Stock valuations always assume a growing perpetuity for their terminal value calculation. Without the concept of a growing perpetuity it would be impossible to value a stock.
What is the present value of a growing perpetuity formula?
The present value of a growing perpetuity formula is the cash flow after the first period divided by the difference between the discount rate and the growth rate. A growing perpetuity is a series of periodic payments that grow at a proportionate rate and are received for an infinite amount of time.
What is a growing perpetuity?
A growing perpetuity is a series of periodic payments that grow at a proportionate rate and are received for an infinite amount of time. An example of when the present value of a growing perpetuity formula may be used is commercial real estate.
How do you value a stock without a growing perpetuity?
Without the concept of a growing perpetuity it would be impossible to value a stock. Loss of Real Value of Money: Since the formula assumes that the growth rate of the perpetuity will always be less than the required rate of return, it is implying a loss scenario.
How does the value of a perpetuity change over time?
The value of a perpetuity can change over time even though the payment remains the same. This occurs as the discount rate used may change. If the discount rate used lowers, the denominator of the formula lowers, and the value will increase. It should be noted that the formula shown supposes that the cash flows per period never change.
What is the formula for a growing perpetuity?
The calculation for the present value of growing perpetuity formula is the cash flow of the first period divided by the difference between the discount and growth rates.
What is the value of the growing perpetuity?
Present Value (Growing Perpetuity) = D / (R - G) This is because, the stream of payments will cease to be an infinitely decreasing series of numbers that have a finite sum.
What happens to the value of a perpetuity over time?
The value of a perpetuity can change over time even though the payment remains the same. This occurs as the discount rate used may change. If the discount rate used lowers, the denominator of the formula lowers, and the value will increase.
What must be true about the growth rate in order for a growing perpetuity to have a finite value?
What must be true about the growth rate for a growing perpetuity to have a finite value? Growth rate is less than discount rate. In what type of situation would it be helpful to solve for the number of periods and rate of return? - If you want to know what return you'll need to reach your goal.
What is an example of a growing perpetuity?
For example, if your business has an investment that you expect to pay out $1,000 forever, this investment would be considered a perpetuity. However, if you expect to receive $1,000 in the first year, and for the investment to grow at a rate of 5% in perpetuity, it would be considered a growing perpetuity.
How do perpetuities work?
A perpetuity is the sum of a regular series of fixed payments that will never end. It is today's value of all those payments in the future. Some people define a perpetuity as an annuity in the general sense (as opposed to the specific insurance contract).
What is the present value of a perpetuity that pays $100 per year?
Using the formula, we get PV of Perpetuity = D / r = $100 / 0.08 = $1250.
Can we calculate the future value of a perpetuity?
Mathematically speaking, the value of a perpetuity is finite, and its value can be determined by discounting its future cash flows to the present using a specified discount rate.
What does continuing in perpetuity mean?
One of the most common is the phrase “in perpetuity.” According to Black's Law Dictionary, the definition of “in perpetuity” is “… that a thing is forever or for all time.” In practice, the phrase “in perpetuity” usually applies to a transfer of rights or clauses that survive contract termination.
What is the difference between a growing annuity and a growing perpetuity?
The difference between an annuity derivation and a perpetuity derivation is related to their distinct time periods. An annuity uses a compounding interest rate to calculate its present value or future value, while a perpetuity uses only the stated interest rate or discount rate.
How do you determine the value of perpetuity?
PV of Perpetuity = ICF / (r – g)The identical cash flows are regarded as the CF.The interest rate or the discounting rate is expressed as r.The growth rate is expressed as g.
How do you calculate the NPV of a perpetuity?
NPV(perpetuity)= FV/i Where; FV- is the future value. i – is the interest rate for the perpetuity.
What is the present value of a growing annuity?
The present value of a growing annuity represents the current value of a future series of payments for a specified time, where the payments are growing at a steady (compound) rate (i.e. 3% per year).
How do you calculate the NPV of a perpetuity?
NPV(perpetuity)= FV/i Where; FV- is the future value. i – is the interest rate for the perpetuity.
What is terminal value formula?
This method assumes the business will continue to generate Free Cash Flow (FCF) at a normalized state forever (perpetuity). The formula for calculating the perpetual growth terminal value is: TV = (FCFn x (1 + g)) / (WACC – g)
What Is Perpetuity?
A perpetuity is a security that pays for an infinite amount of time. In finance, perpetuity is a constant stream of identical cash flows with no end. The concept of perpetuity is also used in several financial theories, such as in the dividend discount model (DDM).
What Is the Difference Between a Perpetuity and an Annuity?
However, the key difference between them is that annuities have a predetermined end date, known as the “maturity date,” whereas perpetuities are intended to last forever. Importantly, both annuities and perpetuities can be valued using DCF analysis.
What is the difference between annuities and perpetuities?
However, the key difference between them is that annuities have a predetermined end date, known as the “maturity date”, whereas perpetuities are intended to last forever.
How to calculate perpetuity?
The basic method used to calculate a perpetuity is to divide cash flows by some discount rate. The formula used to calculate the terminal value in a stream of cash flows for valuation purposes is a bit more complicated. It is the estimate of cash flows in year 10 of the company, multiplied by one plus the company’s long-term growth rate, and then divided by the difference between the cost of capital and the growth rate.
How to determine present value of perpetuity?
The present value of a perpetuity is determined by dividing cash flows by the discount rate.
What is a perpetuity in finance?
A perpetuity is a security that pays for an infinite amount of time. In finance, perpetuity is a constant stream of identical cash flows with no end. The formula to calculate the present value of a perpetuity, or security with perpetual cash flows, is as follows: The concept of a perpetuity is also used in a number of financial theories, ...
What are some examples of perpetual cash flows?
An example of a financial instrument with perpetual cash flows is the British-issued bonds known as consols, which the Bank of England phased out in 2015. By purchasing a consol from the British government, the bondholder was entitled to receive annual interest payments forever. 1 Although it may seem a bit illogical, ...
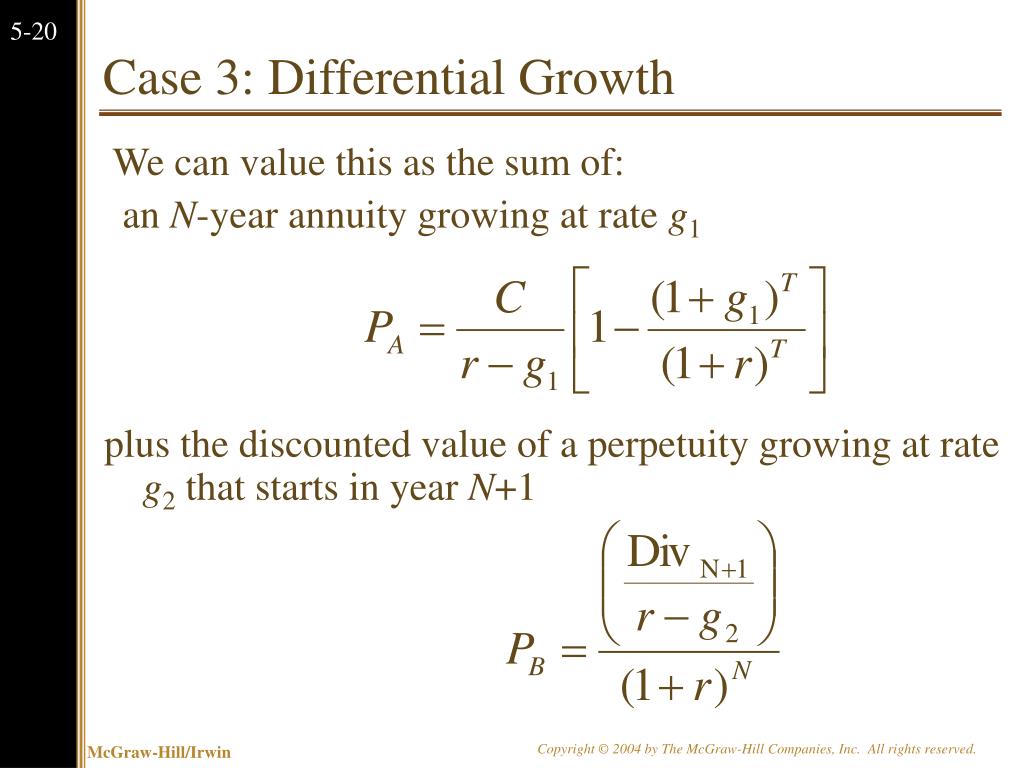
How the Present Value of Growing Perpetuity Formula is derived?
A growing perpetuity is a series of periodic payments that continue indefinitely and grow at a proportionate rate. Therefore, the formula for the present value of a growing perpetuity can be shown as
What happens to perpetuity if the growth rate is higher than the discount rate?
In theory, if the growth rate is higher than the discount rate, the growing perpetuity would have an infinite value.
What is growing perpetuity?
A growing perpetuity is a series of periodic payments that grow at a proportionate rate and are received for an infinite amount of time. An example of when the present value of a growing perpetuity formula may be used is commercial real estate.
Is rental cash flow indefinite?
The rental cash flows could be considered indefinite and will grow over time. It is important to note that the discount rate must be higher than the growth rate when using the present value of a growing perpetuity formula.
Why is a growing perpetuity only summed up?
Just like the perpetuity, a growing perpetuity can only be summed up because the series is infinitely decreasing. The growing perpetuity assumes that we will lose the real value of money at a slower rate as compared to an ordinary perpetuity. ❮ Previous Article. Next Article ❯.
What is a growing perpetuity?
As already stated, a growing perpetuity involves payments that do not remain fixed. Instead these payments keep on growing at the same constant rate of growth. So, if the rate of growth of the payments is 7%, each payment will be 7% more than the payment received before it.
Why do college endowments need to grow?
College endowment funds need to be growing perpetuities. This is because with the passage of time, tuition and other expenses will become more and more expensive. Hence the college endowment funds must keep growing to meet the scholarship demands represented by growing expenses.
Do stock valuations always assume a growing perpetuity?
Stock valuations always assume a growing perpetuity for their terminal value calculation. Without the concept of a growing perpetuity it would be impossible to value a stock.
Is G greater than R?
However, we need to understand that for this formula to hold true, G must always be greater than R. If G is less than R or equal to R, the formula does not hold true. This is because, the stream of payments will cease to be an infinitely decreasing series of numbers that have a finite sum.
Is infinite payment enough?
It is for this reason that receiving infinite payments is not enough. The payments must also keep growing at a certain rate. This will ensure that they are not considerable behind inflation. This is the idea behind a growing perpetuity.
Who wrote the MSG article?
The article is Written By “Prachi Juneja” and Reviewed By Management Study Guide Content Team. MSG Content Team comprises experienced Faculty Member, Professionals and Subject Matter Experts. We are a ISO 2001:2015 Certified Education Provider. To Know more, click on About Us. The use of this material is free for learning and education purpose. Please reference authorship of content used, including link (s) to ManagementStudyGuide.com and the content page url.
What is growing perpetuity?
A growing perpetuity is a cash flow that is projected to be received indefinitely and grow at the same pace indefinitely. For instance, if your company has a £1,000 investment that you intend to pay out in perpetuity, this investment is regarded as perpetuity. If, on the other hand, you anticipate getting £1,000 in the first year and the investment to increase at a pace of 5% per year for the rest of your life, it would be considered growing perpetuity.
What is a dividend discount model?
To determine how much those annuity payments would be worth today, this model employs future dividend cash flows and a periodic interest rate. One example of perpetuity is common stocks which are practically an investment in the operations of a company. Another example would be real estate because as soon as the purchase price of real estate has been paid, the owner is entitled to receive an infinite stream of rental payments.
How to calculate present value of growing perpetuity?
To sum up, to calculate the present value of growing perpetuity you must divide the Expected cash flow in period 1 by the expected rate of return subtracted by the rate of growth of perpetuity payments.
How to calculate the price of perpetuity?
It is the fundamental formula for calculating the price of perpetuity. You have to simply divide the cash flows/payments by the discount rate to calculate the Present Value of perpetuity.
What is perpetuity in finance?
As we’ve seen in previous paragraphs, a perpetuity is a series of future financial flows that never ends. it’s also shown, however, that the value of these financial flows declines over time. Today, $500 may buy us a lot of things, but in 60 years, it will be worth much less. Receiving endless payments is insufficient for this reason. Therefore, Payments are also required. In conclusion, growing perpetuity is based on the concept that payments must also continue to rise at a particular rate. This will ensure that they are not significantly out of step with inflation.
What is a perpetual annuity?
Now that we got that out of the way and understood the main idea behind annuity let’s get into the main topic at hand, perpetuity. Perpetuity is a type of regular annuity with no end, a never-ending stream of cash payments. It’s also known as a perpetual annuity. The notion of perpetuity allows you to evaluate stocks, real estate, and a variety of other investments. Perpetuity is essentially a never-ending stream of cash flows. This means that if we purchase perpetuity right now after paying a certain lump sum, we should expect repayments that last till the end of time.
What are some examples of growing perpetuities?
One of the main growing perpetuities that we see daily is Endowment funds for colleges that must have long-term growth rates. This is because tuition and other expenditures will grow increasingly expensive as time goes on. As a result, endowment funds at colleges must continue to increase in order to satisfy rising scholarship needs. Another important example is stock valuations. For the computation of terminal value, stock valuations usually assume growing perpetuity. It would be difficult to evaluate a company without the idea of a growing perpetuity.
What is the PV of Perpetuity?
PV of Perpetuity. A perpetuity is a type of annuity that receives an infinite amount of periodic payments. An annuity is a financial instrument that pays consistent periodic payments. As with any annuity, the perpetuity value formula sums the present value of future cash flows.
What is the perpetuity value formula?
The perpetuity value formula is a simplified version of the present value formula of the future cash flows received per period. The present value or price of the perpetuity can also be written as
Can the value of a perpetuity change over time?
The value of a perpetuity can change over time even though the payment remains the same . This occurs as the discount rate used may change. If the discount rate used lowers, the denominator of the formula lowers, and the value will increase. It should be noted that the formula shown supposes that the cash flows per period never change.
Does cash flow per period change?
It should be noted that the formula shown supposes that the cash flows per period never change.
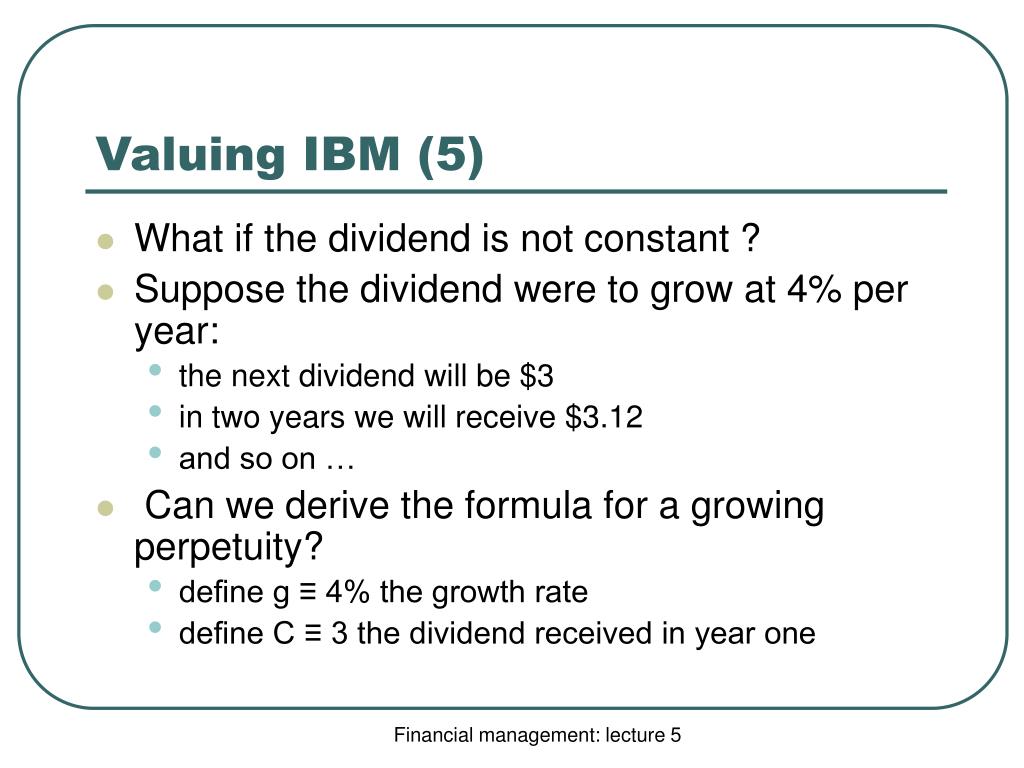
What is supernormal growth?
The purpose of the supernormal growth model is to value a stock that is expected to have higher than normal growth in dividend payments for some period in the future. After this supernormal growth, the dividend is expected to go back to normal with constant growth.
Why do we use the fourth period?
But we use the fourth period because the valuation of the perpetuity of dividends is based on the end of year dividend in period four, which takes into account dividends in year five and on.
How to find the value of a common share?
To find the value of a common share, take the dividends you expect to receive during your holding period and discount it back to the present period. But there is one additional calculation: When you sell the common shares, you will have a lump sum in the future which will have to be discounted back as well.
What is the discount rate for dividends?
For example, if you have a stock that pays a $1.45 dividend which is expected to grow at 15% for four years, then at a constant 6% into the future, the discount rate is 11% .
Why is supernormal growth so difficult?
Calculations using the supernormal growth model are difficult because of the assumptions involved, such as the required rate of return, growth or length of higher returns. If this is off it could drastically change the value of the shares. In most cases, such as tests or homework, these numbers will be given. But in the real world, we are left to calculate and estimate each of the metrics and evaluate the current asking price for shares. Supernormal growth is based on a simple idea, but can even give veteran investors trouble.
How to calculate the value of the remaining dividends?
Still working with the last period of higher growth, calculate the value of the remaining dividends using the V = D 1 ÷ (k - g) equation from the previous section. But D 1, in this case, would be next year's dividend, expected to be growing at the constant rate. Now the discount goes back to the present value through four periods.
What is the most important skill an investor can learn?
Updated Jun 25, 2019. One of the most important skills an investor can learn is how to value a stock. It can be a big challenge though, especially when it comes to stocks that have supernormal growth rates. These are stocks that go through rapid growth for an extended period of time, say, for a year or more. Many formulas in investing, though, are ...