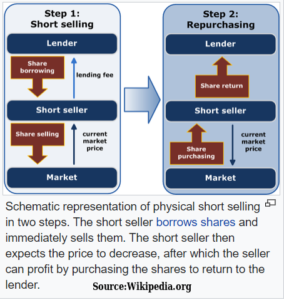
Here's how short selling works:
- A short seller borrows a stock, then sells it immediately on the open market and gets cash in return.
- After some time, the short seller buys the stock back using cash and returns it to the lender.
- If the stock declined in price in the meantime, the cash required to buy back the shares is less than the cash received...
What is short selling strategy?
Short selling is a strategy designed to profit from the price of market-traded security going down, rather than up. Many investors are confused by the concept of short selling, but its essential working is the same as for any stock trade – the trader profits when his selling price is higher than his buying price.
What does selling short do?
Worked example of a profitable short sale
- A short seller borrows from a lender 100 shares of ACME Inc., and immediately sells them for a total of $1,000.
- Subsequently, the price of the shares falls to $8 per share.
- Short seller now buys 100 shares of ACME Inc. ...
How does shorting shares work?
How Does Shorting a Stock Work. Since short-sellers are working with stocks they don’t actually own, they use a broker to acquire them. The broker buys the stocks then lends them to the short-seller, crediting them with the proceeds. The short-seller sells the stock with the intent to buy them back at a lower price.
How to short a stock?
The company’s revenue is forecast to drop by -2.40% over what it did in 2021. A company’s earnings reviews provide a brief indication of a stock’s direction in the short term, where in the case of Banco Santander S.A. No upward and no downward ...

How does short selling a stock work?
Short selling involves borrowing a security and selling it on the open market. You then purchase it later at a lower price, pocketing the difference after repaying the initial loan. For example, let's say a stock is trading at $50 a share. You borrow 100 shares and sell them for $5,000.
What happens when you sell a short?
The investor then sells the stock, retaining the cash proceeds. The short-seller hopes that the price will fall over time, providing an opportunity to buy back the stock at a lower price than the original sale price. Any money left over after buying back the stock is profit to the short-seller.
How does a short seller lose money?
Your total profit would be $250: the $500 profit you made at first, minus the $250 you spend to buy the shares back. But if the stock goes up above the $50 price, you'll lose money. You'll have to pay a higher price to repurchase the shares and return them to the broker's account.
What is short selling example?
Example of Short Selling: An investor believes that Stock A, which is trading at $100 per share, will decline when the company announces its annual earnings in one week. Therefore, the investor borrows 100 shares from a broker while short selling those shares to the market.
Why is short selling good?
Short selling plays an important role in efficient capital markets, conferring positive benefits by facilitating secondary market trading of securities through improved price discovery and liquidity, while also positively impacting corporate governance and, ultimately, the real economy.
What happens if you short a stock and it goes up?
If the stock that you sell short rises in price, the brokerage firm can implement a "margin call," which is a requirement for additional capital to maintain the required minimum investment. If you can't provide additional capital, the broker can close out the position, and you will incur a loss.
Who loses money in a short sale?
The person losing is the one from whom the short seller buys back the stock, provided that person bought the stock at higher price.
How long can you be short on a stock?
There is no mandated limit to how long a short position may be held. Short selling involves having a broker who is willing to loan stock with the understanding that they are going to be sold on the open market and replaced at a later date.
Who pays when a stock is shorted?
Short sellers are wagering that the stock they are short selling will drop in price. If the stock does drop after selling, the short seller buys it back at a lower price and returns it to the lender. The difference between the sell price and the buy price is the short seller's profit.
How do you tell if a stock is being shorted?
For general shorting information about a company's stock, you can usually go to any website with a stock quote service. For more specific short interest info, you would have to go to the stock exchange where the company is listed.
Can you short a stock you own?
A short sell against the box is the act of short selling securities that you already own, but without closing out the existing long position. This results in a neutral position where all gains in a stock are equal to the losses and net to zero.
Can you short on Robinhood?
Shorting stocks on Robinhood is not possible at present, even with a Robinhood Gold membership, the premium subscriptions which allows Robinhood investors to use margin for leveraging returns. Instead, you must either use inverse ETFs or put options.
What does it mean to short sell a stock?
Short selling is the practice of selling borrowed securities – such as stocks – hoping to be able to make a profit by buying them back at a price lower than the selling price. In other words, when you sell short a stock, you’re looking to profit from a decline – rather than an increase – in price. Selling short follows the old stock trading adage ...
What is short selling?
Summary. Short selling is a strategy designed to profit from the price of market-traded security going down, rather than up. Many investors are confused by the concept of short selling, but its essential working is the same as for any stock trade – the trader profits when his selling price is higher than his buying price.
What is stock price?
Stock Price The term stock price refers to the current price that a share of stock is trading for on the market. Every publicly traded company, when its shares are. Trading Securities Trading securities are securities that have been purchased by a company for the purposes of realizing a short-term profit.
How much does it cost to buy back 100 shares of Z?
You received $9,000 for selling short 100 shares of Z. But if Z goes up to $500 a share, buying back 100 shares to pay your broker will cost you $50,000 – $41,000 more than the $9,000 you received when you sold short.
What happens if your buy price is higher than your sell price?
As long as your buy price is below your sell price, you profit to that extent; however, if your buy price is higher than your sell price, you lose money.
How to sell something you don't own?
The way that you can sell something that you don’t own is by borrowing it . When you want to sell short, in order to get the shares to sell, you borrow them from your broker. Margin Trading Margin trading is the act of borrowing funds from a broker with the aim of investing in financial securities.
Why do you need to borrow money from a stock broker?
The purchased stock serves as collateral for the loan. The primary reason behind borrowing money is to gain more capital to invest. – a very simple process with most brokerage firms. The “margin” refers to the security deposit that you put down with your broker as collateral for the borrowed stock shares.
How does shorting stock work?
How Shorting Stock Works. Usually, when you short stock, you are trading shares that you do not own. For example, if you think the price of a stock is overvalued, you may decide to borrow 10 shares of ABC stock from your broker. If you sell them at $50 each, you can pocket $500 in cash.
What happens when you short a stock?
When you short a stock, you expose yourself to a large financial risk. One famous example of losing money due to shorting a stock is the Northern Pacific Corner of 1901. Shares of the Northern Pacific Railroad shot up to $1,000.
What happens if you buy 10 shares of a stock for $250?
If the price of the stock goes down to $25 per share, you can buy the 10 shares again for only $250. Your total profit would be $250: the $500 profit you made at first, minus the $250 you spend to buy the shares back. But if the stock goes up above the $50 price, you'll lose money.
What is the rule for shorting a stock?
Shorting a stock has its own set of rules, which are different from regular stock investing, including a rule designed to restrict short selling from further driving down the price of a stock that has dropped more than 10% in one day , compared to the previous day's closing price. 4.
What is short selling?
Shorting stock, also known as "short selling," involves the sale of stock that the seller does not own or has taken on loan from a broker. 1 Investors who short stock must be willing to take on the risk that their gamble might not work.
Why do you short a stock?
Usually, you would short stock because you believe a stock's price is headed downward. The idea is that if you sell the stock today, you'll be able to buy it back at a lower price in the near future.
What happens if a stock goes up to $50?
But if the stock goes up above the $50 price, you'll lose money. You'll have to pay a higher price to repurchase the shares and return them to the broker's account. For example, if the stock were to go to $250 per share, you'd have to spend $2,500 to buy back the 10 shares you'd owe the brokerage.
How does short selling work?
Here’s how short selling works: A short seller borrows a stock, then sells it immediately on the open market and gets cash in return. After some time, the short seller buys the stock back using cash and returns it to the lender.
What does shorting a stock mean?
The process of shorting a stock is exactly like selling a stock that you already own. If you sell shares that you don’t own, then your sell order initiates a short position, and the position will be shown in your portfolio with a minus in front of it.
What happens when you buy a stock back?
When you buy the stock back, you automatically return it to the lender and close the short position. If you buy the stock back at a lower price than you sold it at, then you pocket the difference and make a profit. The process of shorting a stock is exactly like selling a stock that you already own.
What is put option?
Many traders prefer to bet against stocks using options contracts called put options. The put option gains value as the stock price goes down. Unlike short selling, your maximum loss on a put option is 100%. It will go to zero if the stock doesn’t drop below a certain price by the time the put option expires.
What happens if a stock goes down?
If the stock goes down, the trader makes a profit, but there are several major risks involved. Because of the various risks, short selling can lead to big losses and is considered much riskier than simply buying and holding stocks.
How much did Tesla stock increase in three months?
It increased from about $250 per share to over $900 per share in three months.
What is short selling?
What short selling is and how it works. Buying a stock is also known as taking a long position. A long position becomes profitable as the stock price goes up over time, or when the stock pays a dividend. But short selling is different. It involves betting against a stock and profiting as it declines in price.
What happens when a stock is shorted?
If a stock is actively shorted with a high short float and days to cover ratio, it is also at risk of experiencing a short squeeze. A short squeeze happens when a stock begins to rise, and short-sellers cover their trades by buying their short positions back. This buying can turn into a feedback loop. Demand for the shares attracts more buyers, which pushes the stock higher, causing even more short-sellers to buy back or cover their positions.
What is short selling?
Short selling occurs when an investor borrows a security and sells it on the open market, planning to buy it back later for less money. Short-sellers bet on, and profit from, a drop in a security's price. This can be contrasted with long investors who want the price to go up.
What are the pros and cons of short selling?
Pros and Cons of Short Selling. Selling short can be costly if the seller guesses wrong about the price movement. A trader who has bought stock can only lose 100% of their outlay if the stock moves to zero. However, a trader who has shorted stock can lose much more than 100% of their original investment.
What is shorting margin?
Shorting is known as margin trading . When short selling, you open a margin account, which allows you to borrow money from the brokerage firm using your investment as collateral. Just as when you go long on margin, it's easy for losses to get out of hand because you must meet the minimum maintenance requirement of 25%. If your account slips below this, you'll be subject to a margin call and forced to put in more cash or liquidate your position. 1
How much did GE stock fall in 2019?
By the middle of 2016, GE’s share price had topped out at $33 per share and began to decline. By February 2019, GE had fallen to $10 per share, which would have resulted in a profit of $23 per share to any short sellers lucky enough to short the stock near the top in July 2016. 2.
Why do regulators ban short sales?
Regulators may sometimes impose bans on short sales in a specific sector, or even in the broad market, to avoid panic and unwarranted selling pressure. Such actions can cause a sudden spike in stock prices, forcing the short seller to cover short positions at huge losses.
Why are shares so hard to borrow?
Shares that are difficult to borrow—because of high short interest, limited float, or any other reason—have “ hard-to-borrow ” fees that can be quite substantial. The fee is based on an annualized rate that can range from a small fraction of a percent to more than 100% of the value of the short trade and is pro-rated for the number of days that the short trade is open.
Why is short selling allowed?
However, there are a number of good reasons short selling is allowed, including futures and ETF arbitrage that ensure investors get more accurate prices and more access to liquidity regardless of how they buy equity market exposure.
What is the bid test?
Known as the “bid test,” it requires short sellers to instead offer stock in the market at a price above the current bid and wait for a buyer to pay their higher offer price. The short story on short interest. It’s true that stocks can get to 100% shorted (or more).
Why is fungibility important?
The fungibility of long and loaned stock is important. Any long holding can be lent, and a long holder can recall stock from any borrower, saving them having to track down the specific shares they originally lent. That in turn helps reduce failed trades. It also makes all sellers economically equal.
Why is selling important in the market?
All trades have buyers and sellers, so selling is important to the market. Research overwhelmingly shows that short sellers add to market quality: tightening spreads, adding liquidity, aiding arbitrage and streamlining risk transfer.
What is a mature repo market?
In fact, a mature “repo” market is what helps bond markets function efficiently, even when off-the-run liquidity is low. Then, a short seller will enter the market to short a stock that they consider “richly valued.”. Importantly, their short position isn’t established until they trade with a buyer.
What does it mean when you are 100% shorted?
Being 100% shorted doesn’t mean there are zero net investors in a stock. In fact, it means the opposite. Here is why. Before you short, you must borrow stock. In the past, when you bought a stock, as you handed over your cash, the seller would give you actual share certificates to prove your ownership of the company.
How to establish a short position?
In order to establish a short position, the short seller must first arrange to borrow the stock. That is done so that when the short seller comes to settle their trade, they have stocks to deliver to their buyer (Chart 3). Stock loans aren’t unique to stock markets.
Shorting a Stock: Examples
When you buy a stock — or go long — you can only lose the amount you put in. If the stock costs $10 and you buy 10 shares, you can only lose $100.
Stock Borrowing Costs
Some stocks are hard to borrow for shorting. With hard-to-borrow status comes higher fees. Make sure you factor fees into your risk/reward analysis before you make the trade.
Margin Interest
Even after you pay any initial borrowing costs, you can’t just borrow the stock for free. You have to pay margin interest.
Dividends and Other Payments
This is where your research comes in. You want to control everything you can in the market…
During a Bear Market
When the stock market is headed downward, we often see the bulk of stocks making down price moves. You may find smart trades more easily by looking for short-selling opportunities.
The Intro
A lot of new traders make this mistake, and it’s one that can have a huge impact on your trading portfolio (and career as a whole).
Short selling
So today, I’d like to focus on the most misunderstood yet one of the most important techniques in day trading: Short Selling.
Long VS. Short
In stock market trading, two terms that are used often are long and short.
Shorting Explained
The traditional way of making money in stock markets is to buy low and sell high.
How It Works
Get in touch with your broker to find shares of the stock and ask to borrow the shares. The broker will find you the trader who owns the shares and borrow them. The shares then get allocated to you at a predetermined fee and/or interest.
Risks Involved
As effective as shorting a stock is, there are risks involved in short selling.
The Benefits
Traders who understand the risks and are prepared for the potential losses can yield big wins through short selling.
/the-basics-of-shorting-stock-356327-v2-5bc4c22346e0fb0026b436d3.png)
How Does It Work?
- Many people are at least initially confused by the concept of selling short because it involves selling something you don’t own. Conversations with one trader attempting to explain selling short to another often go something like the following: “It’s just like a regular stock trade, except you sell it first, then buy it to close out your short position. Okay, so you think GE stock is going to go do…
Example – How A Short Trade Plays Out
- When you enter an order to sell short, you are requesting to borrow the necessary stock shares to sell and placing an order to sell the borrowed shares per the order instructions – e.g., at a certain price. For example, you just sold 100 shares of Company Z at the current market priceof $90 per share. Just like any other time when you sell stock, the money from the sale – in this case, $9,00…
Main Points
- Selling short is simply the opposite of buying “long.” It’s just another stock trade – the only truly significant difference is which direction you expect the stock price to move in. If you expect the stock to go up, then you buy long, hoping to profit from a price increase. Conversely, if you expect the stock to go down, then you sell short, hopin...
High Potential Risk
- There is one difference between buying long and selling short that makes short selling a much riskier practice – the level of risk that is inherently involved when selling short. When you buy a stock, your total maximum risk is limited to its price. If Z stock is selling for $90 a share, you cannot lose any more than $90 a share on your investment – the absolute worst-case scenario i…
Advantages
- The first advantage is leverage. Since you can sell short with margin trading, only putting up a percentage of the total value of the stock you’re trading, you can make more money with a smaller investment. Also, incorporating short-selling into your investment strategies doubles your profit opportunities, as you can make money not only from stock price increases but also from stock p…
Disadvantages
- Historically, over time, stock prices tend to move higher – short trading is always trading contrary to the overall trend of the stock market as a whole. When it comes to trading costs, in addition to the interest charges on short selling, traders may also need to pay a “hard to borrow” fee when the stock shares in question are, in fact, hard for the broker to acquire for lending purposes.
More Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Short Selling. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: 1. Stock Price 2. Trading Securities 3. The Winning Mindset of a Trader 4. Position Trader