
The P/E ratio helps investors determine the market value of a stock as compared to the company's earnings. In short, the P/E ratio shows what the market is willing to pay today for a stock based on its past or future earnings. A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
Full Answer
How do you calculate a stock's P/E ratio?
The equation looks like this: Let's say a company is reporting basic or diluted earnings per share of $2, and the stock is selling for $20 per share. In that case, the P/E ratio is 10 ($20 per share ÷ $2 earnings per share = 10 P/E). This information is useful because, if you invert the P/E ratio, you can find out a stock's earnings yield.
What does a high price-earnings (P/E) ratio mean?
The price-earnings (P/E) ratio relates a company's share price to its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio could mean that a company's stock is over-valued, or else that investors are expecting...
What is P/E ratio and why investors care?
The P/E Ratio - What It Is and Why Investors Care. Before you can take advantage of the p/e ratio in your own investing activities, you need to understand what it is. Simply put, the p/e ratio is the price an investor is paying for $1 of a company's earnings or profit.
Does P-E ratio predict a stock's price target at breakout?
But when a stock has gotten off to a great start, its P-E ratio at the breakout can be quite helpful in projecting a potential price target in which investors can actively look for potential sell signals to trigger. Here's how it works.
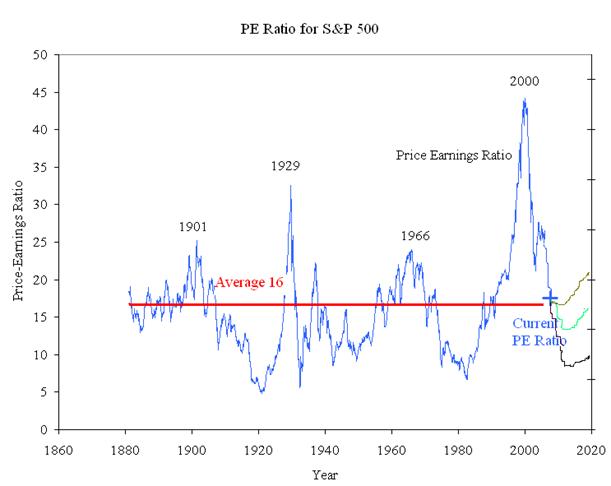
What is a good PE ratio for a stock?
So, what is a good PE ratio for a stock? A “good” P/E ratio isn't necessarily a high ratio or a low ratio on its own. The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better.
What is a good PE ratio 2021?
Compare BEST With Other StocksBEST PE Ratio Historical DataDateStock PriceTTM Net EPS2021-12-314.26$0.602021-09-308.35$-4.652021-06-308.90$-4.5513 more rows
How does PE ratio affect stock price?
The P/E ratio helps investors determine the market value of a stock as compared to the company's earnings. In short, the P/E shows what the market is willing to pay today for a stock based on its past or future earnings. A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
Is it good to buy high PE ratio stocks?
The popular opinion about stocks with high P/E ratios is that they are excellent investment options since investors are willing to pay more for a smaller share in the company's earnings. Hence, they presume this to be an indicator of an optimistic investor perception towards the stock.
Should I buy low PE stocks?
Many investors will say that it is better to buy shares in companies with a lower P/E because this means you are paying less for every dollar of earnings that you receive. In that sense, a lower P/E is like a lower price tag, making it attractive to investors looking for a bargain.
What PE ratio is too high?
Investors tend to prefer using forward P/E, though the current PE is high, too, right now at about 23 times earnings. There's no specific number that indicates expensiveness, but, typically, stocks with P/E ratios of below 15 are considered cheap, while stocks above about 18 are thought of as expensive.
Is a negative PE ratio good?
A high P/E typically means a stock's price is high relative to earnings. A low P/E indicates a stock's price is low compared to earnings and the company may be losing money. A consistently negative P/E ratio run the risk of bankruptcy.
Is 30 a good PE ratio?
P/E 30 Ratio Explained A P/E of 30 is high by historical stock market standards. This type of valuation is usually placed on only the fastest-growing companies by investors in the company's early stages of growth. Once a company becomes more mature, it will grow more slowly and the P/E tends to decline.
When should I buy stock PE ratio?
The justified P/E ratio is calculated independently of the standard P/E. In other words, the two ratios should produce two different results. If the P/E is lower than the justified P/E ratio, then it means that the company is undervalued and purchasing that stock may result in profits over some time.
Should I buy high or low PE ratio?
P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, is a quick way to see if a stock is undervalued or overvalued. And so generally speaking, the lower the P/E ratio is, the better it is for both the business and potential investors.
Is a PE ratio of 28 good?
Digging a Little Deeper Play Now's P/E ratio of 28 means that investors are willing to pay $28 for each $1 of earnings that the company generates. Taking this a step further, some investors interpret a “high P/E” as an overpriced stock.
Is 30 a good PE ratio?
P/E 30 Ratio Explained A P/E of 30 is high by historical stock market standards. This type of valuation is usually placed on only the fastest-growing companies by investors in the company's early stages of growth. Once a company becomes more mature, it will grow more slowly and the P/E tends to decline.
Is a high or low PE ratio better?
P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, is a quick way to see if a stock is undervalued or overvalued. And so generally speaking, the lower the P/E ratio is, the better it is for both the business and potential investors. The metric is the stock price of a company divided by its earnings per share.
Who used the P/E ratio?
The P/E ratio was used by the late Benjamin Graham. Not only was he Warren Buffett's mentor, but he is also credited with coming up with " value investing ." 1
Why do you look at your portfolio through the P/E lens?
But looking at your portfolio through the P/E lens can help you avoid getting swept away in bubbles or panics. It can also help you know whether a stock is getting overvalued and no longer earning enough to warrant its price. Warning. You should never rely on P/E ratios alone when you choose investments.
Why do investors prefer PEG?
Some investors may prefer the price-to-earnings growth ( PEG) ratio instead, because it factors in the earnings growth rate. 7 Other investors may prefer the dividend-adjusted PEG ratio because it uses the basic P/E ratio. It also adjusts for both the growth rate and the dividend yield of the stock. 8.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio or P/E is one of the most widely-used stock analysis tools used by investors and analysts for determining stock valuation. In addition to showing whether a company's stock price is overvalued or undervalued, the P/E can reveal how a stock's valuation compares to its industry group or a benchmark like the S&P 500 Index.
What are the two types of P/E ratios?
These two types of EPS metrics factor into the most common types of P/E ratios: the forward P/E and the trailing P/E. A third and less common variation uses the sum of the last two actual quarters and the estimates of the next two quarters.
What is the inverse of the P/E ratio?
The inverse of the P/E ratio is the earnings yield (which can be thought of like the E/P ratio). The earnings yield is thus defined as EPS divided by the stock price, expressed as a percentage.
What does a high P/E mean?
A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
What is an individual company's P/E ratio?
An individual company’s P/E ratio is much more meaningful when taken alongside P/E ratios of other companies within the same sector. For example, an energy company may have a high P/E ratio, but this may reflect a trend within the sector rather than one merely within the individual company. An individual company’s high P/E ratio, for example, would be less cause for concern when the entire sector has high P/E ratios.
Why is it better to buy shares with a lower P/E?
Many investors will say that it is better to buy shares in companies with a lower P/E, because this means you are paying less for every dollar of earnings that you receive. In that sense, a lower P/E is like a lower price tag, making it attractive to investors looking for a bargain.
What does N/A mean in P/E?
A company can have a P/E ratio of N/A if it's newly listed on the stock exchange and has not yet reported earnings, such as in the case of an initial public offering (IPO), but it also means a company has zero or negative earnings, Investors can thus interpret seeing "N/A" as a company reporting a net loss.
Key Takeaways
You can find a past P/E ratio by dividing the current price of a stock by last year's earnings. Keep in mind that this year's earning's may be very different.
2. Earnings Forecast
This calculation takes the current price of the stock or group of stocks. Then, it's divided by an average of all of the predicted earnings put forth by analysts and the companies themselves.
3. Ten-Year Average
This calculation is most often used to look at the value of an entire market instead of an individual stock. It takes the current price of the market; then, it's divided by corporate earnings as averaged over the past 10 years. This ratio is called P/E 10.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price to earnings ratio (P/E) is one of the most widely used financial measurements when it comes to stock selection.
What does higher PE ratio mean?
A higher PE ratio means that investors are paying more for each unit of net income, making it more expensive to purchase than a stock with a lower P/E ratio. Value investors often search for stocks with relatively low P/E ratios as a means for identifying cheaper stocks that the market has largely passed over.
What is the price to earnings ratio?
Price to earnings ratio is a key financial metric for evaluating whether a stock is fairly valued. The fact that it standardizes stocks of different prices and earnings levels, call for its usage in combination with other metrics to ascertain the actual value of a stock prior to investing.
Why is a low P/E ratio good?
A low P/E ratio is usually good as it allows investors to pay less for every dollar on earnings.
Why are P/E companies so high?
Companies with higher P/E are expected to have higher earnings in the future , and they are usually expected to issue higher dividends. That is why investors are willing to pay a hefty amount for the earnings on offer, and why the price is so high.
What does it mean when a company's P/E is higher than the industry average?
If a company’s P/E is slightly higher than the industry average, then it means that the market expects the company to continue outperforming the industry going forward. A company with a higher P/E will only be justified if it outperforms the market in key parameters such as future sales and EPS growth.
What does a negative P/E mean?
A company that is losing money would have a negative P/E, but because a low P/E is a good sign and an even slightly negative P/E could mean that the company is losing a lot of money, negative P/E values are usually listed as N/A (not available) to avoid confusion.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is one of the most common ratios used by investors to determine if a company's stock price is valued properly relative to its earnings. The P/E ratio is popular and easy to calculate, but it has shortcomings that investors should consider when using it to determine a stock's valuation.
What is P/E in economics?
Remember that the P/E is a measure of expected earnings. As economies mature, inflation tends to rise. As a result, the Federal Reserve increases interest rates to slow the economy and tame inflation to prevent a rapid rise in prices. Certain industries do well in this environment.
Why is the PEG ratio important?
Since the P/E ratio does not factor in future earnings growth, the PEG ratio provides more insight into a stock's valuation. By providing a forward-looking perspective, the PEG is a valuable tool for investors in calculating a stock's future prospects.
How to tell if a stock is overvalued or undervalued?
As stated earlier, to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued, it should be compared to other stock in its sector or industry group. Sectors are made up of industry groups, and industry groups are made up of stocks with similar businesses such as banking or financial services.
Why do investors use P/E?
Investors not only use the P/E ratio to determine a stock's market value but also in determining future earnings growth. For example, if earnings are expected to rise, investors might expect the company to increase its dividends as a result. Higher earnings and rising dividends typically lead to a higher stock price.
What does a high P/E mean?
A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
What is the first part of the P/E equation?
The first part of the P/E equation or price is straightforward as the current market price of the stock is easily obtained. On the other hand, determining an appropriate earnings number can be more difficult. Investors must determine how to define earnings and the factors that impact earnings. As a result, there are some limitations to the P/E ratio as certain factors can impact the P/E of a company. Those limitations include:
Why use P/E ratio?
The most common use of the P/E ratio is to gauge the valuation of a stock or index. The higher the ratio, the more expensive a stock is relative to its earnings. The lower the ratio, the less expensive the stock. In this way, stocks and equity mutual funds can be classified as “growth” or “value” investments.
What is the Shiller P/E ratio?
A third approach is to use average earnings over a period of time. The most well known example of this approach is the Shiller P/E ratio, also known as the CAP/E ratio (cyclically adjusted price earnings ratio).
Is Shiller PE a good predictor of future returns?
A recent study found that the Shiller PE was a reliable predictor of market returns between 1995 and 2020. In contrast, a recent Vanguard study found that the Shiller PE and other P/E ratio measures “had little or no correlation with future stock returns.”.
