In some states, when a corporation is formed, the articles of incorporation must set a "par value" for its stock. Everyone who buys shares in the corporation, including the corporation's founders, must pay at least this amount. If they pay less, they'll owe the corporation the difference.
How do you change the par value of a corporation?
Instead, the most common way that corporations change their par value is with a stock split (or reverse stock split). A stock split is exactly what it sounds like: a division of shares. For instance, imagine your corporation has 25,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $1 each.
What is par value of a stock?
Also known as “face value” or “nominal value,” par value is the initial value you assign to your shares. It’s not, however, the sales price. If you have a par value of $0.01 per share, you can still sell those shares for $100 a pop if you want.
Can a company sell shares below the par value of shares?
Some states require that companies cannot sell shares below the par value of these shares. To comply with state regulations, most companies set a par value for their stocks to a minimal amount. For example, the par value for shares of Apple, Inc. is $0.00001 and the par value for Amazon stock is $0.01.
What is the par value of a startup company?
In the US, par value was created during the time of the great depression in order to ensure a shares could not be sold under a certain price. Today, that concept is somewhat archaic, but it still plays an important role and should be thoughtfully considered when forming a startup company by filing the certificate of incorporation.

What is par value of stock of a startup?
“Par value” or “face value” is the lowest price for which a company can sell stock. “Fair Market Value” is the notional value of stock on the market at the time of sale. A reasonable par value for an early stage company can be as low as $0.00001.
What is par value in corporation?
Par value is the value of a single common share as set by a corporation's charter. It is not typically related to the actual value of the shares. In fact it is often lower. Any stock certificate issued for shares purchased shows the par value. When authorizing shares, a company can choose to assign a par value or not.
What is the purpose of having par value for stock?
Par value is the stock price stated in a corporation's charter. The intent behind the par value concept was that prospective investors could be assured that an issuing company would not issue shares at a price below the par value.
Can companies have par value shares?
Par value is a standard nominal value (for example R1) of which a share will be issued. No par value means that there is no standard value attached to the shares. The current Companies Act only make provision for companies to be registered with no par value shares.
What is the par value of an LLC?
As opposed to corporations, LLCs and other entities do not establish a par value, which is a defined term unique to corporations. However, LLCs and other entities must still establish the price at which the company's founders and other equity holders purchase their equity in the company.
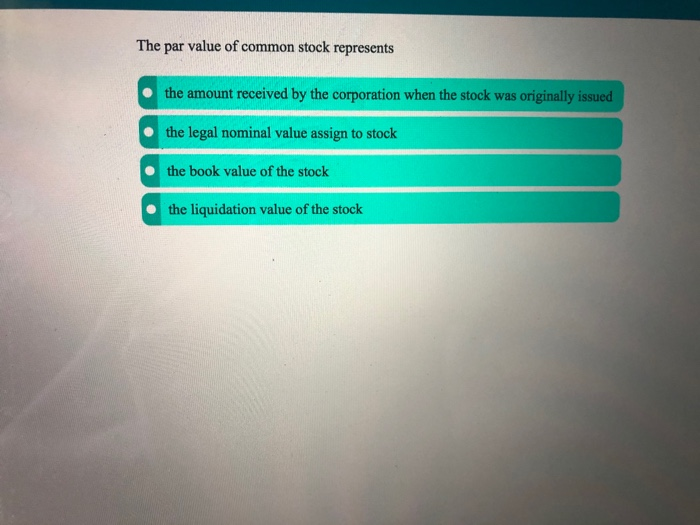
Which best describes par value for stock?
The par value of a stock represents the market value of the stock on the date it is first issued.
What is meant by par value and what is its significance to stockholders?
Par value can be thought of as being the stock share's nominal price. Often, it is the price at which a corporation's initial shares are sold to the public and it is a promise of ensured value in that the corporation will not issue additional shares at a price lower than that.
What amount is a shareholder required to pay for no par shares in a corporation?
No-par value shares have a minimum stated value of P5. 00 per share. Membership in a nonstock corporation and all rights arising therefrom are personal and transferable unless the articles of incorporation or the by laws otherwise provide.
Can you change par value of stock?
Laws vary state to state, but generally speaking, any change to par value typically involves an amendment to your corporate charter (your Articles of Incorporation, or whatever the formation document is called in your state). The easiest change to make is probably switching from “no par value” to par value shares.
How many shares does a company start with?
Typically a startup company has 10,000,000 authorized shares of Common Stock, but as the company grows, it may increase the total number of shares as it issues shares to investors and employees. The number also changes often, which makes it hard to get an exact count.
Why do companies issue no par value shares?
No-Par Value Stock You might be asking yourself why a company would issue shares with no par value. Corporations do this because it helps them avoid liability to stockholders should the stock price take a turn for the worse.
Who determines par value of stock?
Establishing Par Value of Corporate Stock It is up to the incorporators to decide what the par value of the corporate stock will be. Typically, large companies establish a par value of one cent or a fraction of one cent per share.
What is the par value of a company?
Typically, large companies establish a par value of one cent or a fraction of one cent per share. This way they can issue many shares without the founders or other initial purchasers being legally required to pay huge amounts of money for them. For example, the par value for shares of Apple, Inc.
What does "par value" mean in a corporation?
In some states, when a corporation is formed, the articles of incorporation must set a "par value" for its stock.
What happens when a stock has a par value?
When shares have a par value, the amount shareholders pay for them in excess of par is accounted for as paid-in capital on the corporation's balance sheet. For example, if a shareholder pays $5 for 1000 shares with a par value of $1, $4,000 would be credited to the corporation's paid-in capital account and $1,000 to the common stock account.
What is par value?
"Par value," also called face value or nominal value, is the lowest legal price for which a corporation may sell its shares.
Why is par value misleading?
The term par value can be misleading because it has nothing to do with how much a corporation's shares are actually worth. It is only a minimum legal value. A corporation's board of directors may require investors to pay far more than par value for the corporations' shares.
How much do you have to pay for 10,000 shares?
If you purchase 10,000 shares, you'll have to pay at least $10,000 for them. If you pay only $5,000, you'll owe your corporation another $5,000. If your corporation later goes out of business, its creditors can sue to force you to pay that remaining $5,000 to your now defunct corporation to help pay off its debts.
Is the purchase price of no par shares credited to the common stock account?
For accounting purposes, the entire purchase price for no par shares is credited to the common stock account, unless the company decides to allocate a portion to surplus.
What is par value?
Par value, also called "face value" or "nominal value," is the lowest legal price for which a corporation may sell its shares, and is typically set between a fraction of a cent (the lower range is known as a low par value) and a few dollars.
When do founders use par value?
Founders typically use the par value as a price when purchasing their founders shares shortly after incorporating the company. In the typical compensation package for a startup, later shares issued to advisors and employees are generally offered to employees at what is known as fair market value (FMV).
What is the process of determining the fair market value of a company's common stock?
These appraisal firms independently research and determine a fair market value price for the company’s common stock in a process called a 409a valuation.
Why is par value confusing?
The term par value can be confusing because it has nothing to do with the price investors pay to own shares in the company. For example, you can establish a par value of $0.0001 per share but sell shares to investors for $10 per share.
Why is it important for a startup to issue and purchase its shares?
Because a startup’s shares can quickly increase in value as the company develops its product and increases capitalization through customer revenue or raising funds from investors, it is important for founders to issue and purchase their shares at the time of the company’s formation, At that time the fair market value of the shares—and ...
What is fair market value?
“Fair Market Value” is the notional value of stock on the market at the time of sale.
Is it legal to issue no par value stock?
While it is legal in some states including Delaware to issue no par value shares at a company’s outset, it is not often done. While it might seem like a good idea to issue no par value stock to avoid tax liability and issues surrounding taxation and early valuation, issuing stock at no par value means the corporation will be unable to use the Alternative Method, potentially incurring increased tax liability at the end of the year.
What is par value in stock?
Par value for a share refers to the stock value stated in the corporate charter. Shares usually have no par value or very low par value, such as one cent per share. In the case of equity, the par value has very little relation to the shares' market price. 1:46.
Why is par value important?
Par value is important for a bond or fixed- income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. The market price of a bond may be above or below par, depending on factors such as the level of interest rates and the bond’s credit status. Par value for a bond is typically $1,000 or $100 ...
What happens to a bond when the coupon rate is equal to the interest rate?
If coupon rate equals the interest rate then the bond will trade at its par value. However, if interest rates rise then the price of a lower-coupon bond must decline to offer the same yield to investors, causing it to trade below its par value.
What happens to a 4% coupon bond?
If a 4% coupon bond is issued when interest rates are 4%, the bond will trade at its par value since both interest and coupon rates are the same. However, if interest rates rise to 5%, the value of the bond will drop, causing it to trade below its par value.
What is the coupon rate of a bond?
The coupon rate is the interest payments that are made to bondholders, annually or semi-annually, as compensation for loaning the issuer a given amount of money.
Where to find no par stock certificates?
The par value of a company's stock can be found in the Shareholders' Equity section of the balance sheet .
Is a bond with a face value of $1,000 taxable?
For example, a bond with a face value of $1,000 that is currently trading at $1,020 will be said to be trading at a premium, while another bond trading at $950 is considered a discount bond. If an investor buys a taxable bond for a price above par, the premium can be amortized over the remaining life of the bond, ...
How do corporations change their par value?
Instead, the most common way that corporations change their par value is with a stock split (or reverse stock split). A stock split is exactly what it sounds like: a division of shares. For instance, imagine your corporation has 25,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $1 each. If you did a 2:1 stock split, ...
What is par value change?
Laws vary state to state, but generally speaking, any change to par value typically involves an amendment to your corporate charter (your Articles of Incorporation, or whatever the formation document is called in your state).
How much tax do you pay if you have no par value?
However, if you have millions of “no par value” shares, you’ll end up paying tens of thousands of dollars in franchise taxes. On the other hand, if you have millions of shares with very low par value, you can use the other calculation method and potentially pay as little as $400 (the minimum tax for the second method).
What happens if you don't list your shares in your incorporation?
In other states, if you don’t list par value for your shares on your incorporation docs, your filing will be rejected. Sometimes the state will just go ahead and assign you a value if you don’t list one. Rhode Island, for instance, will assign a value of $0.01 per share. In a handful of states, your filing fee to start your corporation will vary ...
Why is par value important?
Traditionally, par value has been important because of the way it figures into your corporation’s legal capital. Your legal capital is the amount of equity that has to stay in the business. Typically, your legal capital is the total par value of your corporation’s common stock (plus the total stated value of any preferred stock).
What happens if you don't have par value?
If your shares don’t have par value, you’re stuck using the first method. This isn’t a big deal if you only have a few shares. For instance, if you have fewer than 5,000 shares, you’ll pay a total of $225.
What states do not require par value?
How does par value differ state to state? Rules are all over the place when it comes to par value. In some states, like Alabama, Ohio, Delaware, and New York, you’re not required to have par value at all—shares can be categorized as “no par value” shares.
What is par value?
Put simply, par value is a minimum price that the issuing corporation can issue its corporate shares at. The idea is to set a price floor below which additional stock cannot be issued (potentially screwing existing shareholders).
Is par value the same as market value?
Again, Par Value is Not Market Value. It bears (re)mentioning that par value is not the same as market value or the actual worth of the company, which is usually set by either the private or (if your company is successful enough to attract the right attention) a public market.
Is par value required for a corporation?
Although the corporations acts or laws of several states have done away with the requirement for par value altogether, par still can play an important role in, and merits careful consideration as part of, forming your startup as a corporation in a jurisdiction where par is necessary.
What is par value in common stock?
With common stocks, the par value simply represents a legally binding agreement that the company will not sell shares below a certain price, such as $0.01.
Why do stocks have par value?
Par value remains fixed for the life of a security, unlike market value, which fluctuates regularly. Because it influences interest and dividend payments, it ’s a key factor for understanding your return on investment in bonds and preferred stock.
What is preferred stock par value?
Par Value for Preferred Stock. It’s helpful to think of preferred stock as a hybrid of bonds and common stock. Preferred stock represents equity in a company—a portion of ownership, like common stock. In addition, though, you are entitled to fixed dividend payments, like a bond’s fixed interest payments.
What is par value in bonds?
Par Value for Bonds. When you buy bonds, you’re lending money for a set amount of time to an issuer, like a government, municipality or corporation. The issuer promises to repay your initial investment—known as the principal—once the term is over, as well as pay you a set rate of interest over the life of the bond.
Is par value the price you pay for a security?
Even though par value may not be the price you pay for a security, it’s still important to be aware of as it may impact the amount of interest or dividend payments you receive.
Is the principal the same as the par value?
The principal in a bond investment may or may not be the same as the par value. Some bonds are sold at a discount, for instance, and pay back their par value at maturity. In any case, the fixed par value is used to calculate the bond’s fixed interest rate, which is referred to as its coupon. A bond’s market value, meanwhile, is ...
Does common stock pay dividends?
In addition, common stock’s par value has no relationship to its dividend payment rate. Instead, common stock dividends are generally paid as a certain dollar value per share you own. Many people will then divide this value by the cost of a share to create its dividend yield.
