
What are pros and cons of a reverse stock split?
- Companies prices come down
- Outstanding shares goes up, with this their financial ratios like EPS, RoE goes down.
- Market cap remains same.
- No Fresh equity are issued hence there is no dilution of equity.
Is a reverse split a good thing or bad?
Reverse stock splits boost a company's share price. A higher share price is usually good, but the increase that comes from a reverse split is mostly an accounting trick.
Should I buy a stock before or after it splits?
When trying to make money and buy stocks before or after split announcements, you should keep in mind that you can make money either way. When you buy before a split, you can enjoy the biggest gains. The market will impose a premium on the split stock and the stock is sure to get a healthy lift.
Do Stocks go up or down after a reverse split?
Reverse stock splits occur when a publicly traded company deliberately divides the number of shares investors are holding by a certain amount, which causes the company’s stock price to increase accordingly. However, this increase isn’t driven by positive results or changes to the company. Rather, the stock price rises because of basic math.
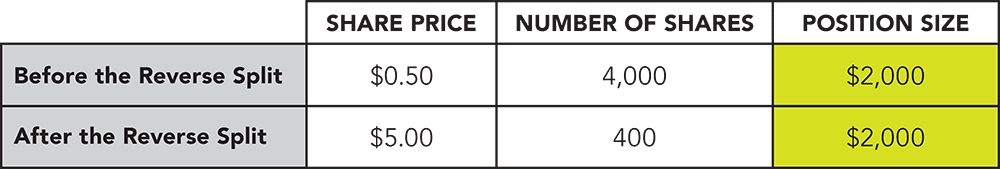
Can you make money on a reverse stock split?
If you own 50 shares of a company valued at $10 per share, your investment is worth $500. In a 1-for-5 reverse stock split, you would instead own 10 shares (divide the number of your shares by five) and the share price would increase to $50 per share (multiply the share price by five).
Does a reverse stock split hurt you?
Initially, a reverse stock split does not hurt shareholders. Investors who have $1,000 invested in 100 shares of a stock now have $1,000 invested in fewer shares. This does not mean the price of the stock will not decline in the future; putting all or part of an investment in jeopardy.
Should I invest before or after a reverse split?
The bottom line: In a perfect world the best time to buy is before or on the announcement date. However, if we miss that trade, it pays to wait patiently until after the split to buy or add to your holdings.
Do you lose money on a reverse stock split?
In some reverse stock splits, small shareholders are "cashed out" (receiving a proportionate amount of cash in lieu of partial shares) so that they no longer own the company's shares. Investors may lose money as a result of fluctuations in trading prices following reverse stock splits.
Who benefits from a reverse stock split?
A reverse stock split reduces the number of a company's outstanding shares and proportionally increases the share price. While a higher share price can help to boost a company's image, reverse splits are generally received by investors as a potential sign of fundamental weakness.
What happens after a reverse split?
A reverse stock split is a measure taken by companies to reduce their number of outstanding shares in the market. Existing shares are consolidated into fewer, proportionally more valuable, shares, resulting in a boost to the company's stock price.
Do stocks rise after a split?
When a stock splits, it can also result in a share price increase—even though there may be a decrease immediately after the stock split. This is because small investors may perceive the stock as more affordable and buy the stock. This effectively boosts demand for the stock and drives up prices.
Is a stock split good for shareholders?
A stock split allows a company to break each existing share into multiple new shares without affecting its market capitalization (total value of all its shares) or each investor's stake in the company. A stock split can be a good sign for both current and prospective shareholders.
Does a stock split hurt shareholders?
When a stock splits, it has no effect on stockholders' equity. During a stock split, the company does not receive any additional money for the shares that are created. If a company simply issued new shares it would receive money for these, which would increase stockholders' equity.
What are the disadvantages of a stock split?
Downsides of stock splits include increased volatility, record-keeping challenges, low price risks and increased costs.
What is a 1 for 16 reverse stock split?
As a result of the Reverse Stock Split, every sixteen (16) shares of the Company's pre-reverse split common stock will be combined and reclassified into one (1) share of common stock.
What does a 1 for 4 reverse stock split mean?
For example, in a 1:4 reverse split, the company would provide one new share for every four old shares. So if you owned 100 shares of a $10 stock and the company announced a 1:4 reverse split, you would own 25 shares trading at $40 per share.
What Is a Reverse Stock Split?
Companies can use different ratios for executing reverse stock splits. For example, a company could decide to initiate a reverse split that convert...
Why Do Companies Execute Reverse Stock Splits?
There are different reasons why a company may choose to execute a reverse stock split. Most often, it’s used as a tool for increasing the share pri...
Do You Lose Money on a Stock Split?
A stock split itself doesn’t cause an investor to lose money, because the total value of their investment doesn’t change. What changes is the numbe...
Is a Reverse Stock Split Good or Bad?
At first glance, a reverse stock split can seem like a red flag. If a company is trying to boost its share price to try and attract new investors,...
Should I Sell Before a Stock Split?
With a reverse stock split, a decision to sell (or not sell) may hinge on why the company is executing the split. If a reverse stock split is being...
Why is reverse stock split bad?
Here’s why: The number one reason for a reverse split is because the stock exchanges—like the NYSE or Nasdaq—set minimum price requirements for shares that trade on their exchanges.
When did Citi reverse split?
Citi probably had the most famous reverse split—a 1 for 10 reverse split in May 2011. Citi became a $40 stock and is now trading at $70. The split was billed as “returning value to the shareholders.”.
Why won't institutional investors invest in stocks?
Savvy institutional investors won’t invest in the stock just because its price suddenly soared, and it will have a hard time raising capital if its balance sheet is poor. Shorters, who follow reverse stock splits and target those stocks, began to put pressure on the stock price, sending it tumbling.
Do penny stocks reverse split?
Most—although not all—reverse splits are seen in small penny stocks that have not been able to attain steady profitability and create value for their shareholders. I found that was the case in most of the biotechs’ recent reverse stock splits.
Is Xerox stock split a reverse split?
It could raise Xerox’s standing among institutional investors and research analysts. It could also lower Xerox’s standing among other investors. Some investors are repelled by reverse stock split. They view a reverse stock split as an insincere strategy for raising the share price.
Why do companies do reverse stock splits?
Why companies perform reverse stock splits. The most obvious reason for companies to engage in reverse stock splits is to stay listed on major exchanges. On the New York Stock Exchange, for example, if a stock closes below $1 for 30 consecutive days, it could be delisted.
Why do reverse stock splits happen?
Reverse stock splits occur when a publicly traded company deliberately divides the number of shares investors are holding by a certain amount, which causes the company’s stock price to increase accordingly. However, this increase isn’t driven by positive results or changes to the company. Rather, the stock price rises because of basic math.
What happens if a company times a reverse stock split?
In this instance, the reverse stock split was a success for both the company and its shareholders.
What happens if a stock price is too low?
If a company’s share price is too low, it’s possible investors may steer clear of the stock out of fear that it’s a bad buy; there may be a perception that the low price reflects a struggling or unproven company. To fight this problem, a company may use a reverse stock split to increase its share price.
What happens to the market capitalization of a company during a reverse stock split?
During a reverse stock split, the company’ s market capitalization doesn’t change, and neither does the total value of your shares. What does change is the number of shares you own and how much each share is worth. If you own 50 shares of a company valued at $10 per share, your investment is worth $500. In a 1-for-5 reverse stock split, you would ...
Is a reverse stock split a red flag?
In either instance, a reverse stock split could be a red flag to investors, but this isn’t always the case. Here are two basic outcomes of a reverse stock split: Positive. Often, companies that use reverse stock splits are in distress. But if a company times the reverse stock split along with significant changes that improve operations, ...
Why do companies do reverse stock splits?
Why companies pursue reverse stock splits. The main reason most companies perform a reverse stock split is to avoid being delisted from a major exchange. For example, the NYSE will start the delisting process for a stock trading below $1 for 30 consecutive trading days.
What is reverse stock split?
It’s often done to increase the liquidity of the stock. Not surprisingly, a reverse stock split flips this equation around and the company decreases the number of outstanding shares. Investors should be aware of the potential impacts ...
What happens when a company reverses its stock?
When a publicly traded company undergoes a reverse stock split, the company cancels outstanding stock and issues new shares to existing shareholders. Existing shareholders receive the same value in stocks, but the number of shares changes based on the reverse stock split ratio.
Is a reverse stock split a red flag?
Source: Unsplash. However, it’s generally accepted that a reverse stock split is more of a red flag than a positive sign for the company’s trajectory . Reverse splits can signal company distress.
Does market capitalization change after a stock split?
A company’s market capitalization doesn’t change after a stock split or a reverse split. Only the equation of shares times price changes. For dividend stocks, the future dividend amounts would adjust proportionately according to the reverse split.
Can a company's market capitalization change after a reverse stock split?
At certain points in a company’s lifetime, the board of directors might decide to engineer a stock split or its opposite, a reverse stock split. A company's market capitalization doesn't change after either type of stock split. Only the number of outstanding shares is adjusted.
What happens to a company's stock before a reverse split?
In a reverse stock split, the company cancels all of its existing outstanding stock and distributes new shares to its shareholders.
What is reverse stock split?
A reverse stock split is a reduction in the number of a company’s shares outstanding in the market. It's the opposite of a stock split. In recent weeks, Tesla and Apple announced stock splits. Is a reverse stock split good for investors?
Why do companies reverse split?
A reverse stock split, which has no impact on the company’s total market capitalization, is often done to avoid a stock's delisting or to boost a company's reputation if its stock price has fallen significantly. Stock exchanges such as the Nasdaq and NYSE have a minimum stock price requirement.
How to comply with stock exchanges?
The easiest way for a company to comply with stock exchanges is to decrease its number of outstanding shares so that its stock price rises. Whereas a higher stock price is typically good, a rise from a reverse stock split is just an accounting trick. Whatever value the company has before the reverse split is just distributed over fewer shares ...
When did Citigroup reverse stock split?
In 2011, Citigroup announced a 1-for-10 reverse stock split that boosted its stock price from $4.50 per share to $45 per share after the split. In June 2020, Office Depot also announced a 1-for-10 reverse split.
Can you lose shares in a reverse stock split?
Yes , you may lose shares in a reverse stock split. For instance, in a 1-for-5 reverse stock split, shareholders would get one share of the company's new stock for every five shares that they owned. If you owned 100 shares before the reverse split, you would own 20 shares after the reverse stock split. Article continues below advertisement.
Why do companies do reverse stock splits?
A company performs a reverse stock split to boost its stock price by decreasing the number of shares outstanding. A reverse stock split has no inherent effect on the company's value, with market capitalization remaining the same after it’s executed. This path is usually pursued to prevent a stock from being delisted or to improve ...
What is reverse stock split?
What Is a Reverse Stock Split? A reverse stock split is a measure taken by companies to reduce their number of outstanding shares in the market. Existing shares are consolidated into fewer, proportionally more valuable, shares, resulting in a boost to the company’s stock price.
How many shares would a shareholder have after a reverse stock split?
In other words, a shareholder who held 1,000 shares would end up with 100 shares after the reverse stock split was complete. A reverse stock split has no inherent effect on the company's value, with its total market capitalization staying the same after it’s executed.
What happens if a stock price falls below $1?
Prevent being delisted from an exchange : If a stock price falls below $1, it is at risk of being delisted from stock exchanges that have minimum share price rules.
Why do companies do reverse splits?
One common reason is to avoid getting delisted, as some major exchanges require that share prices stay above $1 to keep from triggering delisting guidelines.
When did Sun Microsystems reverse stock split?
Sun Microsystems, for instance, did a 1-for-4 reverse stock split back in November 2007, but after just a year, the shares had fallen 85% before bouncing in the wake of Oracle 's (Nasdaq: ORCL) takeover of the tech giant.
When did AIG reverse split?
In 2009, AIG ( NYSE:AIG) did a 1-for-20 reverse split after shares had flirted with the $1 mark for the better part of a year following the market meltdown in 2008.
When did Priceline.com reverse its stock?
In mid-2003, Priceline.com ( NASDAQ:BKNG) did a 1-for-6 reverse stock split, lifting its stock price from around $3.50 per share to $22, as many investors believed that the William Shatner-led Internet travel service would fade away with so many other dot-com companies.
Do stocks underperform after a reverse split?
Be smart about stocks. It's important to realize, though, that these stocks aren't typical. Past research has shown that most stocks underperform the market following a reverse split. That isn't surprising. After all, a company that sees its stock fall so far usually has to have gone through a tough period.
Do splits matter?
Of course, when you look at it from an economic standpoint, splits shouldn't matter to a company's fundamental value. Whether regular or reverse, a split simply changes the number of shares outstanding. Offer two shares for every one existing share, and the price for each should get cut in half.
Can reverse splits be a disadvantage?
That can give smart investors great opportunities, but they're few and far between. Companies that need reverse splits typically start with a big disadvantage. Only very rarely can those companies give investors the huge returns they want in top investments.
Why do companies reverse stock split?
A company may announce a reverse stock split in order to carry out a merger with or acquisition of another company. A company's articles of incorporation limit the number of shares the company can issue; a common practice of company buyouts is to issue new shares of the acquiring (or new) company to the shareholders of the company being acquired ...
What does reverse split mean for stocks?
Reverse splits result in a higher share price. For a stock worth just a dollar or two, this may be necessary in order to meet listing requirements on certain exchanges. As of 2013, for example, the New York Stock Exchange required a minimum share price of $4, along with a minimum share float and minimum market capitalization. A company that wants to attain status on the NYSE "Big Board" and get interest from institutional investors may reverse-split its shares to meet these guidelines. In addition, companies that pay dividends simply adjust the dividend to reflect the new, lower number of shares: a $.25-per-share dividend paid by a company that does a 1:3 reverse split becomes a $.75 dividend: three times the old payout.
What is reverse split?
Reverse splits reduce the share "float," or the number of shares available on the public market. To a potential investor, a reduction in the float is always desirable. With fewer shares outstanding, the earnings-per-share number rises, which in turn supports the share price.
What happens when a stock splits?
When a stock splits, two new shares are created for every one outstanding, and the price is cut in half. The purpose of a stock split is to make the shares more affordable for "retail" investors, who don't have large amounts of capital to invest. In a reverse split, the opposite happens: the number of shares is reduced, and the share price rises.
Does a reverse stock split require a warning?
The Securities and Exchange Commission, which administers securities law, does not require advance warning of a reverse stock split. A company can take this action without the approval of shareholders if its own by-laws allow it. It can formally notify the SEC and investors with a Form 8-K, a "Current Report," or by the annual and quarterly financial reports, if the company is reporting its activities to the SEC.
When do companies reverse split?
When a stock's price gets so low that the company doesn't want it to look like a penny stock , they sometimes institute a reverse split. History has shown less than stellar results for companies that do this. Remember that splits may be a reason to buy shares in a company and reverse splits may be a reason to sell shares.
How does a stock split work?
A stock split doesn't add any value to a stock. Instead, it takes one share of a stock and splits it into two shares, reducing its value by half. Current shareholders will hold twice the shares at half the value for each, but the total value doesn't change. The ratio doesn't have to be 2 to 1, but that's one of the most common splits.
What is a stock buyback?
A stock buyback takes place when a company uses its cash to repurchase stock from the market. A company cannot be a shareholder in itself so when it repurchases shares, those shares are either canceled or made into treasury shares.
Why do companies buy back stock?
Because a buyback reduces the number of shares available to trade in the market, the value of each existing share increases. A company's management may initiate a buyback if they believe the stock is significantly undervalued and as a way to increase shareholder value.
Do stock splits and buybacks happen?
If stock splits and buybacks have been a bit of a mystery to you, you're not alone. While the number of companies initiating stock splits and buybacks ebbs and flows as market conditions change, most long-term investors have been affected by at least one of these events in the past. And if they haven' t, it probably won' t be long before they find ...
Do splits and buybacks give investors a metric?
Splits and buybacks may not pack the same punch as a company that gets bought out, but they do give the investor a metric to gauge the management's sentiment of their company. One thing is for sure: when these actions take place, it's time to reexamine the balance sheet.
Is a share repurchase a positive investment?
This makes a share repurchase a positive action in the eyes of investors . As with any investing strategy, never invest in a company with the hopes that a certain event will take place. However, in the case of a growing and profitable company, a share buyback often happens as a result of strong fundamentals.
