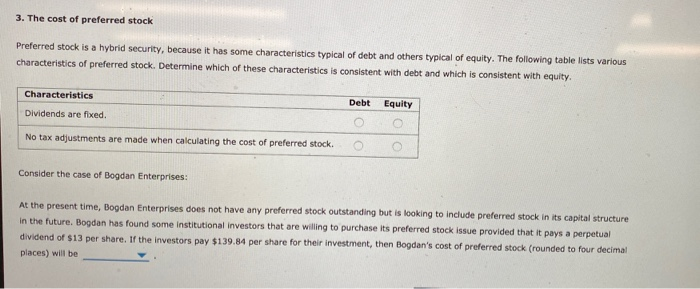
No tax adjustments are made when calculating the component of cost of preferred stock because, unlike interest payments on debt, dividend payments on preferred stock are not tax deductible. the cost to the firm of equity obtained by selling new common stock. These costs are called flotation costs.
What is the dividend on an 8 percent preferred stock?
Dec 07, 2021 · No tax adjustments are made when calculating the component of cost of preferred stock because, unlike interest payments on debt, dividend payments on preferred stock are not tax deductible. the cost to the firm of equity obtained by selling new common stock. These costs are called flotation costs.
What should be used to calculate the weighted average cost of capital?
Is a tax adjustment made to the cost of preferred stock? No tax adjustments are made when calculating Rp because preferred dividends, unlike interest on debt, are not tax deductible, so no tax savings are associated with preferred stock
What is the dividend of a firm's common stock price?
Is a tax adjustment made to the cost of preferred stock? No, because preferred dividends are not tax deductible; so no tax savings are associated with preferred stock 2 …
Why do we use after-tax cost of debt in calculating WACC?
A tax adjustment must be made in determining the cost of _____. long-term debt ... When discussing weighing schemes for calculating the weighted average cost of capital, _____. ... The cost of preferred stock is the ratio of the preferred stock dividend to a firm's net proceeds from the sale of the preferred stock.

Is tax adjustment made to the cost of preferred stock?
Preferred stock dividends are not tax deductible to the company who issues them. Preferred stock dividends are paid out of after-tax cash flows so there is no tax adjustment for the issuing company.
What is the after tax cost of preferred stock?
Calculate the proceeds from the sale and then divide it into the dividend per share for the after-tax cost of preferred stock. $110 / $975= 11.3 percent. This is the after-tax cost of preferred stock to the company.
Why is the cost of preferred stock usually higher than the cost of debt?
The cost of preferred stock is the stated dividend amount paid annually on each share of preferred stock, divided by the current market price of the stock. These dividends are not tax deductible, so the cost of preferred stock is always higher than the cost of debt – for which interest payments are tax deductible.May 14, 2017
Why must the cost of debt be adjusted for taxes?
Why must the cost of debt be adjusted for taxes? Because interest on the debt is tax-deductible which lowers the firm's total cost of debt financing. A firm has a capital structure of 40 percent common stock, 10 percent preferred stock, and 50 percent debt.
How do you calculate after-tax preferred yield?
The effective after-tax yield can be found by multiplying the percentage of yield after taxes by the pre-tax rate of return. If the investment in this example returns 8 percent, that number would be multiplied by 0.70 to get an after-tax yield of 5.6 percent.
How do you calculate cost of preferred stock?
Here's an easy formula for calculating the value of preferred stock: Cost of Preferred Stock = Preferred Stock Dividend (D) / Preferred Stock Price (P). Par value of one share of preferred stock equals the amount upon which the dividend is calculated.
Why is preferred stock not tax deductible?
Key Takeaways Preferred shares are a hybrid form of capital issued by firms that are equity-based but pay out a stable dividend as if they were debt. Because the dividends paid out use after-tax dollars, preferred shares do not offer the firm an immediate tax deduction, as interest paid on debt would.
Why the cost of equity is more expensive than cost of debt and cost of preferred stocks?
Typically, the cost of equity exceeds the cost of debt. The risk to shareholders is greater than to lenders since payment on a debt is required by law regardless of a company's profit margins. Equity capital may come in the following forms: Common Stock: Companies sell common stock to shareholders to raise cash.
Why is preferred stock preferred?
What is "preferred" about preferred stock? Preferred shares are so called because they give their owners a priority claim whenever a company pays dividends or distributes assets to shareholders.
Why do we use after-tax figure for cost of debt but not for cost of equity?
Why do we use aftertax figure for cost of debt but not for cost of equity? -Interest expense is tax-deductible. There is no difference between pretax and aftertax equity costs. How do you determine the appropriate cost of debt for a company?
How is cost of debt computed?
To calculate your total debt cost, add up all loans, balances on credit cards, and other financing tools your company has. Then, calculate the interest rate expense for each for the year and add those up. Next, divide your total interest by your total debt to get your cost of debt.Sep 17, 2020
How do you calculate before tax cost of debt?
Calculating Before-Tax Debt Subtract the company's tax rate expressed as a decimal from 1. In this example, subtract 0.29 from 1 to get 0.71. Divide the company's after-tax cost of debt by the result to calculate the company's before-tax cost of debt.