What happens to the stock market after an election?
After an election, stock market returns tend to be slightly lower for the following year, while bonds tend to outperform slightly after the election. It doesn’t seem to make much difference which party takes office, but it does matter whether control of the White House changes hands.
How do presidential elections affect your investment returns?
“Returns are made over a full business cycle, which is longer than even one presidential term,” he says. “With presidential elections, you need to make sure to have all the components of a diversified portfolio in place, and then stick to a longer-term strategy that’s designed for more than one election cycle.”
How will the post-midterm election period affect the market?
The post-midterm election period is a very different story. The S&P 500 has historically outperformed the market in the 12-month period after a midterm election, with an average return of 16.3%.
How will the midterms affect the stock market?
The midterms take place in the third quarter of the second year of a presidential term. According to Stovall’s data, in midterm election years between 1945 and 2021, stocks saw an average decline of 1.8% in the second quarter and drop another 0.5% in the third quarter.

How politics affect the stock market?
But over the past century, the stock market has mostly run briskly across most of the presidential cycle before losing momentum during election years. Since 1930, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has gained an average of 10.0% in a president's first year and 7.9% in the second, according to YCharts data.
Can a president affect the stock market?
Presidents get a lot of the blame, and take a lot of the credit, for the performance of the stock market while they are in office. However, the truth is that the president's ability to impact the economy and markets is generally indirect and marginal.
How does political instability affect stock price?
Results of the study indicated the negative relationship of stock prices with political instability. Moreover, results of suggested that instable political system ultimately leads decline in stock prices.
Does government policy affect stock prices?
Stock prices fall at the announcements of policy changes, on average. The price fall is expected to be large if uncertainty about government policy is large, as well as if the policy change is preceded by a short or shallow downturn. Policy changes increase volatility, risk premia, and correlations among stocks.
Who was President during the stock market crash?
The 1920s were a period of optimism and prosperity – for some Americans. When Herbert Hoover became President in 1929, the stock market was climbing to unprecedented levels, and some investors were taking advantage of low interest rates to buy stocks on credit, pushing prices even higher.
What was a major cause of the stock market crash?
The main cause of the Wall Street crash of 1929 was the long period of speculation that preceded it, during which millions of people invested their savings or borrowed money to buy stocks, pushing prices to unsustainable levels.
Will riots affect the stock market?
It shows that in countries with more open and democratic institutions, social unrest events have a negligible impact on stock market returns (blue line).
What factors affect stock market?
9 factors that affects the Indian Stock MarketGovernment Policies: ... Monetary Policy of RBI and Regulatory Policies of SEBI: ... Exchange Rates: ... Interest Rate and Inflation: ... Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs): ... Politics: ... Natural Disasters: ... Economic Numbers:More items...
Does the government control the stock market?
The federal government regulates much of the stock market's activity to protect investors and ensure the fair exchange of corporate ownership on the open markets.
How does the government prop up the stock market?
When the Federal Reserve begins entering the market to purchase financial assets, it manipulates price signals in three significant ways: It lowers interest rates, creates a higher demand for assets, and reduces the purchasing power of money units.
Can the government control a stock market crash?
While the U.S. government doesn't directly intervene in the stock market (say, by inflating the prices of stocks when they fall too low), it does have power to peripherally affect financial markets.
What moves the stock market?
If more people want to buy a stock (demand) than sell it (supply), then the price moves up. Conversely, if more people wanted to sell a stock than buy it, there would be greater supply than demand, and the price would fall. Understanding supply and demand is easy.
Once election day is over, stocks are likely to jump -- regardless of which party wins
Will a Republican victory in the upcoming congressional elections help the stock market? Or will the market fare better if Democrats hold on to Congress and continue their much-criticized efforts to fix the struggling economy?
The presidential cycle
The "presidential cycle" historically has also been a good predictor of stock performance. The thinking is that presidents try to make tough economic decisions during the first two years of their tenure, and that often leads to lousy stock-market performance.
The Market Usually Goes Down Before a Presidential Election
CNBC looked at how stock markets perform before an election, assessing the 3 months leading up to each presidential contest since 1992. They found that both the Dow and the S&P 500 typically go down before an election, albeit only slightly. The circumstances vary pretty wildly, but more often than not, there is a slight decline.
Can the Stock Market Predict the Winner?
When an incumbent president is running for reelection, yes, the market absolutely does predict the winner quite effectively. Forbes recently ran a fascinating article about stock market performance before, during, and after presidential elections, and it’s full of surprising historical trivia.
Election Years Are Generally Average for Investors
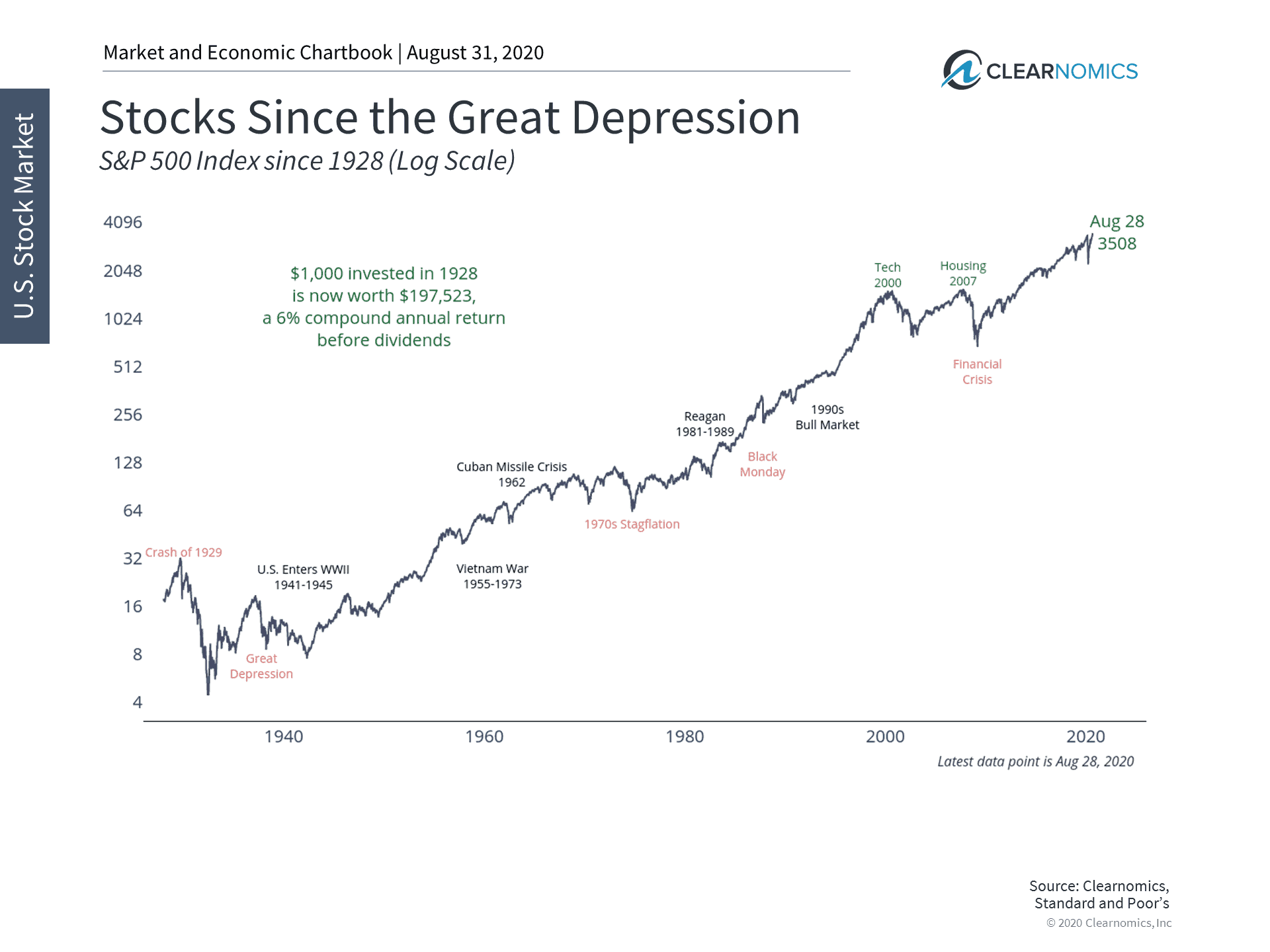
It’s instructive to look at election-year market data going back to before the Great Depression and before America became the global economic superpower that it is today. Financial advice site The Balance analyzed the S&P during election years going back to 1928.
How often are elections held in the US?
US elections are held every four years and always on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November. Electoral campaigns do not follow any official time frames and can vary in length. Still, this means US elections tend to be far more prolonged than other western democracies and can last for as long as 500 or even 600 days from start to finish. Below is a template provided by the US government that outlines the typical cycle of an election:
Who won the 2004 presidential election?
Bush won re-election after beating Democrat candidate John Kerry in the 2004 election. Bush’s popularity had strengthened in his first term as the economy began to recover and the country grieved after the 11 September attacks. The downturn in financial markets began to reverse in early 2003, when the S&P 500 picked up after two years of spiralling lower.