
- Calculating The P/E Ratio. The P/E ratio is calculated by dividing the market value price per share by the company's earnings per share.
- Analyzing P/E Ratios. As stated earlier, to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued, it should be compared to other stock in its sector or industry group.
- Limitations to the P/E Ratio. The first part of the P/E equation or price is straightforward as the current market price of the stock is easily obtained.
- PEG Ratio. A P/E ratio, even one calculated using a forward earnings estimate, does not always show whether or not the P/E is appropriate for the company's forecasted growth rate.
- Example of a PEG Ratio. An advantage of using the PEG ratio is that considering future growth expectations, we can compare the relative valuations of different industries that may have ...
- The Bottom Line. The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is one of the most common ratios used by investors to determine if a company's stock price is valued properly relative to its ...
How do you calculate PE ratio of a stock?
PE ratio is one of the most widely used tools for stock selection. It is calculated by dividing the current market price of the stock by its earning per share (EPS). So PE ratio cannot be considered to be a totally reliable indicator of cheap, good stocks. How do I calculate the PE ratio of a share?
Why does the PE ratio go up when the stock price jumps?
If its stock price jumps but its earnings stay the same (and no earnings increases are expected), the company’s intrinsic value didn’t change; the market’s perception of the company did. In this instance, the earnings in the PE ratio stayed the same, while the price soared, which mathematically sends the overall PE ratio higher.
Is the P/E ratio a useful metric for value investors?
By Joshua Kennon. Updated October 21, 2019. Value investors and non-value investors alike have long considered the price-earnings ratio, known as the p/e ratio for short, as a useful metric for evaluating the relative attractiveness of a company's stock price compared to the firm's current earnings.
What is the P/E of a stock?
In short, the P/E shows what the market is willing to pay today for a stock based on its past or future earnings. A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued. Conversely, a low P/E might indicate that the current stock price is low relative to earnings.
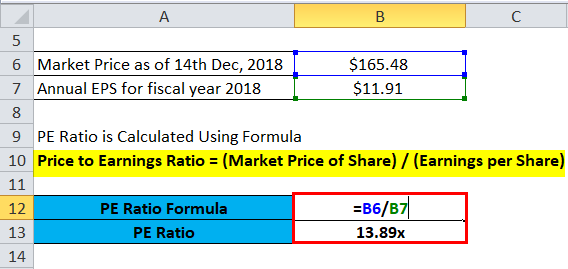
How do you value a stock using the PE ratio?
For example, if a company has earnings of $10 billion and has 2 billion shares outstanding, its EPS is $5. If its stock price is currently $120, its PE ratio would be 120 divided by 5, which comes out to 24. One way to put it is that the stock is trading 24 times higher than the company's earnings, or 24x.
What does PE tell you about a stock?
The price/earnings ratio, also called the P/E ratio, tells investors how much a company is worth. The P/E ratio simply the stock price divided by the company's earnings per share for a designated period like the past 12 months. The price/earnings ratio conveys how much investors will pay per share for $1 of earnings.
What should be PE ratio of a good stock?
As far as Nifty is concerned, it has traded in a PE range of 10 to 30 historically. Average PE of Nifty in the last 20 years was around 20. * So PEs below 20 may provide good investment opportunities; lower the PE below 20, more attractive the investment potential.
Is higher PE ratio better?
P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, is a quick way to see if a stock is undervalued or overvalued. And so generally speaking, the lower the P/E ratio is, the better it is for both the business and potential investors. The metric is the stock price of a company divided by its earnings per share.
Is a high PE ratio good?
In general, a high P/E suggests that investors are expecting higher earnings growth in the future compared to companies with a lower P/E. A low P/E can indicate either that a company may currently be undervalued or that the company is doing exceptionally well relative to its past trends.
Is 30 a good PE ratio?
P/E 30 Ratio Explained A P/E of 30 is high by historical stock market standards. This type of valuation is usually placed on only the fastest-growing companies by investors in the company's early stages of growth. Once a company becomes more mature, it will grow more slowly and the P/E tends to decline.
Is a negative PE ratio good?
A high P/E typically means a stock's price is high relative to earnings. A low P/E indicates a stock's price is low compared to earnings and the company may be losing money. A consistently negative P/E ratio run the risk of bankruptcy.
How do you know if a stock is undervalued?
Price-to-book ratio (P/B) To calculate it, divide the market price per share by the book value per share. A stock could be undervalued if the P/B ratio is lower than 1. P/B ratio example: ABC's shares are selling for $50 a share, and its book value is $70, which means the P/B ratio is 0.71 ($50/$70).
Price Earnings Ratio Formula
P/E = Stock Price Per Share / Earnings Per ShareorP/E = Market Capitalization / Total Net EarningsorJustified P/E = Dividend Payout Ratio / R – Gwh...
P/E Ratio Formula Explanation
The basic P/E formula takes current stock price and EPS to find the current P/E. EPS is found by taking earnings from the last twelve months divide...
Why Use The Price Earnings Ratio?
Investors want to buy financially sound companies that offer cheap shares. Among the many ratios, the P/E is part of the research process for selec...
Limitations of Price Earnings Ratio
Finding the true value of a stock cannot just be calculated using current year earnings. The value depends on all expected future cash flows and ea...
Why do investors use P/E?
Investors not only use the P/E ratio to determine a stock's market value but also in determining future earnings growth. For example, if earnings are expected to rise, investors might expect the company to increase its dividends as a result. Higher earnings and rising dividends typically lead to a higher stock price.
What is the P/E ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is one of the most common ratios used by investors to determine if a company's stock price is valued properly relative to its earnings. The P/E ratio is popular and easy to calculate, but it has shortcomings that investors should consider when using it to determine a stock's valuation.
Why is the PEG ratio important?
Since the P/E ratio does not factor in future earnings growth, the PEG ratio provides more insight into a stock's valuation. By providing a forward-looking perspective, the PEG is a valuable tool for investors in calculating a stock's future prospects.
How to tell if a stock is overvalued or undervalued?
As stated earlier, to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued, it should be compared to other stock in its sector or industry group. Sectors are made up of industry groups, and industry groups are made up of stocks with similar businesses such as banking or financial services.
What does a high P/E mean?
A high P/E could mean that a stock's price is high relative to earnings and possibly overvalued.
What is the first part of the P/E equation?
The first part of the P/E equation or price is straightforward as the current market price of the stock is easily obtained. On the other hand, determining an appropriate earnings number can be more difficult. Investors must determine how to define earnings and the factors that impact earnings. As a result, there are some limitations to the P/E ratio as certain factors can impact the P/E of a company. Those limitations include:
When to use PEG ratio?
Since stock prices are typically based on investor expectations of future performance by a company, the PEG ratio can be helpful but is best used when comparing if a stock price is overvalued or undervalued based on the growth in the company's industry.
How to find current P/E?
The basic P/E formula takes the current stock price and EPS to find the current P/E. EPS is found by taking earnings from the last twelve months divided by the weighted average shares outstanding#N#Weighted Average Shares Outstanding Weighted average shares outstanding refers to the number of shares of a company calculated after adjusting for changes in the share capital over a reporting period. The number of weighted average shares outstanding is used in calculating metrics such as Earnings per Share (EPS) on a company's financial statements#N#. Earnings can be normalized#N#Normalization Financial statements normalization involves adjusting non-recurring expenses or revenues in financial statements or metrics so that they only reflect the usual transactions of a company. Financial statements often contain expenses that do not constitute a company's normal business operations#N#for unusual or one-off items that can impact earnings#N#Net Income Net Income is a key line item, not only in the income statement, but in all three core financial statements. While it is arrived at through#N#abnormally. Learn more about normalized EPS#N#Normalized EPS Normalized EPS refers to adjustments made to the income statement to reflect the up and down cycles of the economy.#N#.
What does low P/E mean in stocks?
Companies with a low Price Earnings Ratio are often considered to be value stocks. It means they are undervalued because their stock price trade lower relative to its fundamentals. This mispricing will be a great bargain and will prompt investors to buy the stock before the market corrects it. And when it does, investors make a profit as a result of a higher stock price. Examples of low P/E stocks can be found in mature industries that pay a steady rate of dividends#N#Dividend A dividend is a share of profits and retained earnings that a company pays out to its shareholders. When a company generates a profit and accumulates retained earnings, those earnings can be either reinvested in the business or paid out to shareholders as a dividend.#N#.
What is justified P/E ratio?
The justified P/E ratio#N#Justified Price to Earnings Ratio The justified price to earnings ratio is the price to earnings ratio that is "justified" by using the Gordon Growth Model. This version of the popular P/E ratio uses a variety of underlying fundamental factors such as cost of equity and growth rate.#N#above is calculated independently of the standard P/E. In other words, the two ratios should produce two different results. If the P/E is lower than the justified P/E ratio, the company is undervalued, and purchasing the stock will result in profits if the alpha#N#Alpha Alpha is a measure of the performance of an investment relative to a suitable benchmark index such as the S&P 500. An alpha of one (the baseline value is zero) shows that the return on the investment during a specified time frame outperformed the overall market average by 1%.#N#is closed.
What is a growth stock?
Companies with a high Price Earnings Ratio are often considered to be growth stocks. This indicates a positive future performance, and investors have higher expectations for future earnings growth and are willing to pay more for them. The downside to this is that growth stocks are often higher in volatility, and this puts a lot of pressure on companies to do more to justify their higher valuation. For this reason, investing in growth stocks will more likely be seen as a risky#N#Risk Aversion Risk aversion refers to the tendency of an economic agent to strictly prefer certainty to uncertainty. An economic agent exhibiting risk aversion is said to be risk averse. Formally, a risk averse agent strictly prefers the expected value of a gamble to the gamble itself.#N#investment. Stocks with high P/E ratios can also be considered overvalued.
What is the difference between EPS and fair value?
It is a popular ratio that gives investors a better sense of the value. Fair Value Fair value refers to the actual value of an asset - a product, stock, or security - that is agreed upon by both the seller and the buyer.
What is it called when you own stock?
An individual who owns stock in a company is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever be dissolved). The terms "stock", "shares", and "equity" are used interchangeably. of different prices and earnings levels.
What is fair value in accounting?
Fair value is applicable to a product that is sold or traded in the market where it belongs or under normal conditions - and not to one that is being liquidated. of the company. The P/E ratio shows the expectations of the market and is the price you must pay per unit of current earnings. Net Income Net Income is a key line item, ...
How to find a company's PE ratio?
To arrive at a company’s PE ratio, you’ll need to first know its EPS, which is calculated by dividing the company’s net profits by the number of shares of common stock it has outstanding. Once you have that, you can divide the company’s current share price by its EPS.
What is a PE ratio?
A company’s price-to-earnings ratio, or PE ratio, is a single number that packs a lot of punch, and one of the most common ways to value a company’s stock shares.
Why is PE ratio low?
For businesses that are highly cyclical, a low PE ratio may signal an undervalued stock, when in reality, it’s been operating in a period of high earnings that’s about to end.
What does a low PE ratio mean?
A low PE ratio may signal that the stock price doesn’t accurately reflect the true value of the company based on its earnings. In this instance, the stock price may stay the same while the company’s earnings increase, which would send the PE ratio lower. Investors may see this as an opportunity to buy the stock with the expectation ...
Why is a stock's PE ratio higher than its historical ratio?
If a stock’s PE ratio is significantly higher than those of other similar companies — or even than the company’s own historical PE ratio — it could be due to growth prospects, but it’s also possible the stock is overvalued.
What happens if a company's stock price jumps?
If its stock price jumps but its earnings stay the same (and no earnings increases are expected), the company’s intrinsic value didn’t change; the market’s perception of the company did.
Do higher PE ratios mean higher growth?
According to Robert Johnson, a chartered financial analyst and CEO of Economic Index Associates in New York, higher PE ratios often go hand-in-hand with such growth stocks. “Typically, stocks selling at higher PE ratios have higher growth expectations than those selling at lower PE ratios,” Johnson says.
Why use P/E ratio?
You can use P/E ratios to calculate a stock’s actual market value and to compare it with other stocks in the same industry.
What is industry average P/E?
The industry average P/E ratio is only a guide to estimate a stock’s relative value. Some stocks continually trade at a P/E that differs from the industry average and might never align with their competitors.
What is the price to earnings ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio is one of the most common financial ratios used to value stocks. This ratio measures the price investors are willing to pay for each dollar of the company’s earnings per share, or EPS. When investors like a company’s future growth potential, they will typically pay more for its stock, resulting in a high P/E ratio.
Why do high risk companies have a low P/E?
When investors like a company’s future growth potential, they will typically pay more for its stock, resulting in a high P/E ratio. High-risk companies with bleak outlooks typically trade at a low P/E. You can use P/E ratios to calculate a stock’s actual market value and to compare it with other stocks in the same industry.
Absolute PE Model by Vitaliy Katsenelson
Back in 2011, I got around to reading and applying Vitaliy Katsenelson’s book Active Value Investing which I also list in my best investment books for value investors.
Understanding the Absolute PE Model
This valuation model derives the intrinsic value of a stock based on the following five conditions.
Qualitative Aspects of the Absolute PE Value Model
Before moving onto examples of how this model is used, a couple of points made in the book should be discussed.
Summing Up: A Valuation Model to Add to Your Toolbox
Every company is unique and you can’t and shouldn’t use a DCF for every stock.
Why use P/E ratio?
The most common use of the P/E ratio is to gauge the valuation of a stock or index. The higher the ratio, the more expensive a stock is relative to its earnings. The lower the ratio, the less expensive the stock. In this way, stocks and equity mutual funds can be classified as “growth” or “value” investments.
What is the Shiller P/E ratio?
A third approach is to use average earnings over a period of time. The most well known example of this approach is the Shiller P/E ratio, also known as the CAP/E ratio (cyclically adjusted price earnings ratio).
Is Shiller PE a good predictor of future returns?
A recent study found that the Shiller PE was a reliable predictor of market returns between 1995 and 2020. In contrast, a recent Vanguard study found that the Shiller PE and other P/E ratio measures “had little or no correlation with future stock returns.”.
What does 3x PE mean?
For instance, a PE ratio of 3x means means the intrinsic value of the company is three times earnings. You can compare these ratios to those of other companies in the same industry to get a sense of how the company is valued. It's one tool you can use in determining which stocks to buy and sell.
How to determine relative value of a company?
You can determine the relative value of a company by comparing its PE or PB to other firms operating in the same industry. Through the use of a PE or PB multiplier, you will be able to determine whether or not a company is over or undervalued.
Why do stocks have high P/E?
The reason stocks tend to have high P/E ratios is that investors try to predict which stocks will enjoy progressively larger earnings. An investor may buy a stock with a P/E ratio of 30 if they think it will double its earnings every year (shortening the payoff period significantly).
Why do investors use the PEG ratio?
Because the P/E ratio isn't enough in and of itself, many investors use the price to earnings growth (PEG) ratio. Instead of merely looking at the price and earnings, the PEG ratio incorporates the historical growth rate of the company's earnings. This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock.
Why are dividend stocks attractive?
It's always nice to have a back-up when a stock's growth falters. This is why dividend-paying stocks are attractive to many investors—even when prices drop, you get a paycheck. The dividend yield shows how much of a payday you're getting for your money. By dividing the stock's annual dividend by the stock's price, you get a percentage. You can think of that percentage as the interest on your money, with the additional chance at growth through the appreciation of the stock.
What does a PEG ratio mean?
A PEG of 1 means you're breaking even if growth continues as it has in the past.
Why is a low P/B ratio good?
In either case, a low P/B ratio can protect you— but only if it's accurate. This means an investor has to look deeper into the actual assets making up the ratio.
What is book value?
The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds. With purely financial firms, the book value can fluctuate with the market as these stocks tend to have a portfolio of assets that goes up and down in value.
What is the P/B ratio?
Made for glass-half-empty people, the price-to-book (P/B) ratio represents the value of the company if it is torn up and sold today. This is useful to know because many companies in mature industries falter in terms of growth, but they can still be a good value based on their assets. The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds.
