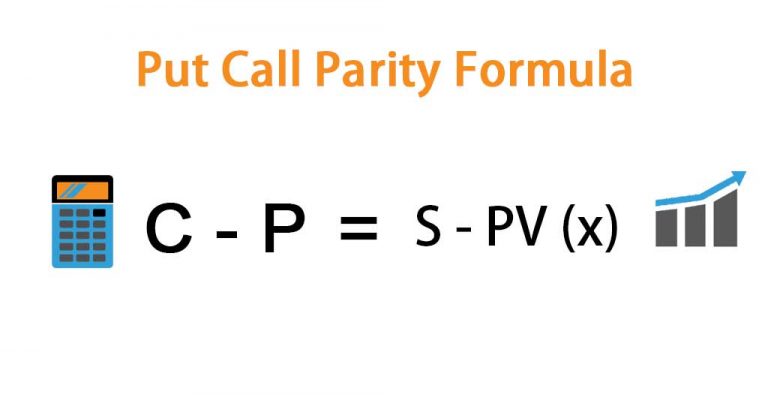Stock Option Parity means that the stock option is trading at its intrinsic value. If a $100 call option were trading at $10 and the stock were at $110, the stock option would be trading at parity. Options trade at parity when they are very deep in the money. A $50 call on a $100 stock could easily be trading at parity.
What is put call parity in options?
Put-Call Parity. Loading the player... Put-call parity is a principle that defines the relationship between the price of European put options and European call options of the same class, that is, with the same underlying asset, strike price and expiration date.
What is a parity price for stock options?
Parity price can help determine the value of stock options, as parity is defined as the price at which an option is trading at its intrinsic value. The concept of parity is also used to compare the value of two currencies.
What are parity prices used for?
Depending on the type of asset that it is used to price, parity prices can be used in a variety of different contexts. Parity is the price at which it becomes profitable for investors to convert their convertible bonds into shares of common stock. Parity can also be used to compare the value of two currencies.
What is the put-call parity equation?
As mentioned above, the put-call parity equation can be written a number of different ways and rearranged to make varying inferences. A couple of common ways it is expressed are as follows: St + pt = ct + X/(1 + r)^T

What does it mean when an option is at parity?
Options parity happens when a stock is trading at its intrinsic value with no extrinsic value (or time value) in the option. Parity will generally happen very close to expiration as theta erodes OTM option pricing or with very deep ITM options that are far from the current underlying price.
How do you do call parity?
The formula for put call parity is c + k = f +p, meaning the call price plus the strike price of both options is equal to the futures price plus the put price.
What is meant by put-call parity?
What is Put-Call Parity? Put-call parity is an important concept in options pricing which shows how the prices of puts, calls, and the underlying asset must be consistent with one another. This equation establishes a relationship between the price of a call and put option which have the same underlying asset.
Under what circumstances does the price of the call equal the price of the put?
Considering F as the forward price. If F=R, then the forward contract created has a value of zero. Since the forward contract is equal to a short put and a long call, it shows that the price of a put would be equivalent to the call's price when the strike price is F.
When puts are more expensive than calls?
Key Takeaways Puts (options to sell at a set price) generally command higher prices than calls (options to buy at a set price). One driver of the difference in price results from volatility skew, the difference between implied volatility for out-of-the-money, in-the-money, and at-the-money options.
What is call price?
The call price (also known as "redemption price") is the price at which the issuer of a callable security has the right to buy back that security from an investor or creditor. Call prices are commonly found in callable bonds or callable preferred stock.
Is implied volatility same for put and call?
Understanding Options: Why Do Calls and Puts Have Different Implied Volatility? Calls and puts should have the same implied volatility. The implied volatility should describe that portion of the options price attributable to the movement in the stock, ie the implied volatility.
What is put and call options with example?
Risk vs Reward – Call Option and Put OptionCall BuyerPut SellerMaximum ProfitUnlimitedPremium receivedMaximum LossPremium PaidStrike price – premiumNo Profit – No lossStrike price + premiumStrike price – premiumIdeal ActionExerciseExpireJun 9, 2021
What is meant by call option?
A call option is a contract between a buyer and a seller to purchase a certain stock at a certain price up until a defined expiration date. The buyer of a call has the right, not the obligation, to exercise the call and purchase the stocks.
Can a call option be worth more than the stock price?
When the stock price is above the strike price, a call is considered in-the-money (ITM). The situation is reversed when the strike price exceeds the stock price — a call is then considered out-of-the-money (OTM). An at-the-money option (ATM) is one whose strike price equals (or nearly equals) the stock price.
What assumption is the put-call parity based on?
Assumptions of Put-Call Parity The put-call parity principle works on the following assumptions. The interest rate does not change with time, and it is constant. The dividends to be received from the underlying stock are known and certain. The underlying stock is liquid, and there are no transfer barriers.
Why does put-call parity not hold for American options?
Since American style options allow early exercise, put-call parity will not hold for American options unless they are held to expiration. Early exercise will result in a departure in the present values of the two portfolios.
What are arbitragers?
What Is an Arbitrageur? An arbitrageur is a type of investor who attempts to profit from market inefficiencies. These inefficiencies can relate to any aspect of the markets, whether it is price, dividends, or regulation. The most common form of arbitrage is price.
Why does put-call parity not hold for American options?
Since American style options allow early exercise, put-call parity will not hold for American options unless they are held to expiration. Early exercise will result in a departure in the present values of the two portfolios.
How do you do nifty arbitrage?
For Nifty Spot Price at 10550, the 10400 Call Option is ITM and 10700 Call is OTM. Arbitrage strategy is a way to earn small profits with very little or zero risk....Box Spread (Arbitrage) Options Strategy.Strategy LevelAdvanceMarket ViewNeutralRisk ProfileNoneReward ProfileLimitedBreakeven Point2 more rows•Apr 19, 2018
What is put call parity?
Put-call parity allows you to calculate the approximate value of a put or a call relative to its other components. If the put-call parity is violated, meaning that the prices of the put and call options diverge so that this relationship does not hold, an arbitrage opportunity exists.
What is the price of an option?
An option's price is the sum of its intrinsic value, which is the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the option's strike price, and time value, which is directly related to the time left until that option's expiry.
What is a fiduciary call?
A fiduciary call is a long call combined with cash equal to the present value (adjusted for the discount rate) of the strike price; this ensures that the investor has enough cash to exercise the option on the expiration date.
Do European call options have put parity?
They are not, however, and the prices of European put and call options are ultimately governed by put-call parity. In a theoretical, perfectly efficient market, the prices for European put and call options would be governed by the equation:
Can you sell the more expensive side of the equation?
You can "sell" the more expensive side of the equation and buy the cheaper side to make, for all intents and purposes, a risk-free profit. In practice, this means selling a put, shorting the stock, buying a call, and buying the risk-free asset ( TIPS, for example).
What is put call parity?
Put-Call parity establishes the relationship between the prices of Europen put options and calls options having the same strike prices, expiry, and underlying. Put-Call Parity does not hold true for the American option as an American option can be exercised at any time prior to its expiry.
What is an option in the money?
In The Money The term "in the money" refers to an option that, if exercised, will result in a profit. It varies depending on whether the option is a call or a put. A call option is "in the money" when the strike price of the underlying asset is less than the market price.
Who first identified the three-sided relationship between a call, a put, and underlying security?
It also shows the three-sided relationship between a call, a put, and underlying security. The theory was first identified by Hans Stoll in 1969. You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link.
What is put call parity?
Put-call parity is an important concept in options. Options: Calls and Puts An option is a form of derivative contract which gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset by a certain date (expiration date) at a specified price (strike price). There are two types of options: calls and puts.
Why is parity important in put and call?
The put-call parity theory is important to understand because this relationship must hold in theory. With European put and calls, if this relationship does not hold, then that leaves an opportunity for arbitrage. Arbitrage Arbitrage is the strategy of taking advantage of price differences in different markets for the same asset.
What is strike price in put options?
Strike Price The strike price is the price at which the holder of the option can exercise the option to buy or sell an underlying security, depending on. price.
What is call option?
Call Option A call option, commonly referred to as a "call," is a form of a derivatives contract that gives the call option buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock or other financial instrument at a specific price - the strike price of the option - within a specified time frame.
What are the two types of positions an investor can take?
In the trading of assets, an investor can take two types of positions: long and short. An investor can either buy an asset (going long), or sell it (going short). call option and a short.
Can you exercise a put option at any time?
US options can be exercised at any time. Put Option A put option is an option contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying security at a specified price (also known as strike price) before or at a predetermined expiration date.
Arbitrage
Let us begin by defining arbitrage and how arbitrage opportunities serve the markets. Arbitrage is, generally speaking, the opportunity to profit arising from price variances on one security in different markets.
Defining Derivatives
Options are derivatives; they derive their value from other factors. In the case of stock options, the value is derived from the underlying stock, interest rates, dividends, anticipated volatility and time to expiration. There are certain factors that must hold true for options under the no arbitrage principle.
Synthetic Relationships
With stock and options, there are six possible positions from three securities when dividends and interest rates are equal to zero – stock, calls and puts:
Impact of Dividends & Interest Rates
The next logical question is how ordinary dividends and interest rates impact the put call relationship and option prices. Interest is a cost to an investor who borrows funds to purchase stock and a benefit to investors who receive and invests funds from shorting stock (typically only large institutions receive interest on short credit balances).
What is put call parity?
What Is Put-Call Parity? In an efficient market, a portfolio that holds both a long call option and a short put option for the same asset, strike price and expiration date should generate the same return as a portfolio that holds an equivalent long position futures contract. This is called “put-call parity.”.
What is a short call position?
A short call position means you sold a call contract and must acquire and sell an asset at a set price if the buyer of the contract exercises their option. A short put position means you sold a put contract and must buy an asset for a given price if the buyer of the contract exercises their option.
Is option trading for every investor?
Options trading is not for every individual investor. It requires much more attention and knowledge than ordinary stock and bond investing. But for some individual investors, as well as accredited investorsand institutional investors, who want to trade options, put-call parity is a key concept. It describes a functional equivalence between ...