4 ways to tell if a stock is overvalued
- Valuation multiples are elevated. One of the quickest ways to get a gauge of a company’s valuation is to look at...
- Company insiders are selling. Another way to tell if a company might be overvalued is to pay attention to what...
- PEG ratio. The price-to-earnings growth ratio, or PEG, is a way to compare the P/E ratio to a...
How to determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued?
Key things to look out for are:
- Price to earnings (P/E ratio)
- Earnings per share (EPS)
- Price to book (P/B ratio)
- Operating profit margin
- Debt ratios
- Dividend payout ratio
What does it mean if a stock is overvalued?
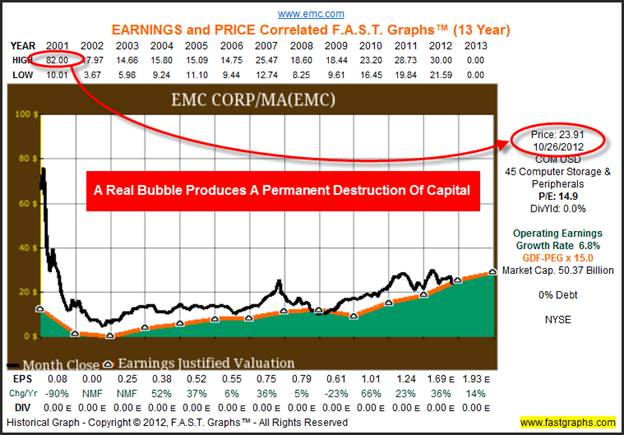
Overvalued stocks are those stocks whose current price does not do justice to the earning potential and have an inflated PE Ratio as compared to its fundamental value (found using DCF valuation, Comparable Comps) and therefore, analysts expect its share price to fall sharply in a market with due course of time.
Is the market really overvalued?
There is one final way of determining whether the market is overvalued or not, and it relies on the fact that, at the end of the day, when something is overvalued, it’s all relative, and you need to compare it to what you could otherwise do with those same money.
Is the stock market still a good investment?
This year has been rough so far for the stock market ... When you're investing more heavily in bonds and other conservative investments, a market crash is less likely to wreck your retirement plans. That said, it's still wise to invest at least a portion ...
/financial-services--viewing-financial-markets-for-investing-507826251-5b74b591c9e77c0050d56369.jpg)
How do you know if something is overvalued or undervalued?
If the value of an investment (i.e., a stock) trades exactly at its intrinsic value, then it's considered fairly valued (within a reasonable margin). However, when an asset trades away from that value, it is then considered undervalued or overvalued.
What makes a stock overvalued?
An overvalued stock has a current price that is not justified by its earnings outlook, typically assessed by its P/E ratio. A company is considered overvalued if it trades at a rate that is unjustifiably and significantly in excess of its peers.
What are signs of an undervalued stock?
The lower the PEG, the more the company's shares are considered cheap. If the indicator is between 0 and 1, the company is probably undervalued. When it's more than 1, it could be overvalued. If it's negative, it means the company is at a loss, or that its profits are expected to decrease!
What is good PE ratio?
A “good” P/E ratio isn't necessarily a high ratio or a low ratio on its own. The market average P/E ratio currently ranges from 20-25, so a higher PE above that could be considered bad, while a lower PE ratio could be considered better.
Is it OK to buy overvalued stocks?
Buying overvalued stocks can be risky, as they might drop closer to their intrinsic value at any time, especially over the short term. Yes, over the long term, the intrinsic value of healthy and growing companies will grow. But it's still possible to simply pay too much for a stock.
How do you identify stocks that will go up?
Pay attention to the stocks other people recommend and search their tickers on Google, and see what comes up. A more advanced approach involves using a stock screener to find stocks that fit certain criteria (i.e. EPS growth, recent stock price movement, sector, revenue growth, and other factors).
How do you know if a stock is worth buying?
Here are nine things to consider.Price. The first and most obvious thing to look at with a stock is the price. ... Revenue Growth. Share prices generally only go up if a company is growing. ... Earnings Per Share. ... Dividend and Dividend Yield. ... Market Capitalization. ... Historical Prices. ... Analyst Reports. ... The Industry.More items...
Should you buy a stock if its undervalued?
If you believe that a stock is undervalued, you should invest in it because the stock's price will eventually increase to its fair value. This approach is less risky than trading overvalued stocks because you are investing in a company that has been incorrectly priced by the market.
Why use ratios in stock valuation?
Key Takeaways. Ratios can be used for an estimation of a stock’s value. Stock ratio values can be faster and easier options than fundamental intrinsic value models. Alternative ratio methods can help in estimating the value of a non-public company or a company in distress.
What is stock ratio analysis?
Stock ratio analysis can provide a quick look at the reasonability of a stock’s price, as well as its likelihood of being overvalued or undervalued. Analysts can also use ratios in fundamental intrinsic value models.
What does a PEG ratio mean?
The degree to which a PEG ratio value indicates an over or underpriced stock varies by industry and by company type. Also, a PEG ratio below one is typically thought to indicate that a stock may be underpriced, but this can vary by industry.
What is P/E valuation?
In general, P/E is often classified as a type of valuation ratio. Given a company’s historical earnings per share results, it could be easy for an investor to find an estimated price per share of a stock using the average of P/Es from some comparable companies.
Is intrinsic value the same as current market value?
The intrinsic value is usually different than the current market value. While intrinsic value is often relied on as a base case, many investors and analysts often use a variety of ratios for providing a quicker and easier estimation of a stock’s price. Ratio analysis is also often viewed in conjunction with intrinsic value calculations.
What is an overvalued stock?
An overvalued stock is the opposite of an undervalued stock. When a stock is undervalued, it trades at a share price that’s below what the stock is actually worth. This type of stock is typically most appealing to value investorswho rely on a buy-and-hold strategy. Shorting Overvalued Stock in a Volatile Market.
What to do if stocks are overvalued?
If stocks are overvalued, employing a shorting strategy could help you reap gains in your portfolio, but it’s not without its risk. Short-sellinginvolves borrowing stocks, selling them at their current price, then repurchasing them later at a lower price so you can return them to the investment firm you borrowed from.
What does a higher PEG mean?
A higher PEG can signify an overvalued stock, while a lower PEG can mean a stock is undervalued. Price-to-dividend ratio. If the stock in question pays dividendsto investors, you might also consider the price-to-dividend ratio to determine value.
Can you lose money investing in overvalued stocks?
You may invest in a stock that you think is certain to drop in price, but if that doesn’t happen and the stock’s price actually begins to rise instead, you could lose money. That’s why knowing how to identify overvalued stocks is so important.
Why is a stock overvalued?
A stock is essentially overvalued when the market capitalization isn’t supported by profits. Of course, there are a lot of ways to look at profit margins, and three are commonly used by companies to explain their financials: 1. Price-Earnings.
How much can a company trade for in the S&P 500?
This is true of any major company in the S&P 500, although some companies can trade for as high as 50 times earnings or more . The reason this often occurs is because of the valuation method used. Let’s look at each of the three commonly used evaluation methods to explain why they’re used and what they really show.
How does reputation affect stock value?
For example, a stock that has been recently purchased by high profile individuals can be overvalued by the market . In general, stocks that are attracting a lot of attention from industry-relevant media outlets and well-known investors can sell for an inflated price due to the hype surrounding them. Take the profile of a stock into consideration when calculating its true value.
Why is it important to know the indicators of inflated valuations?
It's imperative to carefully research every stock in which you are considering investing and to know the indicators of inflated valuations so that you can save time, effort and money. These five elements of stock assessment will give you a better understanding of how to identify a potentially overvalued stock.
How To Tell If A Stock Is Overvalued
Numerous metrics indicate the stock market is richly valued. Nowadays, it’s easy to find stocks carrying lofty valuations. However, some stocks present less attractive risk-reward ratios than others.
Compare Valuation Numbers
The valuation numbers give us a quick glimpse into the stock’s valuation. Comparing the valuation numbers of appropriate companies will shed light on a stock’s valuation prospects.
Understand The Company
Digging through the numbers and listening to earnings calls are the two best ways to fully understand a company. Media articles present a narrow glimpse of a company’s prospects and overall future. They pull their information from the earnings calls and reviewing a stock’s numbers. Go to the source to learn more about a stock.
Inflation Is Coming
Inflation is rearing its ugly head into the economy. Even though inflation hasn’t received much attention from the media, it’s easy to spot in the grocery store, barber shop, and everywhere in between.
What does it mean when a stock is overvalued?
An overvalued stock is one that is currently trading at a valuation that is too high, considering the company’s fundamentals. This occurs because investors bid up the stock price based on future assumptions for the stock and/or sector. Catalysts for these assumptions include new products, projected growth. and hype surrounding the sector.
Why is a stock undervalued?
At times, a stock may be undervalued because investors are ignoring the name or segment or simply don’t want exposure to the sector.
What does a PEG ratio of 1.0 mean?
A PEG ratio greater than 1.0 means that the stock is overvalued, while below 1.0 means is is undervalued. When the PEG ratio is exactly 1.0, then the stock is trading at fair valuation.
What to look for when investing in a stock?
Before investing in a stock, it is important to look at the debt picture of the company. Even if a business has a high growth rate, the balance sheet may have a lot of debt. If everything does not go as planned for the company, there will be still be obligations to pay back the debt.
Is a stock down over time?
The answer is not simply looking at a stock chart and seeing how a company’s stock has performed over a certain period. If a stock is down over time, it does not mean the stock is undervalued, but requires a little bit more research. There is no need to be overwhelmed; you don’t need an MBA or Ph.d to determine if a stock is overvalued ...
Is it important to view quarterly results?
If you are looking to buy or sell a stock, it is still important to view the business’ quarterly results. Also take the time to consider the viewpoint of management regarding the current and future business environments. This could have a big impact your on your overall return.
Do I need an MBA to know if a stock is overvalued?
There is no need to be overwhelmed; you don’t need an MBA or Ph.d to determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued. There are times a stock could be trading at a multi-year low and actually be overvalued, while the opposite–being undervalued while trading at an all-time high—could occur as well. Advertisement.
How to assess the value of a stock?
Generally speaking, there are two primary approaches in how you can assess the value of a stock. The first is absolute valuation (also called intrinsic valuation), in which you try to estimate a certain value of an asset based on its fundamental characteristics.
What does it mean when the stock price is lower than its fair value?
3. Price < Value. The current stock price is lower than its fair value, meaning that the stock is undervalued.
How is the PEG ratio calculated?
The PEG ratio is calculated by dividing the P/E ratio by the EPS growth estimate of the company:
What does a PEG ratio of 1 mean?
In theory, a PEG ratio of below 1 suggests that the company is undervalued, while a PEG ratio of 1 should reflect a fairly valued stock, A PEG ratio above 1 would indicate that the stock is rather overvalued.
What are the flaws in the P/E ratio?
A major flaw of the P/E ratio is its lack of any future assumptions. In its basic form, the only two components of the price-to-earnings ratio are the recent earnings and the current stock price.
What is the most commonly used metric when it comes to investing?
The most commonly used metric when it comes to investing is the price-to-earnings ratio. The earnings multiple reflects the current price of a stock in relation to the earnings of the company in a quick and easily understandable way.
Which stocks have higher P/E?
Different companies across multiple industry sectors will have different standards of P/Es. For example, a tech stock such as Netflix ( NFLX) will generally have a much higher P/E ratio than a financial company like JPMorgan ( JPM ).
Ratios and Sectors
P/E Ratio
- The price-to-earnings ratio(P/E) can have multiple uses. By definition, it is the price a company’s shares trade at divided by its earnings per share (EPS) for the past twelve months. The trailing P/E is based on historical results, while forward P/E is based on forecasted estimates. In general, P/E is often classified as a type of valuation ratio. Given a company’s historical earnings per sharere…
Peg Ratio
- The price-to-earnings growth ratio (PEG) is an extended analysis of P/E. A stock's PEG ratio is the stock's P/E ratio divided by the growth rate of its earnings. It is an important piece of data to many in the financial industry as it takes a company's earnings growth into account, and tends to provide investors with a big picture view of profitability growth compared to the P/E ratio.2 Whil…
Price-to-Book
- The price to book(P/B) is another ratio that incorporates a company’s share price into the equation. The price to book is calculated by share price divided by book value per share. In this ratio, book value per share is equal to a company’s shareholder’s equity per share, with shareholders’ equity serving as a quick report of book value. Similar to P/E, the higher the P/B, th…
Price-To-Dividend
- The price-to-dividend ratio (P/D) is primarily used for analyzing dividend stocks. This ratio indicates how much investors are willing to pay for every $1 in dividend payments the company pays out over twelve months. This ratio is most useful in comparing a stock's value against itself over time or against other dividend-paying stocks.4
Alternative Methods Using Ratios
- Some companies don’t have operating income, net income, or free cash flow. They also may not expect to generate any of these metrics far into the future. This can be likely for private companies, companies recently listing initial public offerings, and companies that may be in distress. As such, certain ratios are considered to be more comprehensive than others and there…