/calculating-the-intrinsic-value-of-perferred-stocks-58dc09de3df78c516271d210.jpg)
Determining the Value of a Preferred Stock
- Unique Features of Preferred Shares. Preferred shares differ from common shares in that they have a preferential claim on the assets of the company.
- Valuation Models. If preferred stocks have a fixed dividend, then we can calculate the value by discounting each of these payments to the present day.
- Growing Dividends. If the dividend has a history of predictable growth, or the company states a constant growth will occur, you need to account for this.
- Considerations. Although preferred shares offer a dividend, which is usually guaranteed, the payment can be cut if there are not enough earnings to accommodate a distribution; you need to account ...
- The Bottom Line. Preferred shares are a type of equity investment that provides a steady stream of income and potential appreciation.
How do you calculate preferred stock?
- Find the initial cost of the investment.
- Find total amount of dividends or interest paid during investment period.
- Find the closing sales price of the investment.
- Add sum of dividends and/or interest to the closing price.
- Divide this number by the initial investment cost and subtract 1.
What companies have preferred stock?
Preferred Stocks Directory
- Preferred shares are shares issued by a corporation as part of its capital structure.
- Preferred stock have a “coupon rate” — the interest rate you will be paid. ...
- Dividends are either cumulative — meaning that dividends continue to accrue if they have been suspended, but they are not paid until the company decides to pay them after suspension ...
How do you calculate the cost of preferred stock?
Things You'll Need
- Flotation cost to the company (percent)
- Dividend for the preferred stock (dollars)
- Market price of the preferred stock (dollars)
- Calculator (optional)
How to determine which preferred stock to buy?
Part 3 Part 3 of 3: Executing Your Trade
- Decide how many shares you want to buy. If you've followed the stock for a few weeks before making your purchase, you know the average price it's trading at ...
- Choose your order type. Since preferred stock is traded just like common stock, you have 4 ways you can place an order for the stock.
- Place your order with your broker. ...
How is preferred stock valued?
The value of a preferred stock equals the present value of its future dividend payments discounted at the required rate of return of the stock. In most cases the preferred stock is perpetual in nature, hence the price of a share of preferred stock equals the periodic dividend divided by the required rate of return.
What does 6% preferred stock mean?
Definition of preferred stock For example, 6% preferred stock means that the dividend equals 6% of the total par value of the outstanding shares. Except in unusual instances, no voting rights exist. Types include cumulative preferred stockand participating preferred stock.
How do you calculate preferred stock balance?
For example, assume the par value of the preferred stock $12. Multiply the number of preferred shares outstanding by the par value of the preferred stock. Continuing the same example, $100,000 x $12 = $1,200,000. This figure represents the dollar value of the preferred stock outstanding.
What does 10% cumulative preferred shares mean?
Cumulative preferred stock is a type of preferred stock with a provision that stipulates that if any dividend payments have been missed in the past, the dividends owed must be paid out to cumulative preferred shareholders first.
What is the downside of preferred stock?
Disadvantages of preferred shares include limited upside potential, interest rate sensitivity, lack of dividend growth, dividend income risk, principal risk and lack of voting rights for shareholders.
Is preferred stock recorded at par value?
To comply with state regulations, the par value of preferred stock is recorded in its own paid-in capital account Preferred Stock. If the corporation receives more than the par amount, the amount greater than par will be recorded in another account such as Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par - Preferred Stock.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is an element of shareholder equity that has characteristics of both equity and debt. A preferred share carries additional rights above and beyond those conferred by common stock. Preferred shareholders may have an advantage over common stock shareholders in dissolution, bankruptcy or liquidation, for instance.
What are the factors that determine the value of an investment?
The value of any investment is directly influenced by two significant factors: the amount of income or cash flow generated by the entity and the risk to a hypothetical willing buyer (not under a compulsion to buy and aware of all the relevant facts) who would purchase the shares (invest).
What happens if an appraiser believes a discount or premium is necessary?
If the appraiser believes a discount or premium is necessary, either increase the appropriate yield to apply to the preferred stock’s dividends or take a discount from the value determined by applying a yield unadjusted for marketability considerations. PRODUCTS, SCOPE, SKILLS.
Do preferred shares have dividends?
Preferred shares also generally have a dividend requirement, which makes them appear similar to debt. The dividend structure usually has rights attached to it, such as whether the dividends are cumulative or whether the shares participate in enterprise earnings.
Do appraisers have to value preferred stock?
Note: Appraisers who value a business having both common and preferred shares must value the preferred shares first, deducting that value from the total equity of the enterprise before valuing the common shares. CHARACTERISTICS OF PREFERRED STOCK.
Do CPAs value preferred shares?
The dividend structure usually has rights attached to it, such as whether the shares participate in enterprise earnings. To value a business having both common and preferred shares, CPAs should value the preferred shares first and deduct that value from the entire equity of the entity.
How is fixed dividend preferred stock valued?
Fixed dividend preferred stock is valued with the dividend discount approach, which uses the traditional discounting formula to calculate the present value of the stream of dividend payments .
What is preferred dividend?
Preferred dividends typically pay a fixed dividend, meaning the dividends stay the same. They don't vary with how well the company does. Common stock, on the other hand, has a more flexible dividend, increasing when the company does well or skipped altogether when times are bad.
Why is preferred stock considered a hybrid?
It's like equity in that it provides ownership and it's like debt in that preferred dividends are like the interest payments debt holders receive. It's called preferred stock because preferred stockholders get preferential treatment when it comes to receiving their dividend. Preferred stockholders are paid after the bondholders (those who own bonds issued by the company) but before the holders of common stock. So preferred stock is perceived to be less risky than common stock since there might not be anything left over after the preferred stockholders get paid.
Is preferred stock less risky than common stock?
So preferred stock is perceived to be less risky than common stock since there might not be anything left over after the preferred stockholders get paid.
TLDR
Companies often issue both common and preferred stock to reward those putting in sweat equity and those investing. Understanding which shares to issue to whom is a critical decision for startup founders.
What is Startup Preferred Stock?
Stock, or equity, is often one of the most critical assets in a startup. Equity can help a startup attract top talent as well as early-stage investors. In a new business, two types of stock are typically offered: common and preferred. Common stock is a share of ownership in the startup, typically accompanied by voting rights.
What is the Difference Between Common Stock and Preferred Stock?
As stated above, a common stock owner has purchased ownership in the startup along with voting rights, enabling them to vote on issues such as who will serve on the board of directors or on specific management decisions. The more ownership you have, the more significant impact your vote holds.
How Do You Calculate the Cost of Preferred Stock?
Calculating the price for a startup's preferred stock is often difficult as the business is new, without a track record of sales or other financial indicators of success. However, early startups' preferred stock can be priced. Let’s see how.
How to Calculate Par Value of Preferred Stock?
Par value of one share of preferred stock equals the amount upon which the dividend is calculated. In other words, par value is the face value of one share of stock.
How to Calculate Cumulative Preferred Stock?
Cumulative preferred stock is preferred stock, which pays cumulative dividends if a dividend payment was missed. A cumulative dividend is “a required fixed distribution of earnings made to shareholders.” Preferred shares are the most common stock class providing a right to receive cumulative dividends.
Benefits
It’s essential to objectively establish your business's value as a startup, which directly impacts your preferred stock price. By establishing these figures early in your business venture, you can show your business's value to potential investors, which is instrumental to growing your startup.
What happens to preferred stock when it goes bankrupt?
The basic tenet of preferred stock is that it will receive dividend payments before common stock. If the company declares bankruptcy, and has to liquidate all of its assets, holders of preferred stock will receive payouts before holders of common stock see a dime.
What are the two types of stocks?
If you're new to investing, you might not be aware that not all stocks are the same form. The two main types of stocks are common stock and preferred stock . The biggest difference between the two has to do with the rights and perks they bestow upon their owners. When you buy shares of stock, you are also buying a small piece of ownership in a company, and the type of stock you buy will dictate your role, mostly with regard to voting rights and dividend payments. 1
What is intrinsic value?
Intrinsic value is the focus here, and unlike other methods, it does not look at the larger market, or current trading prices, or past patterns; nor does it attempt to predict future prices. Instead, it bases a stock's value on what an investor will pay for it.
Do shareholders have voting rights?
When it comes time to vote for new board members of a company, for instance, shareholders with common stock will likely be the ones weighing in. Most often, each share of common stock comes with a voting right. The more shares you own, the more power you'll have in company-wide votes.
What is the most important factor to consider when evaluating preferred stock?
The important steps in determining the preferred stock valuation would include: Normally the most important factor to consider is the dividend rate and liquidation preferences. The valuation of preferred shares is based off this dividend rate and how it compares to that of high-grade publicly traded preferences shares.
What is preferred share valuation?
Like valuing any other financial asset, the valuation of preferred shares is the present value of the expected future cash flows discounted by a rate of return. This rate would be reflective of the risk connected with the preferred shares. If the preferred shares are dividend paying, then an income approach would be applied for discounting the future dividend payments to its present value. For the discount rate, this can either be calculated based on the inherent risk, or obtained from the public market for similar types of financial securities.
What is the second feature of preferred shares?
The second feature of preferred shares are its voting rights. Some preferred shares will be either voting or nonvoting shares, affecting their ability to make decisions on behalf of the company. The right to vote in the company decisions will also play a role in how an analyst may view the valuation of preferred shares.
What is the last factor to consider when purchasing preferred shares?
The last factor to consider is if the preferred shares have any redemption rights. These rights allow the shareholder to redeem their shares at a certain price upon a pre-set condition. The preferred shares valuation would be determined by the ability of the company to pay back these preferred shares.
What is dividend rate?
The dividend rate can be either a fixed number or a percentage of the par value of the shares, or the amount invested by the preferred shareholders. The dividend rate will greatly determine the valuation of preferred shares in the company.
What can you choose on the bottom of a preferred share class?
You can selection the seniority, participation rights, and dividend details of the share class. These details will stay with all the share grants under this equity class.
What is preferred share?
Whereas common shares are mainly staking claim in the ownership of a company, preferred shares provide incentives for outsiders to invest in the company , including fixed dividends and preferential treatment upon the exit of the company. Also the type of owners differ for these two types of shares.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
Why are preferred stocks considered hybrid securities?
Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds. Technically, they are securities, but they share many characteristics with debt instruments . Preferred stocks are sometimes called hybrid securities.
Why are preferred dividends suspended?
Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rates rise?
If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls. If rates decline, the opposite would hold true.
Preferred Stock Valuation Definition
The free online Preferred Stock Valuation Calculator is a quick and easy way to calculate the value of preferred stock. It’s to learn how to calculate preferred stock value because all you need to do is enter in your discount rate (desired rate of return) and the preferred stock’s dividend. Press calculate and that’s it!
How to Calculate Preferred Stock Valuation
Let's be honest - sometimes the best preferred stock valuation calculator is the one that is easy to use and doesn't require us to even know what the preferred stock valuation formula is in the first place! But if you want to know the exact formula for calculating preferred stock valuation then please check out the "Formula" box above.
Add a Free Preferred Stock Valuation Calculator Widget to Your Site!
You can get a free online preferred stock valuation calculator for your website and you don't even have to download the preferred stock valuation calculator - you can just copy and paste! The preferred stock valuation calculator exactly as you see it above is 100% free for you to use.
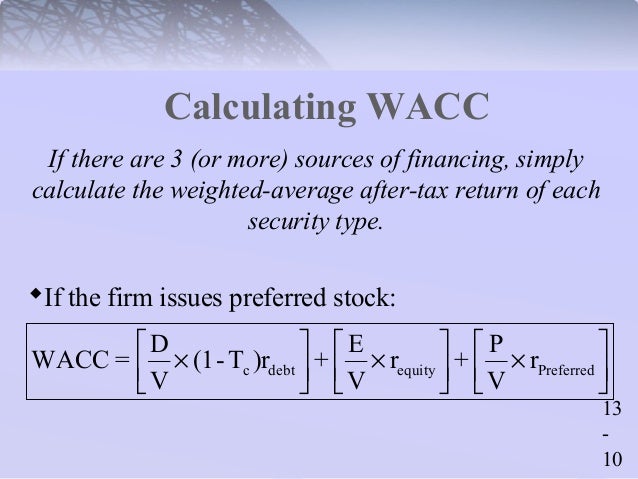
What is the Cost of Preferred Stock?
The Cost of Preferred Stock represents the rate of return required by preferred shareholders and is calculated as the annual preferred dividend paid out (DPS) divided by the current market price.
Cost of Preferred Stock Overview
The recommended modeling best practice for hybrid securities such as preferred stock is to treat it as a separate component of the capital structure.
Cost of Preferred Stock Formula
The cost of preferred stock represents the dividend yield on the preferred equity securities issued.
Nuances to the Cost of Preferred Stock
Sometimes, preferred stock is issued with additional features that ultimately impact its yield and the cost of the financing.
Cost of Preferred Stock Excel Template
Now that we’ve defined the concept behind the cost of preferred equity, we can move on to an example modeling exercise in Excel. To access the model template, fill out the form below:
Cost of Preferred Stock Example Calculation
In our modeling exercise, we’ll be calculating the cost of preferred stock for two different dividend growth profiles:
What is preferred stock?
Like common stock (which is what is most often bought and sold on the market), preferred stock can carry voting rights in the company, but like bonds, it has fixed cash payments that are made on a predetermined schedule.
Why are preferred shares higher than bonds?
And for that reason they often trade like bonds, moving down in price when interest rates go up (and up when rates fall). Those high "coupons," however, can give preferred stock higher equity-type returns overall.
Why is credit quality important in preferred stock?
Because the preferred stock investors won't receive any payment in the event of a default or bankruptcy, the credit quality of the company is very important, he explains. Cautious investors may wish to stick with companies that have so-called investment grade ratings on their bonds.
Do preferred stock holders get paid in bankruptcy?
That bigger return is in part compensation for the additional risk taken on by the investor, because in the event of bankruptcy, preferred holders only get paid if there is any money left after bond obligations are settled.
Unique Features of Preferred Shares
- Preferred shares differ from common shares in that they have a preferential claim on the assets of the company. That means in the event of a bankruptcy, the preferred shareholders get paid before common shareholders.1 In addition, preferred shareholders receive a fixed payment th…
Growing Dividends
- If the dividend has a history of predictable growth, or the company states a constant growth will occur, you need to account for this. The calculation is known as the Gordon Growth Model. V=D(r−g)V=\frac{D}{(r-g)}V=(r−g)D By subtracting the growth number, the cash flows are discounted by a lower number, which results in a higher value.
Considerations
- Although preferred shares offer a dividend, which is usually guaranteed, the payment can be cut if there are not enough earnings to accommodate a distribution; you need to account for this risk. The risk increases as the payout ratio (dividend payment compared to earnings) increases. Also, if the dividend has a chance of growing, then the value of the shares will be higher than the result …
The Bottom Line
- Preferred shares are a type of equityinvestment that provides a steady stream of income and potential appreciation. Both of these features need to be taken into account when attempting to determine their value. Calculations using the dividend discount model are difficult because of the assumptions involved, such as the required rate of return, growth, or length of higher returns. Th…
Preferred Stock vs. Common Stock
How Preferred Stock Works
- Let's walk through an example to explain how you can make a steady income when you invest in preferred stock. Suppose that you buy 1,000 shares of preferred stock at $100 per share for a total investment of $100,000. Each share of preferred stock pays a $5 dividend, resulting in a 5% dividend yield (you get this percentage by dividing the $5 dividend by the $100 stock price). Tha…
The Formula
- Since the example involves a simple form of preferred stock, you own what is known as a "perpetuity," which is a stream of equal payments paid at regular intervals without an end date. There is a simple formula for valuing perpetuities and basic growth stocks called the Gordon Growth Model, or the Gordon dividend discount model. The formula is "k ÷ (i - g) = v."2In this equ…
The Calculation
- Here are some intrinsic value calculations for simple preferred stock. If the preferred stock has an annual dividend of $5 with a 0% growth rate (meaning that the company never increases or decreases the dividend), and you require a rate of return of 10%, the calculation would look like this: 1. $5 ÷ (0.10 - 0) 2. Simplified, this becomes $5 ÷ 0.10...
A Limitation to The Intrinsic Value Calculation
- One limitation of the intrinsic value formula is that you cannot have a growth ratethat exceeds your desired rate of return. If you do, your calculator will return an error or indicate infinity. That's because perpetuity is expected to last forever—from now until the end of time—and the math will back it up. If the rate of growth exceeds the required rate of return, the value of the investment is…