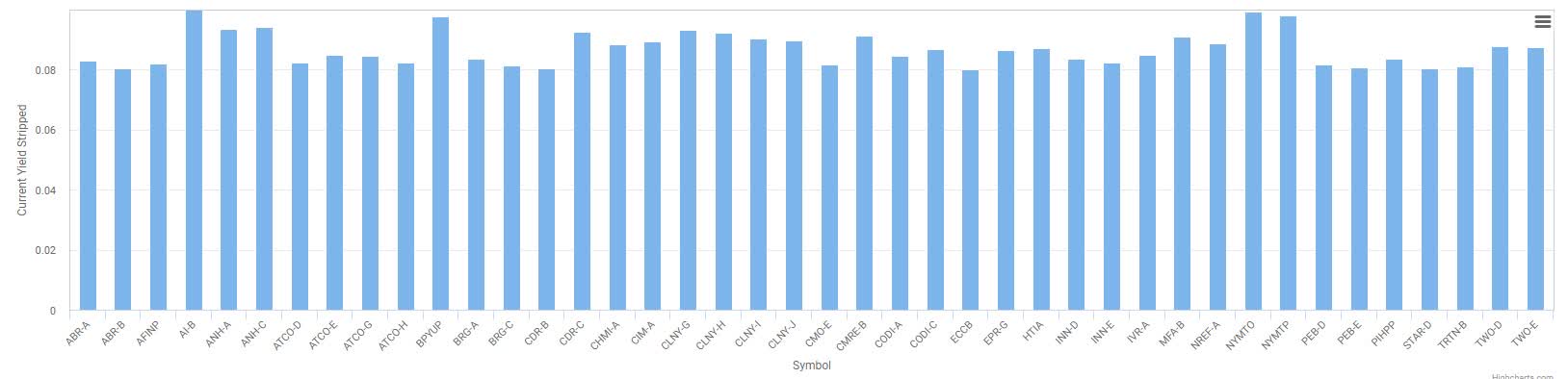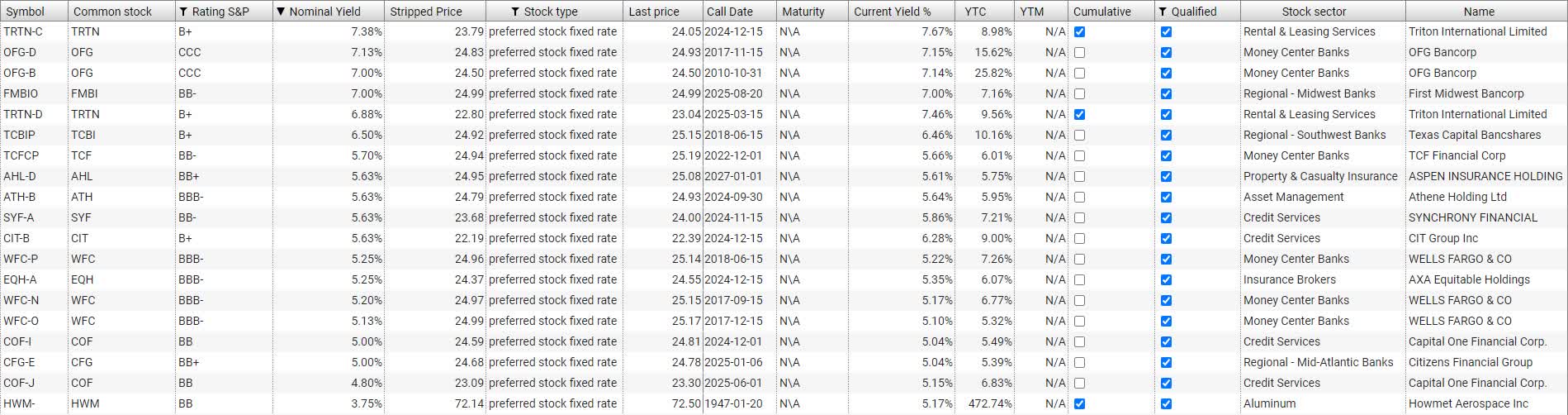
How to find the best preferred stocks?
When looking for the best preferred stock ETFs, here are 3 key elements to keep an eye out for:
- Low expenses
- High dividend yield
- Sufficient liquidity
What are the risks of preferred stock?
The True Risks Behind Preferred Stock ETFs
- General Risks. A big risk of owning preferred stocks is that shares are often sensitive to changes in interest rates.
- Particular Risks. Preferred stocks are rated by the same credit agencies that rate bonds. ...
- iShares U.S. Preferred Stock ETF. ...
- First Trust Preferred Securities and Income ETF. ...
What are preferred stock shares?
What is "preferred" about preferred stock?
- Many preferred share issues use a percentage in the title. ...
- Preferred stock dividends are generally not considered automatic entitlements but instead are typically declared individually by the board of directors. ...
- Companies may issue multiple series of preferred shares, each of which has different economic rights. ...
Why is preferred stock better?
Key Similarities
- Interest rate sensitivity. Both bonds and preferred stock prices fall when interest rates rise. ...
- Callability. Both securities may have an embedded call option (making them "callable") that gives the issuer the right to call back the security in case of a fall in interest ...
- Voting rights. ...
- Capital appreciation. ...
- Convertibility. ...
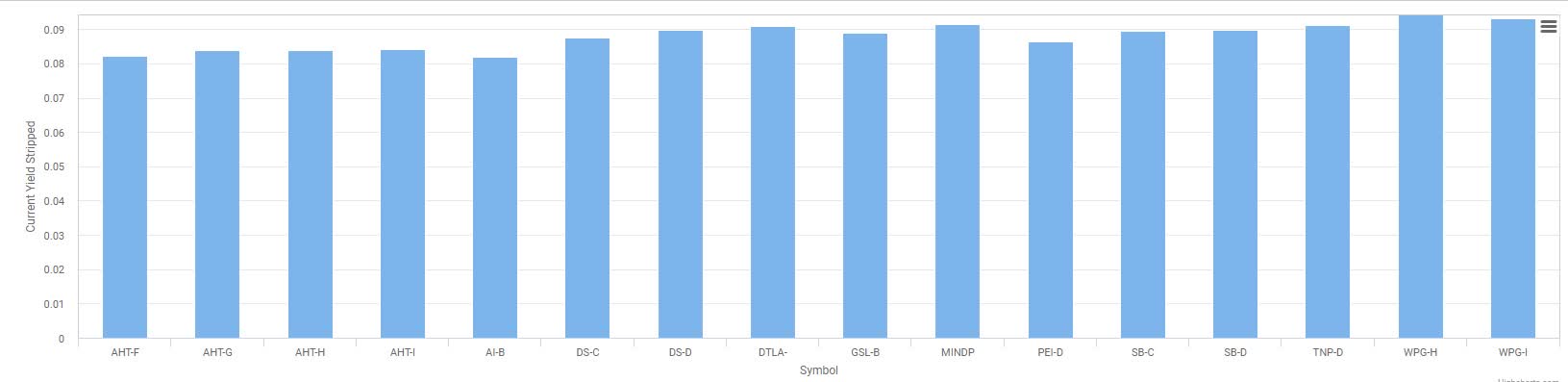
How are preferred stocks priced?
Preferred shares are issued with a face value, but this is effectively an arbitrary price chosen by the issuing company. Because preferred shares pay steady dividends, but lack voting rights, they will typically trade in the market for a value different from the same firm's common shares.
Does preferred stock have a fixed dividend?
First, preferreds receive a fixed dividend as dividend obligations to preferred shareholders must be satisfied first. Common stockholders, on the other hand, may not always receive a dividend. Secondly, preferreds typically do not share in the price appreciation (or depreciation) to the same degree as common stock.
What is the difference between preferred stock and common stock?
The main difference between preferred and common stock is that preferred stock gives no voting rights to shareholders while common stock does. Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders.
What are the features of preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are hybrid securities that have the characteristics of both bonds and stocks. Preferred stocks have dividend priority over common stock. The holders of preferred shares receive dividends before the holders of common shares. Preferred stockholders generally do not have voting rights in the company.
Why is preferred stock better than common?
Preferred stock may be a better investment for short-term investors who can't hold common stock long enough to overcome dips in the share price. This is because preferred stock tends to fluctuate a lot less, though it also has less potential for long-term growth than common stock.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
Companies issue preferred stock as a way to obtain equity financing without sacrificing voting rights. This can also be a way to avoid a hostile takeover. A preference share is a crossover between bonds and common shares.
What do you mean by preferred stock?
Preference shares, more commonly referred to as preferred stock, are shares of a company's stock with dividends that are paid out to shareholders before common stock dividends are issued. If the company enters bankruptcy, preferred stockholders are entitled to be paid from company assets before common stockholders.
What is preferred stock example?
For example, if a corporation issues 9% preferred stock with a par value of $100, the preferred stockholder will receive a dividend of $9 (9% times $100) per share per year. If the corporation issues 10% preferred stock having a par value of $25, the stock will pay a dividend of $2.50 (10% times $25) per year.
How are preferred stock dividends paid?
Preferred dividends are paid at a fixed rate. Annual dividends are calculated as a percentage of the par value, which is the price of the preferred stock at the time it was issued.
What's a preferred dividend?
Definition: Preferred Dividends are cash distributions that are paid to the owners of a company's preferred shares. In other words, this is the amount of money preferred shareholders receive from the company's retained earnings each year.
What is the dividend rate on preferred stock?
Find the Dollar Rate Multiply the par value for the preferred stock by the dividend percentage. For example, if the dividend percentage is 7.5 percent and the stock was issued at $40 per share, the annual dividend is $3 per share.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What is an ARPS stock?
Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS). These preferreds pay dividends based on several factors stipulated by the company. Dividends for ARPS are keyed to yields on U.S. government issues, providing the investor limited protection against adverse interest rate markets.
Why do preferred bonds have unlimited life?
Preferreds technically have an unlimited life because they have no fixed maturity date, but they may be called by the issuer after a certain date. The motivation for the redemption is generally the same as for bonds — a company calls in securities that pay higher rates than what the market is currently offering. Also, as is the case with bonds, the redemption price may be at a premium to par to enhance the preferred's initial marketability.
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
How to calculate current yield on preferred stock?
For example, if a preferred stock is paying an annualized dividend of $1.75 and is currently trading in the market at $25, the current yield is: $1.75 ÷ $25 = .07, or 7%. In the market, however, yields on preferreds are typically higher than those of bonds from the same issuer, reflecting the higher risk the preferreds present for investors.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
What is preferred stock?
A preferred stock is a type of “hybrid” investment that acts like a mix between a common stock and a bond. Like common stocks, a preferred stock gives you a piece of ownership of a company. And like bonds, you get a steady stream of income in the form of dividend payments (also known as preferred dividends ).
Why are preferred stocks getting closer to investors?
In a world where bond returns are barely enough to keep pace with inflation, some investors are looking for an alternative that will help them receive a reliable income stream. That’s why preferred stocks are getting a closer look by some investors.
How much do preferred stock dividends pay?
A preferred stock’s dividend payments are usually higher than bond payments and they’re set at a fixed rate, usually somewhere between 5–7%. 1 They’re also paid out before common stock dividends, but after bondholders receive their payments. This makes them very attractive to investors looking to replace bonds that are barely beating inflation with an investment that brings in better returns.
What are the drawbacks of preferred stock?
Here’s another drawback to preferred stocks: Even though preferred stockholders technically have a piece of ownership in a company, they have no voting rights like common stakeholders do. That means they don’t really get any say in how the company is run.
How long does it take to sell preferred stock?
While common stocks can be sold in a matter of seconds, preferred stocks can take days or sometimes even weeks to find a buyer willing to take them off your hands . . . and that’s when things are going well. Good luck trying to sell a preferred stock of a struggling company . . .
What do you get when you cross a common stock with a bond?
Do you know what you get when you cross a common stock with a bond? (Nope, this is not the start of some lame dad joke). You get something called a preferred stock.
Do preferred stocks have a start and end date?
While bonds usually have a start and end date, preferred stocks are perpetual. That means you’ll keep receiving dividend payments as long as you own the stock. Keep in mind that in some cases, however, the company that sold you the preferred stock can buy the stock back from you at its par value after a certain period of time depending on what type of preferred stock you buy.
What is preferred stock?
Like bonds, preferred stocks are a form of fixed-income security. They entitle the investor to dividend payments on a set schedule and are designed to generate income, not growth. This is the biggest difference between preferred and common stock. Let's say you buy a preferred stock for $25 that has a 5% yield.
Why do preferred stocks move?
Preferred stock share prices can certainly move, typically in response to interest rate fluctuations or the perceived health of the business, but the price isn't related to the profits of the underlying company. Unlike bonds, however, preferred stocks are readily tradable on major stock exchanges.
What happens to preferred stocks in bankruptcy?
In other words, in the event of a bankruptcy, bondholders would get paid first before preferred stockholders could recoup their investment.
Why are preferred stocks better than common stock?
On the positive side, this is why preferred stocks tend to pay higher yields than bonds from the same company.
What is the best way to invest in preferred stocks?
For the majority of investors, using index funds to invest in preferred stocks is the best option. The iShares U.S. Preferred Stock ETF ( NASDAQ:PFF) is the largest preferred stock exchange-traded fund, or ETF, by a significant margin and allows investors to put their money to work in a broad basket of preferred stocks.
What happens if a company's common stock doubles in value?
Here's an important point to know. If the company's common stock doubles in value, the preferred stock isn't likely to do the same. You do not share in the equity appreciation generated by the business.
Is preferred stock the same as bond?
Preferred stocks are an interesting type of security with many qualities of fixed-income investments, but they aren't the same thing as bonds. While they have characteristics of bonds, they also trade on major exchanges like common stocks, but they are an entirely different type of investment. With that in mind, here's an overview ...
What is preferred stock?
Preferred shares are shares issued by a corporation as part of its capital structure. Preferred stock have a ‘coupon rate’ — the interest rate you will be paid. This interest rate remains constant on most–but not all, preferred issues.
How long do preferred stock options last?
Most Preferred Stocks have an optional redemption period in which the shares may be redeemed, at the issuers option, generally this is 5 years afer issue, but may be more or less.
What is the floating rate of libor?
These issues have floating rates from the day they are issued and always contain a floating rate formula with an overriding minimum coupon, usually 3-4.5%. Most of these issues use 3 month libor as part of the equation and add a fixed rate to 3 month libor. As of 2/2018 most of these issues may be “safe” issues, but the coupons are substandard.
What is Preferred Stock?
Preferred stock is a form of equity that may be used to fund expansion projects or developments that firms seek to engage in. Like other equity capital, selling preferred stock enables companies to raise funds. Preferred stock has the benefit of not diluting the ownership stake of common shareholders, as preferred shares do not hold the same voting rights that common shares do.
How do corporations calculate the cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. Once they have determined that rate, ...
What is the term for the first cash flow payment after a liquidation?
Because of the nature of preferred stock dividends, it is also sometimes known as a perpetuity. Perpetuity Perpetuity is a cash flow payment which continues indefinitely.
What is unlevered cost of capital?
Unlevered Cost of Capital Unlevered cost of capital is the theoretical cost of a company financing itself for implementation of a capital project, assuming no debt. Formula, examples. The unlevered cost of capital is the implied rate of return a company expects to earn on its assets, without the effect of debt. WACC assumes the current capital
What is a CFI?
CFI is the official global provider of the Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™. Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today!
Does common equity have a par value?
However, preferred stock also shares a few characteristics of bonds, such as having a par value. Common equity does not have a par value.
Is preferred stock more valuable than common stock?
In theory, preferred stock may be seen as more valuable than common stock, as it has a greater likelihood of paying a dividend and offers a greater amount of security if the company folds.
What is the Cost of Preferred Stock?
The Cost of Preferred Stock represents the rate of return required by preferred shareholders and is calculated as the annual preferred dividend paid out (DPS) divided by the current market price.
Cost of Preferred Stock Overview
The recommended modeling best practice for hybrid securities such as preferred stock is to treat it as a separate component of the capital structure.
Cost of Preferred Stock Formula
The cost of preferred stock represents the dividend yield on the preferred equity securities issued.
Nuances to the Cost of Preferred Stock
Sometimes, preferred stock is issued with additional features that ultimately impact its yield and the cost of the financing.
Cost of Preferred Stock Excel Template
Now that we’ve defined the concept behind the cost of preferred equity, we can move on to an example modeling exercise in Excel. To access the model template, fill out the form below:
Cost of Preferred Stock Example Calculation
In our modeling exercise, we’ll be calculating the cost of preferred stock for two different dividend growth profiles:
Why do preferred stocks move higher?
Convertible preferred stocks can generally move higher in price than traditional preferred stocks because they generally don't have a call date.
What happens to preferred stock dividends after call date?
After the call date has passed, the rate will generally be the current three-month LIBOR rate plus some floor rate . In the example of NYMTM ( NYMTM ), the rate will be set to the three-month LIBOR yield plus 6.429% if NYMTM is not called on 1/15/2025. This floating rate is set in the prospectus. Thus, once the call date has passed, the actual dividends paid out can rise and fall depending on changes in the three-month LIBOR rate.
What is reset rate preferred stock?
Reset-rate preferreds are similar to fixed-to-floating rate preferreds in that they offer a fixed rate until they reach their call dates. At that point, if the preferred stock is not called, the dividend is reset to the U.S. five-year Treasury note plus some floor interest rate. In the case of ARGO-A, if it is not called on 9/15/2025, the dividend will then be set to the yield of the five-year T-note plus 6.712%. After the call date, the dividend will only be reset every five years.
Why are high yield preferred stocks going up?
Although long-term Treasury rates have risen from their post-COVID lows, high yield preferreds have gone way up in price due to much higher confidence in the economy and in the companies which have higher credit risk. So there has been a negative correlation between high yield preferred stock prices and bond prices.
Why is it important to know the stripped price?
The reason that understanding "stripped price" is important is that "stripped price" should be used when calculating YTC or current yield. Here's a yield-to-call calculator you can use. But when you enter the current price into this calculator, you need to enter the current "stripped price" if you want to get the most accurate result.
How long is the trial period for High Dividend Opportunities?
If you want full access to our Model Portfolio and all our current Top Picks, feel free to join us for a 2-week free trial at High Dividend Opportunities.
Do LIBOR and SOFR have a maturity date?
Thus, you do have protection against short-term hikes in interest rates, but because preferred stocks are perpetual (have no maturity date), they correlate more to long-term interest rates.
What Is Preferred Stock?
Preferred stocks aren’t so different from the common stocks which you purchase from a company. The major difference is that preferred stockholders enjoy added security and privileges common stockholders never have access to.
Why is preferred stock called preferred stock?
And investors prefer this type of stock because it enjoys preferential treatment from the company issuing it.
What does it mean when a preferred stock is outstanding?
What does that mean? Simply put, it means that preferred stocks can remain valid forever. And unless the company repurchases the stock, it remains outstanding forever.
How does preferred stock work?
Preferred stock works in almost the same way as bonds do: their holders get paid fixed dividends at common time intervals. So, if you are looking for a fixed-income investment to put your money into, preferred stock is the place to look.
Why is common stock called common stock?
The reason why it’s called common stock is that the holders of this stock are usually the last to receive their dividends once a company starts paying out.
What are the two types of stocks?
When looking to invest in the stock market, there are two broad types of stocks you can pick from—common stock or preferred stock.
Why do investors prefer preferred stock?
Investors, on their own part, tend to favor preferred stock for a number of reasons, chief among them is that preferred stock yields a better return on investment.