
Required Rate of Return formula = Expected dividend payment / Stock price + Forecasted dividend growth rate. On the other hand, for calculating the required rate of return for stock not paying a dividend is derived using the Capital Asset Pricing Model Capital Asset Pricing Model The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) defines the expected return from a portfolio of various securities with varying degrees of risk.
Full Answer
How do you calculate required rate of return on dividends?
Finally, the required rate return is calculated by dividing the expected dividend payment (step 1) by the current stock price (step 2) and then adding the result to the forecasted dividend growth rate (step 3) as shown below, Required rate of return formula = Expected dividend payment / Stock price + Forecasted dividend growth rate
What is the'dividend growth rate'?
WHAT IS THE 'Dividend Growth Rate'. The dividend growth rate is the annualized percentage rate of growth that a particular stock's dividend undergoes over a period of time. Next Up. Dividend Discount Model - DDM. Capital Dividend.
What is the rate of return on a d0 dividend?
Question: A stock just paid a dividend of D0 = $1.50. The required rate of return is rs = 10.1%, and the constant growth rate is g = 4.0%. What is the current stock price? This problem has been solved! A stock just paid a dividend of D0 = $1.50. The required rate of return is rs = 10.1%, and the constant growth rate is g = 4.0%.
Do dividend stocks with a 10% return on average attract capital appreciation?
The stock with a long-term dividend growth rate of about 10% will show a similar 10% return, give or take a percent, over the long term. This is why I have often said that as long as my stocks continue their dividend growth the capital appreciation will eventually follow.
How do you find stock price with dividend and required rate of return?
That formula is:Rate of Return = (Dividend Payment / Stock Price) + Dividend Growth Rate.($1.56/45) + .05 = .0846, or 8.46%Stock value = Dividend per share / (Required Rate of Return – Dividend Growth Rate)$1.56 / (0.0846 – 0.05) = $45.$1.56 / (0.10 – 0.05) = $31.20.
How do you calculate stock dividend growth rate?
Mathematically, this dividend growth rate formula can be expressed as : Dividend growth rate= (Dn/D0)1/n-1.
How do you calculate required rate of return on a stock?
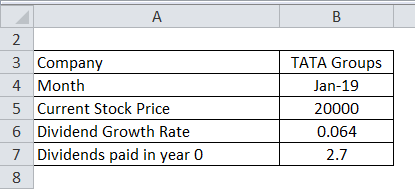
Required Rate of Return = (Expected Dividend Payment / Current Stock Price) + Dividend Growth RateRequired Rate of Return = (2.7 / 20000) + 0.064.Required Rate of Return = 6.4 %
Do you include dividends in rate of return?
The rate of return for a stock includes capital appreciation and any dividends paid.
What is dividend growth rate?
What Is Dividend Growth Rate? The dividend growth rate is the annualized percentage rate of growth that a particular stock's dividend undergoes over a period of time. Many mature companies seek to increase the dividends paid to their investors on a regular basis.
Is dividend yield and dividend growth rate the same?
A company's dividend or dividend rate is expressed as a dollar figure and is the combined total of dividend payments expected. The dividend yield is expressed as a percentage and represents the ratio of a company's annual dividend compared to its share price.
What is the relationship between required return and stock price?
If the required return rises, the stock price will fall, and vice versa. This makes sense: if nothing else changes, the price needs to be lower for the investor to have the required return. There is an inverse relationship between the required return and the stock price investors assign to a stock.
How do you use CAPM to value stock?
To calculate the value of a stock using CAPM, multiply the volatility, known as “beta“, by the additional compensation for incurring risk, known as the “Market Risk Premium”, then add the risk-free rate to that value.
Is required rate of return the same as WACC?
Since the required rate of return is a component of the WACC formula, the formula can be modified and used to identify the required rate of return. Where: WACC is the discount rate or required rate of return. E is the value of Equity.
How do dividends affect returns?
Dividends lower the value of a stock because profits are distributed to shareholders rather than being invested back into the company, which is believed to be a devaluing of the company and this devaluing is taken into consideration by the reduction in the share price.
How do you calculate stock growth with dividend reinvestment?
The total value with dividend reinvestment equals the final stock price multiplied by the sum of the initial number of shares plus all dividend reinvestment shares. The number of shares is the initial number of shares plus all the shares purchased with reinvested dividends.
How important are dividends as a source of return?
Five of the primary reasons why dividends matter for investors include the fact they substantially increase stock investing profits, provide an extra metric for fundamental analysis, reduce overall portfolio risk, offer tax advantages, and help to preserve the purchasing power of capital.
How do you calculate 5 year dividend growth rate?
Dividend Growth Rate FormulaFormula (using Arithmetic Mean) = (G1 + G2 + …….. + Gn) / n.Formula using Compounded Growth) = (Dn / D0)1/n – 1.Dividend Growth Rate Formula = (Dn / D0)1/n – 1.Let us take the example of Apple Inc.'s dividend history during the last five financial years starting from 2014.
How do you calculate dividend growth rate in Excel?
Dividend Growth Rate = (Dn/D0)1/n – 1Dividend Growth Rate = (13.91/9.30) ^ (1/4) – 1.Dividend Growth Rate = 11.09%
How do you calculate stock growth with dividend reinvestment?
The total value with dividend reinvestment equals the final stock price multiplied by the sum of the initial number of shares plus all dividend reinvestment shares. The number of shares is the initial number of shares plus all the shares purchased with reinvested dividends.
How is D1 calculated?
The formula simply is: Terminal Value = (D1/(r-g)) where: D1 is the dividend expected to be received at the end of Year 1. R is the rate of return expected by the investor and.
What is dividend growth rate?
The dividend growth rate is the annualized percentage rate of growth that a particular stock's dividend undergoes over a period of time. Many mature companies seek to increase the dividends paid to their investors on a regular basis.
What is dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model is based on the idea that a stock is worth the sum of its future payments to shareholders, discounted back to the present day.
What is dividend growth rate?
What is the Dividend Growth Rate? The dividend growth rate (DGR) is the percentage growth rate of a company’s dividend. Dividend A dividend is a share of profits and retained earnings that a company pays out to its shareholders. When a company generates a profit and accumulates retained earnings, those earnings can be either reinvested in ...
What is CAGR in finance?
CAGR is a great measure of growth, as it isolated the effect of compounding on growth, which is sometimes concealed on other metrics for growth. CAGR stands for compound annual growth rate. Capital Gains Yield Capital gains yield (CGY) is the price appreciation on an investment or a security expressed as a percentage.
Is DGR quarterly or monthly?
Frequently, the DGR is calculated on an annual basis. However, if necessary, it can also be calculated on a quarterly or monthly basis. The dividend growth rate is an important metric, particularly in determining a company’s long-term profitability. Since dividends are distributed from the company’s earnings.
What is required rate of return?
The required rate of return (RRR) is the minimum amount of profit (return) an investor will seek or receive for assuming the risk of investing in a stock or another type of security. RRR is also used to calculate how profitable a project might be relative to the cost of funding that project. RRR signals the level of risk that's involved in ...
Why is required rate of return so difficult to determine?
The required rate of return is a difficult metric to pinpoint because individuals who perform the analysis will have different estimates and preferences. The risk-return preferences, inflation expectations, and a firm's capital structure all play a role in determining the required rate.
What does RRR mean in finance?
RRR signals the level of risk that's involved in committing to a given investment or project. The greater the return, the greater the level of risk. A lesser return generally means that there is less risk. RRR is commonly used in corporate finance when valuing investments.
What is the Gordon growth model?
Another approach is the dividend-discount model, also known as the Gordon growth model (GGM). This model determines a stock's intrinsic value based on dividend growth at a constant rate. By finding the current stock price, the dividend payment, and an estimate of the growth rate for dividends, you can rearrange the formula into:
What is weighted average cost of capital?
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the cost of financing new projects based on how a company is structured. If a company is 100% debt financed, then you would use the interest on the issued debt and adjust for taxes, as interest is tax deductible, to determine the cost.
When dealing with corporate decisions to expand or take on new projects, what is the required rate of return?
When dealing with corporate decisions to expand or take on new projects, the required rate of return (RRR) is used as a benchmark of minimum acceptable return, given the cost and returns of other available investment opportunities.
Does RRR factor inflation?
When looking at an RRR, it is important to remember that it does not factor in inflation. Also, keep in mind that the required rate of return can vary among investors depending on their tolerance for risk. 1:29.
What is required rate of return?
The required rate of return (RRR) is the minimum return an investor will accept for owning a company's stock, as compensation for a given level of risk associated with holding the stock. The RRR is also used in corporate finance to analyze the profitability of potential investment projects.
How to calculate RRR?
To calculate RRR using the CAPM: 1 Subtract the risk-free rate of return from the market rate of return. 2 Multiply the above figure by the beta of the security. 3 Add this result to the risk-free rate to determine the required rate of return.
What is RRR in retirement?
The RRR is a subjective minimum rate of return; this means that a retiree will have a lower risk tolerance and therefore accept a smaller return than an investor who recently graduated college and may have a higher appetite for risk. The RRR is also known as the hurdle rate, which like RRR, denotes the appropriate compensation needed for ...
What is dividend discount model?
A popular variation of the dividend discount model is also known as the Gordon Growth Model .
What is the RRR?
The RRR is also known as the hurdle rate, which like RRR, denotes the appropriate compensation needed for the level of risk present. Riskier projects usually have higher hurdle rates, or RRRs, than those that are less risky. 1:29.
Does RRR factor in liquidity?
RRR does not factor in the liquidity of an investment. If an investment can't be sold for a period of time, the security will likely carry a higher risk than one that's more liquid. Also, comparing stocks in different industries can be difficult since the risk or beta will be different.
Does RRR factor inflation?
Limitations of Required Rate of Return (RRR) The RRR calculation does not factor in inflation expectations since rising prices erode investment gains. However, inflation expectations are subjective and can be wrong. Also, the RRR will vary between investors with different risk tolerance levels.
What is preferred equity?
Preferred equity will usually pay the stockholder a fixed dividend, unlike common shares. If you take this payment and find the present value of the perpetuity, you will find the implied value of the stock.
What is supernormal growth?
The purpose of the supernormal growth model is to value a stock that is expected to have higher than normal growth in dividend payments for some period in the future. After this supernormal growth, the dividend is expected to go back to normal with constant growth.
Why is supernormal growth so difficult?
Calculations using the supernormal growth model are difficult because of the assumptions involved, such as the required rate of return, growth or length of higher returns. If this is off it could drastically change the value of the shares. In most cases, such as tests or homework, these numbers will be given. But in the real world, we are left to calculate and estimate each of the metrics and evaluate the current asking price for shares. Supernormal growth is based on a simple idea, but can even give veteran investors trouble.
Can you use a constant growth rate?
Sometimes when you're presented with a growth company, you can't use a constant growth rate. In these cases, you need to know how to calculate value through both the company's early, high growth years, and its later, lower constant growth years. It can mean the difference between getting the right value or losing your shirt .
What is dividend growth rate?
Dividend Growth Rate: The average rate at which the dividend rises each year. Required Rate of Return: The minimum amount of return an investor requires to make it worthwhile to own a stock, also referred to as the “cost of equity”.
How to calculate dividends?
The formulas are relatively simple, but they require some understanding of a few key terms: 1 Stock Price: The price at which the stock is trading 2 Annual Dividend Per Share: The amount of money each shareholder gets for owning a share of the company 3 Dividend Growth Rate: The average rate at which the dividend rises each year 4 Required Rate of Return: The minimum amount of return an investor requires to make it worthwhile to own a stock, also referred to as the “cost of equity”
Why is dividend discount model used?
Generally, the dividend discount model is best used for larger blue-chip stocks because the growth rate of dividends tends to be predictable and consistent. For example, Coca-Cola has paid a dividend every quarter for nearly 100 years and has almost always increased that dividend by a similar amount annually.
Can you use DDM to evaluate stocks?
So if you're going to use DDM to evaluate stocks, keep these limitations in mind. It's a solid way to evaluate blue-chip companies, especially if you're a relatively new investor, but it won't tell you the whole story.
Is the dividend discount model a good fit for some companies?
Limitations of the DDM. The dividend discount model is not a good fit for some companies. For one thing, it’s impossible to use it on any company that does not pay a dividend, so many growth stocks can’t be evaluated this way.
What Is The Required Rate of Return (Rrr)?
What The Required Rate of Return (RRR) Considers
- To calculate the required rate of return, you must look at factors such as the return of the market as a whole, the rate you could get if you took on no risk (risk-free rate of return), and the volatility of a stock (or overall cost of funding a project). The required rate of return is a difficult metric to pinpoint because individuals who perform the analysis will have different estimates and prefere…
Discounting Models
- One important use of the required rate of return is in discounting most types of cash flow models and some relative-value techniques. Discounting different types of cash flow will use slightly different rates with the same intention: to find the net present value(NPV). Common uses of the required rate of return include: 1. Calculating the present value of dividend income for the purpo…
Equity and Debt
- Equity investing uses the required rate of return in various calculations. For example, the dividend discount model uses the RRR to discount the periodic payments and calculate the value of the stock. You may find the required rate of return by using the capital asset pricing model(CAPM). The CAPM requires that you find certain inputs including: 1. The risk-free rate (RFR) 2. The stock'…
Dividend Discount Approach
- Another approach is the dividend-discount model, also known as the Gordon growth model (GGM). This model determines a stock's intrinsic value based on dividend growth at a constant rate. By finding the current stock price, the dividend payment, and an estimate of the growth rate for dividends, you can rearrange the formula into: Stock Value=D1k−gwhere:D1=Expected annua…
Required Rate of Return (RRR) in Corporate Finance
- Investment decisions are not limited to stocks. In corporate finance, whenever a company invests in an expansion or marketing campaign, an analyst can look at the minimum return these expenditures demand relative to the degree of risk the firm expended. If a current project provides a lower return than other potential projects, the project will not go forward. Many factor…
Capital Structure
- Weighted Average Cost of Capital
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the cost of financing new projects based on how a company is structured. If a company is 100% debt financed, then you would use the interest on the issued debt and adjust for taxes, as interest is tax deductible, to determine the cost. In realit… - True Cost of Capital
Finding the true cost of capital requires a calculation based on a number of sources. Some would even argue that, under certain assumptions, the capital structure is irrelevant, as outlined in the Modigliani-Miller theorem. According to this theory, a firm's market value is calculated using its …
The Bottom Line
- When dealing with corporate decisions to expand or take on new projects, the required rate of return (RRR) is used as a benchmark of minimum acceptable return, given the cost and returns of other available investment opportunities. Depending on the factors being evaluated, different models can help arrive at the required rate of return (RRR) for an investment or project.