
- Log into your brokerage account or trading software.
- Select the ticker symbol of the stock you want to bet against.
- Enter a regular sell order to initiate the short position, and your broker will locate the shares to borrow automatically.
- After the stock goes down, you enter a buy order to buy the stock back.
- When you buy the stock back, you automatically return it to the lender and close the short position.
- If you buy the stock back at a lower price than you sold it at, then you pocket the difference and make a profit.
How to make money shorting a stock?
Mar 30, 2020 · These are the six steps to sell a stock short: Log into your brokerage account or trading software. Select the ticker symbol of the stock you want to bet against. Enter a regular sell order to initiate the short position, and your broker will locate the shares to borrow... After the stock goes down, ...
What is the best way to short a stock?
Mar 13, 2022 · One way to make money on stocks for which the price is falling is called short selling (also known as "going short" or "shorting"). Short selling sounds like a …
What does it mean to 'short' a stock?
Jan 10, 2022 · In order to use a short-selling strategy, you have to go through a step-by-step process: Identify the stock that you want to sell short. Make sure that you have a margin account with your broker and the necessary permissions to open a short position in a... Enter your short order for the appropriate ...
What stocks should I short sell?
Mar 14, 2022 · Short selling is—in short—when you bet against a stock. You first borrow shares of stock from a lender, sell the borrowed stock, and then buy back the shares at a lower price assuming your speculation is correct. You then pocket the difference between the sale of the borrowed shares and the repurchase at a lower price. Short selling for dummies
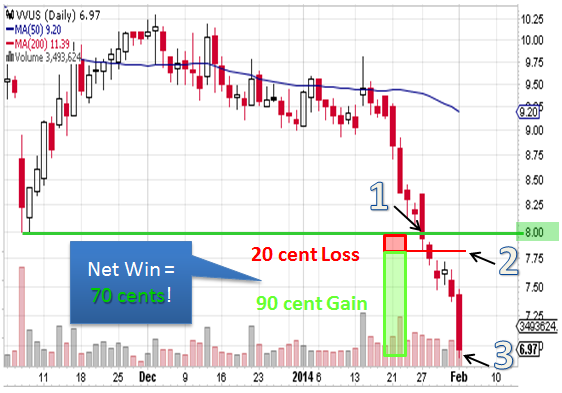
How much money you need to short a stock?
Initial Margin Since shorting a stock requires a margin account, this minimum margin requirement applies to short sales as well. Many firms, including Charles Schwab and Fidelity, require you to have at least $5,000 in your account if you want to sell a stock short.
Can I short a stock I own?
A short sell against the box is the act of short selling securities that you already own, but without closing out the existing long position. This results in a neutral position where all gains in a stock are equal to the losses and net to zero.
What happens if you short a stock and it goes up?
When a stock is heavily shorted, and investors are buying shares — which pushes the price up — short sellers start buying to cover their position and minimize losses as the price keeps rising. This can create a “short squeeze”: Short sellers keep having to buy the stock, pushing the price up even higher and higher.Jan 29, 2021
What happens if you can't cover a short?
Short covering is closing out a short position by buying back shares that were initially borrowed to sell short using buy to cover orders. Short covering can result in either a profit (if the asset is repurchased lower than where it was sold) or for a loss (if it is higher).
Short-term strategy
Selling short is primarily designed for short-term opportunities in stocks or other investments that you expect to decline in price.
A short trade
Let's look at a hypothetical short trade. Assume that on March 1, XYZ Company is trading at $50 per share. If a trader expects that the company and its stock will not perform well over the next several weeks, XYZ might be a short-sell candidate.
Timing is important
Short-selling opportunities occur because assets can become overvalued. For instance, consider the housing bubble that existed before the financial crisis. Housing prices became inflated, and when the bubble burst a sharp correction took place.
A tool for your strategy
Shorting can be used in a strategy that calls for identifying winners and losers within a given industry or sector. For example, a trader might choose to go long a car maker in the auto industry that they expect to take market share, and, at the same time, go short another automaker that might weaken.
Be careful
The process of shorting a stock is relatively simple, yet this is not a strategy for inexperienced traders. Only knowledgeable, practiced investors who know the potential implications should consider shorting.
Example of a Short Sale
For example, if an investor thinks that Tesla (TSLA) stock is overvalued at $625 per share, and is going to drop in price, the investor may "borrow" 10 shares of TSLA from their broker, who then sells it for the current market price of $625.
What Are the Risks?
Short selling involves amplified risk. When an investor buys a stock (or goes long), they stand to lose only the money that they have invested. Thus, if the investor bought one TSLA share at $625, the maximum they could lose is $625 because the stock cannot drop to less than $0. In other words, the maximum value that any stock can fall to is $0.
Why Do Investors Go Short?
Short selling can be used for speculation or hedging. Speculators use short selling to capitalize on a potential decline in a specific security or across the market as a whole. Hedgers use the strategy to protect gains or mitigate losses in a security or portfolio.
When Does Short Selling Make Sense?
Short selling is not a strategy used by many investors largely because the expectation is that stocks will rise in value. The stock market, in the long run, tends to go up although it certainly has its periods where stocks go down.
If you've ever wanted to make money from a company's misfortune, selling stocks short can be a profitable -- though risky -- way to invest
Matt is a Certified Financial Planner based in South Carolina who has been writing for The Motley Fool since 2012. Matt specializes in writing about bank stocks, REITs, and personal finance, but he loves any investment at the right price. Follow him on Twitter to keep up with his latest work! Follow @TMFMathGuy
Why would you short a stock?
Typically, you might decide to short a stock because you feel it is overvalued or will decline for some reason. Since shorting involves borrowing shares of stock you don't own and selling them, a decline in the share price will let you buy back the shares with less money than you originally received when you sold them.
How do you short a stock?
In order to use a short-selling strategy, you have to go through a step-by-step process:
A simple example of a short-selling transaction
Here's how short selling can work in practice: Say you've identified a stock that currently trades at $100 per share. You think that stock is overvalued, and you believe that its price is likely to fall in the near future. Accordingly, you decide that you want to sell 100 shares of the stock short.
What are the risks of shorting a stock?
Keep in mind that the example in the previous section is what happens if the stock does what you think it will -- declines.
Be careful with short selling
Short selling can be a lucrative way to profit if a stock drops in value, but it comes with big risk and should be attempted only by experienced investors. And even then, it should be used sparingly and only after a careful assessment of the risks involved.
What Is Short Selling
Short selling, or to "sell short," means that an investor, or short seller, borrows shares/units of an investment security, usually from a broker, and sells the borrowed security, expecting that the share price will fall. If the share price does fall, the investor buys those same shares/units back at a lower price and can make a profit.
Risks of Shorting a Stock
Short-selling is primarily a short-term investment strategy designed for stocks or other investment securities expected to decline in price. The main risk associated with shorting a stock is that the shares will increase in price. Other risks of shorting a stock include margin calls and forced short covering.
Requirement to Short a Stock
Shorting stock requires a margin account because short selling involves selling stock that is borrowed and not owned. Because of this, margin accounts have strict requirements, such as the "initial margin requirement," which is a minimum amount of money that needs to be in the account at the time of the trade.
Cost of Borrowing
The cost of borrowing a stock to short can vary but typically ranges from 0.3% to 3% per year. The fees are applied on a daily basis. The borrowing fee can be much higher than 3%, and can even exceed 100% in extraordinary cases, as it is influenced by multiple factors. For example, similar to loan costs, the lender charges a leasing rate.
Examples of Shorting a Stock
A good way to learn about short selling is to consider a few examples - one where the stock seller makes a profit, and another where the short seller experiences a loss.
Synthetic Short Stock Alternative
A synthetic short stock alternative is an options strategy where an investor buys a put option and sells a call option at an equal or nearly equal strike price. Following this strategy, the investor profits if the stock price falls.
Frequently Asked Questions
Brokers typically provide a list of stocks that are available for shorting. They may break out the lists by separating the stocks as either "easy-to-borrow" or "hard-to-borrow."
A Beginner's Guide for How to Short Stocks
Joshua Kennon is an expert on investing, assets and markets, and retirement planning. He is the managing director and co-founder of Kennon-Green & Co., an asset management firm.
Why Sell Short?
Usually, you would short stock because you believe a stock's price is headed downward. The idea is that if you sell the stock today, you'll be able to buy it back at a lower price in the near future.
How Shorting Stock Works
Usually, when you short stock, you are trading shares that you do not own.
What Are the Risks of Short Selling?
When you short a stock, you expose yourself to a large financial risk.
How Is Short Selling Different From Regular Investing?
Shorting a stock has its own set of rules, which are different from regular stock investing, including a rule designed to restrict short selling from further driving down the price of a stock that has dropped more than 10% in one day, compared to the previous day's closing price. 4
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In theory, you can short a stock as long as you want. In practice, shorting a stock involves borrowing stocks from your broker, and your broker will likely charge fees until you settle your debt. Therefore, you can short a stock as long as you can afford the costs of borrowing.
What Is Shorting a Stock?
Short selling amounts to betting that a given stock will decline in value - in Wall Street lingo, that's called having a "short" possession. Having a "long" possession means you actually own the stock, and are betting that it will rise in value.
Why Would You Short a Stock?
The fact is, the investors most likely to short a stock are deep-pocketed ones - think pension funds, stock brokerage firms, hedge funds, and other institutional investors. They may be speculating about a stock, but it's just as likely they'll short a stock for other, more defensive-minded reasons from a portfolio management point of view.
How to Short a Stock in Five Steps
Although the myriad moving parts involved in a short sale make the process risky, the actual steps needed to execute a complete short sale are fairly direct. Here's how to get the job done:
The Aftermath of a Short Stock Deal
The good news, in theory, is that it doesn't take too long to figure out if you're going to make a profit on a short sale.
Buyer Beware
In a unique way, a short sale amounts to the old retail warning about "buyer beware."
What Is Short Selling?
Before I explain short selling, let’s do a brief refresher course on investing in the stock market …
How to Short A Stock
You’ll need a margin account to short stocks, which means that you’re able to borrow shares in a stock from your broker.
How Do You Short a Stock on E-Trade or Robinhood?
The process of shorting a stock on E-Trade is pretty much the same as shorting shares on TD Ameritrade.
4 Short Selling (Shorting) Tips
Learning this takes time, but you can potentially shorten the learning curve by paying attention to the pros. Let’s look at some of the key factors to keep in mind when shorting stocks with TD Ameritrade and other brokers.
Trading Challenge
If you’re serious about the stock market and its potential impact on your finances, join the Trading Challenge. It’s my way of nurturing the new generation of investors — hungry, eager people who have specific goals and dreams.
The Bottom Line
Learning short selling can help make you a more prolific and profitable trader. I do it all the time because I know I can make money from it.
Technical Trends
Look at a chart of the stock you are thinking about shorting. What is the general trend? Is the stock under accumulation or distribution ?
Estimates Ratcheted Down
When a company misses its quarterly earnings estimates, management will usually try to explain to investors what happened in a conference call or press release. Following this, Wall Street analysts work to compose a report and distribute it to their brokers.
Tax-Loss Selling on the Horizon
In the fourth quarter, you will note that companies trading in the lower end of their 52-week trading range will often trade even lower. This is because individuals and mutual funds want to book some of their losses before year-end to reap the tax benefits.
Insider Selling
There are plenty of reasons why an insider might sell his or her stock. This may include buying a home or simply a desire to book some profits. However, if a number of insiders are selling the stock in large quantities, it may be a wise move to view this as a harbinger of things to come.
Fundamentals Deteriorating
You don't need to find a company that is on the verge of bankruptcy to successfully short its stock. Sometimes you need to see only a mild deterioration in a company's overall fundamentals for big holders of the stock, such as mutual funds, to get fed up and dump the shares.
Declining Sector Trends
While a company will occasionally buck a larger trend, most companies within a given sector or industry trade in relative parity. That means supply and demand issues facing one company are likely to impact others at some point down the road. Use this information to your advantage. Make phone calls to a company's suppliers and/or customers.
The Bottom Line
Investors need to be aware not only that short selling presents an opportunity to generate tangible gains, but also that signals can alert an investor when a stock is about to take a fall. This knowledge will make you an immeasurably better investor.

Short-Term Strategy
A Short Trade
- Let's look at a hypothetical short trade. Assume that on March 1, XYZ Company is trading at $50 per share. If a trader expects that the company and its stock will not perform well over the next several weeks, XYZ might be a short-sell candidate. To capitalize on this expectation, the trader would enter a short-sell order in their brokerage account. When filling in this order, the trader ha…
Timing Is Important
- Short-selling opportunities occur because assets can become overvalued. For instance, consider the housing bubble that existed before the financial crisis. Housing prices became inflated, and when the bubble burst a sharp correction took place. Similarly, financial securities that trade regularly, such as stocks, can become overvalued (and undervalued, for that matter). The key to …
A Tool For Your Strategy
- Shorting can be used in a strategy that calls for identifying winners and losers within a given industry or sector. For example, a trader might choose to go long a car maker in the auto industry that they expect to take market share, and, at the same time, go short another automaker that might weaken. Shorting may also be used to hedge (i.e., reduce exposure to) existing long positi…
Be Careful
- The process of shorting a stock is relatively simple, yet this is not a strategy for inexperienced traders. Only knowledgeable, practiced investors who know the potential implications should consider shorting.