Full Answer
What is the constant dividend growth model?
The constant dividend growth model, or the Gordon growth model, is one of several techniques you can use to value a stock that pays dividends. Because a company can potentially exist without end, this model assumes that a stock will continue to grow its dividends at a constant rate forever.
How to find the price of a dividend-paying stock?
To find the price of a dividend-paying stock, the GGM takes into account three variables: D = the estimated value of next year's dividend r = the company's cost of capital equity g = the constant growth rate for dividends, in perpetuity
Why should we keep the dividend growth rate constant?
By keeping the dividend growth rate constant, we can determine the share price at any time in the future, so long as we know the current dividend amount, the growth rate, and the required rate of return at the future time. Since the dividend stream continues and grows perpetually, we simply input the dividend amount and recalculate.
What is a constant dividend payout ratio?
In a constant dividend payout ratio policy, the amount of dividends paid to shareholders fluctuate directly in proportion to the earnings of a company. Therefore, such a dividend policy comes with the potential to generate very volatile dividend payouts.
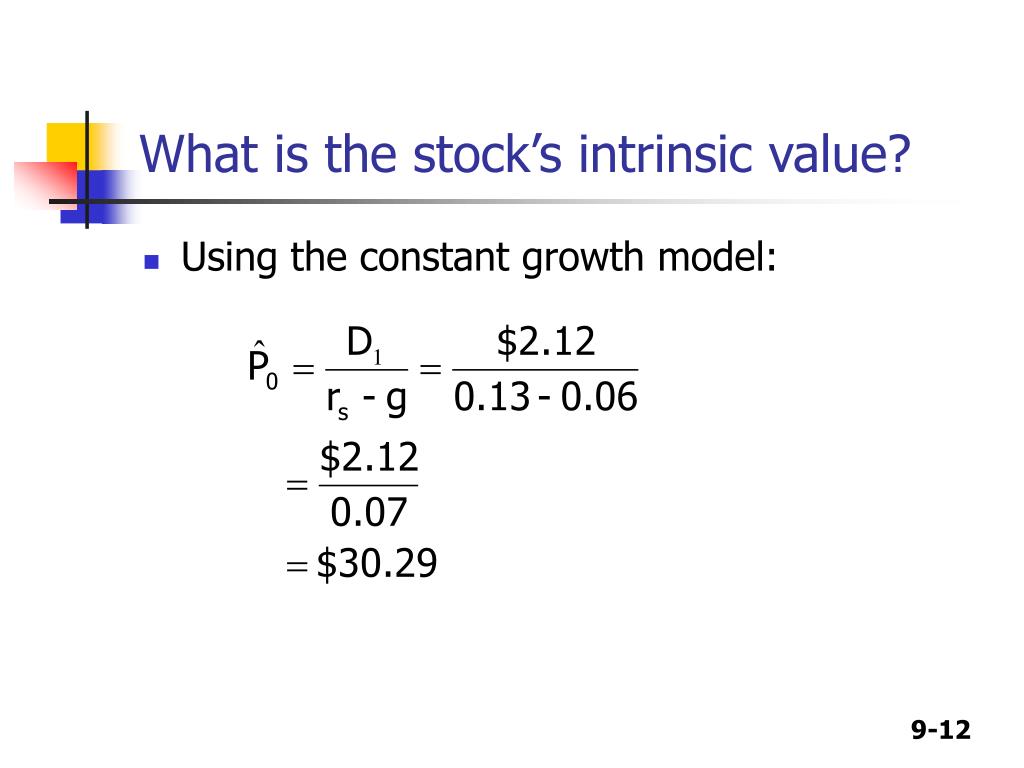
What is the stock price according to the constant growth dividend model?
The formula for the present value of a stock with constant growth is the estimated dividends to be paid divided by the difference between the required rate of return and the growth rate.
How do you calculate constant growth stock value?
The Constant Growth Model The formula is P = D/(r-g), where P is the current price, D is the next dividend the company is to pay, g is the expected growth rate in the dividend and r is what's called the required rate of return for the company.
What is a constant growth stock?
A constant growth stock is a share whose earnings and dividends are assumed to increase at a stable rate in perpetuity.
When valuing a stock using the constant growth model D1 represents the?
When valuing a stock using the constant-growth model, D1 represents the: the next expected annual dividend. Jensen Shipping has four open seats on its board of directors.
How do you find the constant growth rate of dividends?
The Gordon Growth Model formula is P = D1 / ( r - g ) where:P = current stock price.D = next year's dividend value.g = expected constant dividend growth rate, in perpetuity.r = required rate of return.
What are the three basic patterns of dividend growth?
What are the three basic patterns of dividend growth? Constant growth, zero growth, and differential growth.
What is the zero growth model?
The zero-growth model assumes that the dividend always stays the same, i.e., there is no growth in dividends. Therefore, the stock price would be equal to the annual dividends divided by the required rate of return. It is the same formula used to calculate the present value of perpetuity.
How do you find the non constant growth dividend?
17:5924:53Non-Constant Growth Dividends | EXAMPLES - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay so with a formula here's our formula again p 0 equals 2t 1 divided by K a minus G and do youMoreOkay so with a formula here's our formula again p 0 equals 2t 1 divided by K a minus G and do you want we get it by taking D 0. Times 1 plus G.
Why do investors have a strong preference for dividends?
Five of the primary reasons why dividends matter for investors include the fact they substantially increase stock investing profits, provide an extra metric for fundamental analysis, reduce overall portfolio risk, offer tax advantages, and help to preserve the purchasing power of capital.
What is the stock valuation formula?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS).
Which type of stock pays a fixed dividend?
Preferred stockPreferred stock shareholders receive their dividends before common stockholders receive theirs, and these payments tend to be higher. Shareholders of preferred stock receive fixed, regular dividend payments for a specified period of time, unlike the variable dividend payments sometimes offered to common stockholders.
How do you calculate price per share of preferred stock?
This formula calculates the average issue price per share of preferred stock: [(number of shares issued X par value) + paid in capital] / number of shares issued.
What is the constant growth rate?
A constant growth rate is defined as the average rate of return of an investment over a time period required to hit a total growth percentage that an investor is looking for.
How do you find constant growth rate in Excel?
To calculate the Compound Annual Growth Rate in Excel, there is a basic formula =((End Value/Start Value)^(1/Periods) -1. ... Actually, the XIRR function can help us calculate the Compound Annual Growth Rate in Excel easily, but it requires you to create a new table with the start value and end value.More items...
What is a constant growth stock How are constant growth stocks valued quizlet?
The constant growth model is an approach to dividend valuation that assumes a constant future dividend. 3. Assuming that economic conditions remain stable, any management action that would cause current and prospective stockholders to raise their dividend expectations should decrease a firm's value.
What is constant growth?
constant growth. Definition English: Variation of the dividend discount model that is used as a method of valuing a company or stocks. This variation assumes two things; a fixed growth rate and a single discount rate.
Is the S&P 500 dividend aristocrat?
The report shows that dividend-paying stocks, especially the S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats, were less volatile that the broader S&P 500. The report quotes data from Ned Davis Research, which suggests that since 1972, stocks with high-growth dividends have outperformed the broader markets in higher inflationary periods.
Is Lockheed Martin a good dividend stock?
Lockheed Martin is one of the 10 best dividend stocks to buy for consistent growth and income. The defense giant has increased its dividend consistently in the last 18 years. The company is continuing its dominance in the aerospace and military equipment market, winning noteworthy contracts every month.
Is Altria a good dividend stock?
With a 6% dividend yield, 50 years of consistent dividend hikes and a strong growth potential in terms of core business, Altria is one of the best dividend stocks to buy for growth and steady income. Jefferies recently upgraded MO stock to Buy, citing the company’s presence in the smokeless products sector which is expected to see a lot of growth. Jefferies increased its price target for the stock to $58.
Is Cisco a dividend company?
Cisco has increased its dividend consistently for the last 10 years. The company offers a sweet spot between high growth, long-term gains and steady income. It operates in a high-growth market of network equipment, software and Cloud computing. The stock has gained 28% over the last 12 months.
How do dividends affect stock prices?
Dividends can affect the price of their underlying stock in a variety of ways. While the dividend history of a given stock plays a general role in its popularity, the declaration and payment of dividends also have a specific and predictable effect on market prices .
How to calculate dividends per share?
DPS can be calculated by subtracting the special dividends from the sum of all dividends over one year and dividing this figure by the outstanding shares.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield and dividend payout ratio (DPR) are two valuation ratios investors and analysts use to evaluate companies as investments for dividend income. The dividend yield shows the annual return per share owned that an investor realizes from cash dividend payments, or the dividend investment return per dollar invested. It is expressed as a percentage and calculated as:
Why are dividends so attractive?
When companies display consistent dividend histories, they become more attractive to investors. As more investors buy in to take advantage of this benefit of stock ownership, the stock price naturally increases, thereby reinforcing the belief that the stock is strong. If a company announces a higher-than-normal dividend, public sentiment tends to soar.
What happens to stock after ex dividend?
After a stock goes ex-dividend, the share price typically drops by the amount of the dividend paid to reflect the fact that new shareholders are not entitled to that payment. Dividends paid out as stock instead of cash can dilute earnings, which can also have a negative impact on share prices in the short term.
How much does a dividend drop at $200?
As with cash dividends, smaller stock dividends can easily go unnoticed. A 2% stock dividend paid on shares trading at $200 only drops the price to $196.10, a reduction that could easily be the result of normal trading. However, a 35% stock dividend drops the price down to $148.15 per share, which is pretty hard to miss.
Why are dividends discounted?
Because share prices represent future cash flows, future dividend streams are incorporated into the share price, and discounted dividend models can help analyze a stock's value.
What are the best dividend stocks to buy?
Their brands number more than 50. You may have consumed one or more of their products. A few examples include: Applegate.
What are the risks of higher dividend yields?
But, higher dividend yields usually mean greater investment risk . These risks include the potential for a dividend reduction in the future.
How many years has Hormel increased its dividend?
We have a Dividend King here. Hormel has increased its dividend annually for 54 consecutive years. Dividend Kings are those rare companies that have increased their dividends annually for at least 50 years.
How many categories does a company hold the number 1 or number 2 market share in?
The company’s brands hold the number 1 or number 2 market share in more than 35 categories.
Is Walmart a good dividend company?
Want to start your year with dividends in January? Then Walmart is a good choice.
Is Nextera a utility stock?
NextEra is a bit unique for a utility dividend stock. First of all, utilities normally have higher dividend yields.
Do you have to pay commissions to buy dividend stocks?
Also, make sure you keep your stock trading costs to a minimum. There is no need to pay commissions when you buy or sell a dividend stock.
What is dividend growth?
The dividend growth model is a valuation model. Using this model, the financial analysts and investors calculate the fair value of a stock and then decide if the stock is worth investing in or not.
What is undervalued in dividend growth?
The first one is undervalued. An undervalued stock means the present value of the stock is more than the market value of the stock.
What is the difference between overvalued and undervalued stocks?
The first one is undervalued. An undervalued stock means the present value of the stock is more than the market value of the stock. The other one is overvalued. It means that the market values the stock for more than what it is worth. Or, the present value of the stock is less ...
What happens if the market price of a stock is greater than $42.86?
If the market price of the stock is greater than $42.86, then the stock is overvalued and an unwise decision for Mr X.
What does it mean when a stock is overvalued?
The other one is overvalued. It means that the market values the stock for more than what it is worth. Or, the present value of the stock is less than the market value of the stock.
Can a dividend model work without dividends?
This model cannot work without dividends per share, growth rate and the rate of return.
What is dividend aristocrats index?
This is a collection of several companies that have increased their dividends for at least 25 consecutive years. That means that every company in the index successfully gave investors raises not just during the good times in the market, but also during more volatile downturns, such as the dot-com crash of the early 2000s, the financial crisis of 2008-2009, and the COVID-19 pandemic so far. They may be a safer investment than the average dividend-paying stock.
What is dividend policy?
A dividend happens when a company sends money (or, very rarely, stock) to its shareholders. When a company gets to the point that it consistently earns more than management can effectively reinvest in the business, establishing a dividend policy and sending those excess profits back to investors is a smart move.
Is Clearway Energy a good investment?
The company invests in, acquires, and operates these facilities, selling the power on very long-term contracts to utility companies. If you're looking for a lower-volatility, safer way to profit from renewables, Clearway Energy is an excellent choice.
Is dividend aristocracy good?
Dividend Aristocrats are often excellent companies, but you can find great income investments elsewhere, too.
Is American Express a good dividend stock?
American Express (NYSE:AXP): Financial services such as consumer and business lending are another place to find a handful of top dividend stocks, and American Express is one of the best. While not a Dividend Aristocrat, AmEx has a decades-long track record of either raising or maintaining its dividend through every economic environment. That's a credit to its high-quality lending standards and its focus on higher-income consumers who are less likely to default on their debts during weak economic periods. This makes it both a safe investment for long-term investors and a reliable source of dividends.
Is Realty Income a dividend aristocrat?
The company owns a wide array of largely e-commerce-resistant properties, earning strong cash flows from tenants on long-term leases. Realty Income is one of the newest members of the Dividend Aristocrats, having joined the index in January 2020 after reaching 25 consecutive years of dividend increases (along with 50 straight years of paying investors every month ).
What is constant growth?
The constant growth formula is relatively straightforward for estimating a good price for a stock based on future dividends. Remember that it's extremely unlikely any company will truly continue to pay steadily rising dividends forever, so it should only be used in conjunction with other ways of evaluating the company and only for considering stable businesses.
What happens when you sell a stock at a higher price?
At a higher price, investors won't get the desired rate of return, so they'll sell the stock and lower the price. At a lower price it will be a bargain since they'll get a higher rate than required, meaning other investors will bid up the price.
How much is a fair price for a stock?
A fair price, under this model, is P = 5/ (0.10-0.05) = $100 per share . At a higher price, investors won't get the desired rate of return, so they'll sell the stock and lower the price. At a lower price it will be a bargain since they'll get a higher rate than required, meaning other investors will bid up the price.
When investors put money into a stock, do they hold onto the stock?
When investors put money into a stock, they often are hoping to hold onto the stock for a certain amount of time and then sell it to another investor for a higher price .
Do blue chip stocks pay dividends?
Some stocks are known for paying a steady dividend over time. These are usually blue chip stocks in stable industries, such as big and established industrial companies, utilities and similar businesses. Some also return money to investors by buying back stock, essentially swapping money for outstanding stock held by investors.
What is the most consistent stock in the world?
The most consistent stocks in the world are called “blue chip” stocks. The name comes from the highest value chips used in poker. But blue chip doesn’t mean high priced.
Why is Lancaster a rare dividend king?
Lancaster Colony (LANC) Lancaster Colony is a rare dividend king because it has a small market capitalization. The company raised its dividend payout for the 54th straight year in 2017. Only 13 other companies have ever accomplished this feat.
What is the dividend aristocrat?
The S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats is a stock index of companies who have increased their stock dividend for 25 years or more. What’s greater than an aristocrat? A king. “Dividend King” is an informal label given to companies that have increased their dividend payouts for 50 years or more.
How long has 3M been dividend paying?
3M has increased its dividend payout for 58 years in a row. 3M is one of the most successful companies of all time. It’s over 100 years old, in which time it’s obtained over 100K patents—and there’s no sign that the company’s patent growth is slowing down.
Why are dividend kings called blue chip stocks?
That’s why they’re called the dividend kings. If you’re looking to the stock market with hopes of accumulating long-term wealth, consistent high-performance is the holy grail. The most consistent stocks in the world are called “blue chip” stocks. The name comes from the highest value chips used in poker.
Is Hormel a dividend king?
Thanks to 51 straight years of dividend increases Hormel is now a dividend king. Over the past 20 years Hormel has grown its payout by 10.8%.
How to calculate dividends for a company?
The $1.80 dividend is the dividend for this year and needs to be adjusted by the growth rate to find D 1, the estimated dividend for next year. This calculation is: D 1 = D 0 x (1 + g) = $1.80 x (1 + 5%) = $1.89. Next, using the GGM, Company X's price per share is found to be D (1) / (r - g) = $1.89 / ( 7% - 5%) = $94.50.
What is supernormal dividend growth?
A third variant exists as the supernormal dividend growth model, which takes into account a period of high growth followed by a lower, constant growth period. During the high growth period, one can take each dividend amount and discount it back to the present period. For the constant growth period, the calculations follow the GGM model. All such calculated factors are summed up to arrive at a stock price.
What Is the Dividend Discount Model?
The dividend discount model (DDM) is a quantitative method used for predicting the price of a company's stock based on the theory that its present-day price is worth the sum of all of its future dividend payments when discounted back to their present value. It attempts to calculate the fair value of a stock irrespective of the prevailing market conditions and takes into consideration the dividend payout factors and the market expected returns. If the value obtained from the DDM is higher than the current trading price of shares, then the stock is undervalued and qualifies for a buy, and vice versa.
Why does the dividend model fail?
The model also fails when companies may have a lower rate of return (r) compared to the dividend growth rate (g). This may happen when a company continues to pay dividends even if it is incurring a loss or relatively lower earnings.
What is the risk of investing in stocks?
Shareholders who invest their money in stocks take a risk as their purchased stocks may decline in value. Against this risk, they expect a return/compensation. Similar to a landlord renting out his property for rent, the stock investors act as money lenders to the firm and expect a certain rate of return. A firm's cost of equity capital represents the compensation the market and investors demand in exchange for owning the asset and bearing the risk of ownership. This rate of return is represented by (r) and can be estimated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) or the Dividend Growth Model. However, this rate of return can be realized only when an investor sells his shares. The required rate of return can vary due to investor discretion.
Can a DDM be applied to stocks?
However, it can still be applied to stocks which do not pay dividend s by making assumptions about what dividend they would have paid otherwise.
Is GGM a good model for dividend growth?
This assumption is generally safe for very mature companies that have an established history of regular dividend payments. However, DDM may not be the best model to value newer companies that have fluctuating dividend growth rates or no dividend at all. One can still use the DDM on such companies, but with more and more assumptions, the precision decreases.
What is constant dividend growth?
The Constant Dividend Growth Model is a simple derivation of a perpetual stream of growing dividend payments relative to the required rate of return in the market.
Why do dividends grow?
There are many reasons, the most basic being simply inflation. As the price level grows, so will revenues, costs, and profits. As these profits grow, so would the dividend payouts, even if the purchasing power of these dividends remains the same. Another reason for this is that companies tend to mature in the long run, and will no longer need to retain the same level of earnings for growth. At this stage, the dividend payout tends to grow faster than the rate of inflation for successful companies.
How does perpetuity affect the price of a share?
The price of the share will simply be the dividend payment divided by the required rate of return. Since the dividend payment is constant, the only factor that affects the share price is the required rate of return.
What is constant growth model?
Constant Growth Model is used to determine the current price of a share relative to its dividend payments, the expected growth rate of these dividends, and the required rate of return by investors in the market
Why are dividends important in Gordon's model?
Dividends are the most crucial to the development and implementation of the Gordon Model. Investors buy shares in a company, and have two possible ways of receiving a financial benefit, they either receive dividends from the company, or they sell their shares and receive a capital gain if the price received is higher than the price paid.
Can a shareholder receive dividends while owning a share?
When this happens, the new shareholder will expect to receive dividends while owning the share. If we assume that this process will repeat itself, we find that the stream of dividends is in fact infinite.
