a company. The dividend yield measures the annual payout in dividends than an investor can expect to receive per share held:
What is a stable dividend payout?
A stable dividend payout, and one that is comparable to other dividend-issuing companies in the same industry, is usually a good indicator that a company will be able to maintain its dividends. Short-term traders may view an excessively high dividend payout as a signal to short the stock in anticipation of reduced dividends in the future.
How many shares are in a small dividend?
A stock dividend is considered a small stock dividend if the number of shares being issued is less than 25%. For example, assume a company holds 5,000 common shares outstanding and declares a 5% common stock dividend. In addition, the par value per stock is $1, and the market value is $10 on the declaration date. In this scenario, 5,000 x 5% = 250 new common shares will be issued. The following entries are made:
Why do stock dividends depress the market?
The market may perceive a stock dividend as a shortage of cash, signaling financial problems. Market participants may believe the company is financially distressed, as they do not know the actual reason for management issuing a stock dividend. This can put selling pressure on the stock and depress its price.
What is stock dividend?
A stock dividend, a method used by companies to distribute wealth to shareholders, is a dividend payment made in the form of shares rather than cash. Stock dividends are primarily issued in lieu of cash dividends when the company is low on liquid cash on hand. The board of directors. Board of Directors A board of directors is a panel ...
How many shares does Colin own?
Colin is a shareholder of ABC Company and owns 1,000 shares. The board of directors of ABC Company recently announced a 10% stock dividend. Assuming that the current stock price is $10 and there are 100,000 total shares outstanding, what is the effect of a 10% stock dividend on Colin’s 1,000 shares?
How does a dividend affect a company's stock?
Maintaining an “investable” price range. As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
Why do companies issue dividends instead of cash?
Issuing a stock dividend instead of a cash dividend may signal that the company is using its cash to invest in risky projects. The practice can cast doubt on the company’s management and subsequently depress its stock price.
Why does the price per share decrease?
Although it increases the number of shares outstanding for a company , the price per share must decrease accordingly. An understanding that the market capitalization of a company remains the same explains why share price must decrease if more shares are issued.
Why are payout dates important?
On the record and payout dates, there are no price adjustments made by the stock exchanges. Those dates are mainly administrative markers that don't affect the value of the stock. From an investment perspective, the important date is the ex-dividend date, as that is the date that determines whether you are entitled to a dividend or not. Payout dates are important to investors, as that is the day they actually receive their money. However, it doesn't affect the value of the company on the open market.
How long do you have to hold a stock to get dividends?
Although most corporate dividends are "qualified" and taxed at a special rate, you have to hold a stock for 61 days or more to earn that status. This means your first couple of dividends will be taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
How long after the record date can you pay dividends?
The payout date can be days, weeks or even months after the record date.
What are the factors that affect stock prices?
Numerous factors affect stock prices. Supply and demand plays a major role in the rise and fall of stock prices. Fear and greed are also driving factors. Something else plays a role when a company pays a dividend, however.
How long has Csiszar been a financial planner?
Csiszar earned a Certified Financial Planner designation and served for 18 years as an investment counselor before becoming a writing and editing contractor for various private clients. In addition to his online work, he has published five educational books for young adults. Related Articles.
Do dividends have to be recorded on the books?
Dividends are typically paid in cash and given to shareholders quarterly, although some companies pay dividends irregularly or make payouts in the form of shares of stock. Payouts are only made to shareholders that are recorded on the books of the issuing company. A person must be on record as a shareholder by what's known as the record date in order to receive a dividend.
Can a stock be bid up on the ex-dividend date?
However, the market is guided by many other forces. If a stock is deemed to be undervalued by investors, the stock price may be bid up, even on the ex-dividend date. Similarly, if investor perception of the value of a stock on any given day sours, the stock may sell off much more than the simple drop due to the dividend.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield on a stock is the annual dividend divided by the stock price. So if the stock price falls and the dividend remains the same (as it usually does, dividends are typically changed annually or less often), the dividend yield will go up.
How to calculate dividend yield?
You may be thinking of the dividend YIELD instead. The dividend yield is calculated by the simple formula Yi eld = Annual Dividend/Current Share Price. In this formula the dividend is fixed, as I stated, but the share price fluctuates with the market. So the dividend yield does in fact increase as the stock price falls. In the example above, if the current share price is $20 per share,
When does the stock price fall on the ex dividend date?
It’s also true that when a dividend is paid, or more precisely on the ex-dividend date, the first date on which a buyer of the stock will not receive the dividend , the stock price will fall by the amount of the dividend.
Why do we pay dividends?
That’s the point of dividends: to reward long term investors over speculators.
Do dividends increase or decrease?
Dividends are paid by an amount, not a percentage. If the stock price decreases the yield will increase but the dividend amount remains the same.
Is dividend a cost efficient investment?
But a dividend is a cost efficient way for a long term investor to unlock some of the profit from a profitable company without having to pay fees: ordinarily if you sel
Can a company raise dividends and then the stock falls?
A company can decide to raise the dividend and then the stock falls. That’s life. One had nothing to do with the other.
What is dividend payout ratio?
The dividend payout ratio (also known as simply the payout ratio) gives investors an idea of how much profit a company is returning to shareholders as opposed to how much money they are keeping on hand for reinvestment, to pay off debt, or to hold as cash (i.e. retained earnings). The formula for the dividend payout ratio is as follows:
Why invest in dividend stocks?
Investing in dividend stocks is a time-honored way of growing wealth slowly. Following the simple three-part strategy of choosing a company wisely, looking to reinvest your dividends, and if necessary investing in dividend mutual funds and ETFs are good ways to identify and take advantage of dividend stocks that are increasing their dividends regularly. Dividend investing is not about chasing the highest yield you can find. There are often reasons why a company is offering a high yield. Like many things in life, if it looks too good to be true, it usually is.
Why are dividend stocks considered defensive?
Dividend stocks are regarded as defensive stocks because of their ability to weather the volatility of both bull and bear markets.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield is the ratio of a company’s annual dividend compared to its share price represented as a percentage. To calculate dividend yield, let’s look at this example:
How to calculate yield?
To calculate the yield, you would simply divide the announced per share annual dividend by the share price.
What is market rank?
MarketRank evaluates a company based on community opinion, dividend strength, institutional and insider ownership, earnings and valuation, and analysts forecasts.
How to choose a fund?
However, choosing a fund can be like walking into a Baskin-Robbins. There are a lot of varieties and it’s still up to you to decide on which funds are right for you. You'll want to look at the stocks that are included and check their dividend yield, their consistency with paying the dividend over time, their expense ratio (low is good) and the size of the company, or market capitalization. From lowest to highest risk, there are large caps, mid-caps, and small caps.
Why is a stable dividend payout ratio good?
A stable dividend payout ratio over time is considered a favorable sign for investors, as it indicates a financially sound company with earnings adequate to support continued positive dividend yields for investors. Analysts prefer the payout ratio to dividend yield, as a company's current yield is subject to the whims of the market and may be an unsustainable figure over the long term.
Why do companies raise their dividends?
A company might also raise its dividend to attract additional equity investments by offering more attractive dividend returns to investors. A stable dividend payout ratio is typically viewed as a healthy sign.
How to calculate dividend yield?
On the other hand, dividend yield is computed by dividing the annual dividend per share by the current share price.
What is dividend yield?
While dividend yield is perhaps a more commonly viewed figure by retail investors, the dividend payout ratio is a metric more favored by capital investors. The dividend payout ratio shows the percentage of a company’s earnings being paid to shareholders in the form of dividends. On the other hand, dividend yield is computed by dividing ...
Why do dividends increase?
There are two primary reasons for increases in a company’s dividend per share payout . The first is simply an increase in the company's net profits out of which dividends are paid . If the company is performing well and cash flows are improving, there is more room to pay shareholders higher dividends.
Why is a dividend increase positive?
Since a dividend represents a portion of company profits that is being paid to shareholders, news of a dividend increase is typically viewed as a positive development because it suggests that the company is confident in its future. However, a dividend increase can also be a sign that the company is running out of growth opportunities ...
Why do companies postpone capital expenditures?
Unfavorable financing rates may also lead the company to postpone major capital expenditures. A rapidly growing company may wish to consolidate its gains and reassess its market position before committing further funds to expansion. There is also the possibility a company may decide to increase its dividend payout to attract further equity investment by offering more attractive dividend returns to investors. 3
How to know the right price to buy stocks?
The prices of the shares fluctuate every second in stock markets and this makes it hard for the experts to know the right price to purchase the stocks. Trade analysts make use of various models to identify the right price of the share. One of such methods is based entirely on dividends. This method says that the right price of the share is the present value of all those future dividends. So, if the dividends are higher, one can expect an increase in the share price too. However, in India, a number of companies also reinvest the profits for business growth and thus they only give out a small portion of their profits as dividends to their investors.
When do shares rise?
The prices of the shares normally see a rise when the company is about to announce the dividends. Once the dividends are distributed, the share price plummets immediately. In many cases this fall in the share price is almost equal to the dividend that has been announced. For example, if a company X has distributed the dividends worth Rs. 50, one can most likely expect a fall in the stock price by the same amount one day after the distribution has been done. This price is called as the ex-dividend price.
What happens when a company declares dividends?
Whenever a company declares the dividend, the amount can be either higher or lower than expected. This can show a huge impact on the price of the stock and it can fluctuate based on the declaration made. We can take an example of two scenarios here:
Is dividend higher than expected?
Dividend announced is higher than expected: When such a scenario occurs, the market sentiment of the company will certainly cause an increase in the stock price and even the investors wonder if the company is seeing a substantial growth.
Why do companies pay dividends?
Whenever someone decides to buy stocks, he/she consider the expected return. Stock investors make money through two main sources – from an increase in stock prices and from dividends even when stock prices fall. So, dividends are one of the two primary sources to get a return on investment. That is why some stock investors prefer dividend stocks and thus, companies paying out dividends are more enticing for such investors.
Why does the share price drop after the dividend is paid?
They don’t pay premium prices because they aren’t eligible for a dividend. But, why does the share price drop after the dividend is paid? Because the company loses its cash in hand by paying dividends and hence its overall gets reduced. When the overall value of a company reduces, the fall in share prices also follows the fall in value.
What is dividend payout?
Dividends are a part of profits that a company earns in a specific financial period and divides it to its shareholders. Dividends are provided only by dividend stocks and dividend-paying companies are generally well-established. A dividend is a kind of reward that companies pay to their shareholders in cash, stock dividend, or some other form for their trust and investment. A stock dividend is a dividend payout where a company issues shares to stockholders as a dividend payment. Why is there a drop in share price after dividend payout?
Why does the price of shares rise after the dividend announcement?
The reason is new investors who buy stocks on or after the ex-dividend date do not qualify for receiving dividends. Therefore, new buyers refuse to pay premium prices and begin to quote lower prices, and thus, existing stockholders must lower their asking price for those willing to sell. The share price significantly decreases as a result of lower bids. That’s how share prices significantly decrease on the ex-dividend date.
How do dividends affect investors?
The first interesting effect of dividend payments is that dividend-paying companies attract more investors. As we already know that dividend-paying companies showcase their financial health, performance, and stability through dividend payouts. Investors all across the globe consider dividend-paying companies more worthy of investment than other companies. Companies paying dividends on regular basis attract more investors. When more and more investors take interest in buying shares of a dividend-paying company, the share price increases.
What will be your first consideration when buying stocks?
Let’s suppose that you are a stock investor and want to invest in stocks. What will be your first consideration? Of course, it will be an expected return. Whenever someone decides to buy stocks, he/she consider the expected return. Stock investors make money through two main sources – from an increase in stock prices and from dividends even when stock prices fall. So, dividends are one of the two primary sources to get a return on investment. That is why some stock investors prefer dividend stocks and thus, companies paying out dividends are more enticing for such investors.
How Are Dividends paid?
Dividends and Short-Term Price Movements
- Investor Sentiment
One of the benefits and perils of a company issuing dividends is that dividends can have a significant effect on investor sentiment about that company. A company that is known for issuing consistent dividends over many years is likely to appeal to long-term value investors and to be s… - Ex-dividend Date
The ex-dividend date, which is the date from which new shareholders are no longer eligible to receive the upcoming dividend payout, is an important short-term driver of a stocks’ price. A stock’s price will typically increase in the days leading up to the ex-dividend date to account for t…
Dividends and Long-Term valuation
- Dividend Yield and Dividend Payout Ratio
The dividend yield and dividend payout ratio are two metrics used to evaluate the value of anticipated dividends from a company. The dividend yield measures the annual payout in dividends than an investor can expect to receive per share held: Dividend Yield = Annual Dividen… - Dividends per Share
Dividends per share indicates the actual value that a company is paying out in dividends each year. Changes in the dividend per share are typically what investors look at to determine whether a company is performing well or poorly based on its dividends. Dividends per Share = (Total Divide…
Conclusion
- Dividends are an important part of stocks as they can affect both short- and long-term price movements. Dividends have a significant effect on investor sentiment and actual share value. In addition, long-term investors often look at dividends as a primary component of the fair price of a company’s shares, while short-term investors can incorporate dividend payouts into their tradin…
Understand Dividend Terminology
Stock Price on Ex-Dividend Date
- Stock market specialists will mark down the price of a stock on its ex-dividend date by the amount of the dividend. For example, if a stock trades at $50 per share and pays out a $0.25 quarterly dividend, the stock will be marked down to open at $49.75 per share. However, the market is guided by many other forces. If a stock is deemed to be underva...
Record and Payout Dates
- On the record and payout dates, there are no price adjustments made by the stock exchanges. Those dates are mainly administrative markers that don't affect the value of the stock. From an investment perspective, the important date is the ex-dividend date, as that is the date that determines whether you are entitled to a dividend or not. Payout dates are important to investor…
Taxation of Dividends
- Taxation is another concern for dividend investors. Although most corporate dividends are "qualified" and taxed at a special rate, you have to hold a stock for 61 days or more to earn that status. This means your first couple of dividends will be taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. If you intend to buy and sell stocks immediately before and after their ex-dividend dates simply to …