First, contact the company to obtain permission to sell your shares. Also, you'll need agreement on the manner of sale. The company can provide you with a valuation of its stock.
Should I hold company stock in my 401k?
Should you hold your own employer’s stock in your 401K? The conventional answer, and my default response, is… no. However that is a topic that is worth some discussion. While I wouldn’t encourage you to buy your employer’s stock in your 401k plan it doesn’t necessarily follow that you should immediately sell it if you already own it.
What company has the best 401K?
Although the 401K has traditionally performed for some individuals ... Now, your next step is finding the best gold IRA company to invest with. Goldco is our No. 1 choice for many reasons. It is currently the leading precious metal IRA company in the ...
Is a 401k really worth investing in?
One of the greatest benefits of a 401 (k) comes from employer matches on contributions. If you're lucky, your company will agree to match your contributions up to a certain amount. You should almost always meet the company match. It's basically free money.
Can you hold private company stock in a 401k plan?
The plan document does not mandate investment in company stock or offering it in the plan.

Do you pay capital gains tax on 401(k)?
Under the right circumstances, you pay only the capital gains tax rate on appreciation, rather than regular income rates.
Does 401(k) help with taxes?
As you probably know, a 401 (k) plan allows pre-tax money to be invested, which reduces your taxable income and helps you pay a lower tax bill the year it was earned .
Is 401(k) withdrawal taxed?
Because the money has never been taxed, when you make trades within a 401 (k) plan, those trades do not create a taxable event, since you square up with the IRS upon withdrawal in retirement.
Do you pay taxes on 401(k) in-kind?
Under the NUA treatment, if you withdraw your company shares from the 401 (k) in-kind (that is, as shares rather than dollars) into a regular brokerage account, you pay regular income tax only on the amount up to your cost basis in the stock.
Why do you rollover assets?
If a significant portion of your wealth is held in company stock, you may want to rollover the assets to improve your tax-deferred portfolio’s diversification.
How much can a max rollover into an IRA?
Have the stock distributed in-kind and sell it. Max can rollover $500,000 into a Traditional IRA, and have the $250,000 in company stock distributed in-kind to a taxable account. If he sells the stock immediately, he’ll owe ordinary income tax on $50,000, and long term capital gains tax on $200,000 (provided that the stock in question was held for at least a year and a day).
Can a stock lose value?
It’s important to note that the stock could gain or lose value or the capital gains rates could change over time. If the stock loses value or the capital gains rates increase, then some or all of the tax advantage gained through an NUA strategy could be lost.
Can Max rollover a 750,000 IRA?
Max can rollover the $750,000 account balance into a Traditional IRA, and owe ordinary income tax when he takes distributions. Possible tax ramifications: If you assume a 28% tax bracket for Max, and the value of the account remains constant, he’ll pay about $210,000 in taxes over time.
Can Max sell his stock in kind?
Have the stock distributed in-kind and hold it. Alternatively, Max could take the stock in-kind and not sell it. He’ll still owe ordinary income taxes on the $50,000 cost basis, since it is a distribution from his retirement plan, but the NUA remains untaxed until Max sells the shares and the gains are realized.
Can you rollover 401(k) to IRA?
Any additional earnings may grow tax-deferred and, when distributions are taken, the money will be taxed as ordinary income. However, a rollover into an IRA may not be the most beneficial choice for participants who count appreciated company stock among their 401 (k) plan assets because it may be possible to take advantage of a potential tax break related to net unrealized appreciation. This option is explained explicitly in IRC Section 402 (e) (4).
Why do you liquidate a company's stock?
In addition, the rules regarding net unrealized appreciation are another reason why investors might take a deliberate approach to liquidating company stock. Blanchett says investors who hold company stock in their 401 (k)s will have to weigh the potential tax savings of being able to take advantage of the NUA rules against the loss of diversification that accompanies holding a substantial stake in company stock. A tax advisor can provide guidance for the best course of action; the longer your time horizon to liquidation, the greater the risk of a high allocation to employer stock.
Why do stock shares sink?
And then there are human-capital considerations: Employees who invest heavily in company stock have both their human capital and financial capital riding on the fortunes of a single company; difficulties at their employer could cause their stock shares to sink at the same time they suffer job loss or an income reduction.
Why is Blanchett's allocation to company stock zero?
Because of portfolio-diversification and human-capital considerations, Blanchett notes that the optimal allocation to company stock, from a "pure research perspective," is zero. Such a Draconian approach might not be practical for some investors, however. Blanchett notes that 10% of total portfolio assets is a reasonable upper limit for company-stock ownership.
Why is it more likely that the investor who owns a heavy stake in the company also owns additional shares in?
Moreover, because company stock ownership is much heavier among larger-cap stocks than smaller ones , it's much more likely that the investor who owns a heavy stake in the company also owns additional shares in that same company through any mutual funds in the portfolio.
Is employee stock ownership bad?
Blanchett concedes that employee-stock ownership, while less than ideal, is “less bad” in a small handful of situations, such as when one's company is especially large and well-diversified. In that case, however, it’s also more likely that the stock would appear elsewhere in the investor’s portfolio. Company stock is also less dangerous if the employee is able to purchase it at a discount, as is the case with some 401 (k) plans, or if the employee's portfolio is already extremely large and well diversified. The flip side is that company-stock ownership can cause the greatest harm to investors who can least afford it: those with small and relatively undiversified portfolios.
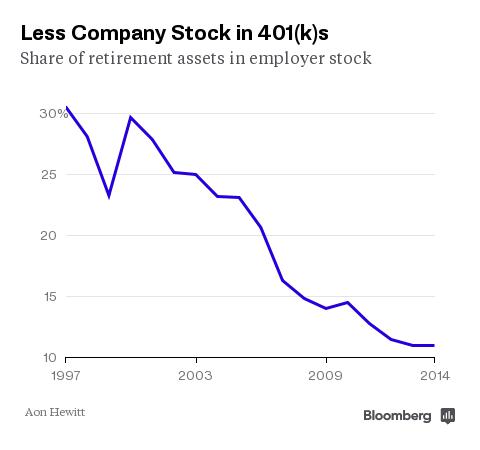
Is company stock on 401(k) plan?
Whereas nearly half of employers offered company stock in their 401 (k) plans a decade ago, either as part of the 401 (k)-plan menu or as part of an employee stock-ownership plan, that figure had dropped to less than 40% as of 2019 , according to the Callan Institute.
Do 401(k) plans have nudges?
In light of the fact that 401 (k) participants are famously hands-off, plans have increasingly added “nudge” features to get more people saving: Roughly two thirds of plans now offer automatic enrollment, for example, up from just about half in 2012. Roth accounts have also shot up in popularity. Whereas 37% of plans offered a Roth option in 2009, about 70% of plans do so today.
How much is Bob's 401(k) worth?
Bob is 59, about to retire, and has company stock in his 401 (k) plan that's currently worth $15,000, but has a cost basis of $10,000. He's currently in the 25% ordinary income tax bracket, which means that he pays a 15% tax on long-term capital gains—and would pay that on a sale of company stock that had been moved from a 401 (k) ...
What happens if Mike doesn't sell his stock?
Also, if Mike didn't sell the stock before he dies, the beneficiaries of his IRA will pay ordinary income tax on all of the money they receive, including the current value of the stock.
What happens to stock in an IRA after 72?
That is, once you turn 72, a certain amount of the value of the account must be taken out annually.
What is the penalty for early withdrawal of 401(k)?
Weigh the Early-Withdrawal Penalty. Another potential downside is that if you are not at least 55 and leaving your job, you will have to pay a 10% penalty on the taxable amount in your 401 (k), which for the stock is its cost-basis value.
How much do you have to withhold from an IRA distribution?
When you distribute from your employer's plan, the employer is required to withhold 20% from the distributions for the IRS, but you might be able to get around this. Have your employer transfer the non-stock assets directly to your IRA. Then have the stock distributed to you in kind. That way, there is nothing left in the plan for the IRS. But if you can't avoid the tax, make sure your employer withholds only 20% on the cost basis, not the entire amount.
What is the difference between a stock's value when acquired and its current value?
The difference between the stock's value when acquired and its current value, known as its net unrealized appreciation (NUA), is then subject only to capital gains tax, rather than the more costly income tax.
Do you pay taxes on stock transfer from 401(k)?
How that appreciation in the stock's value is ultimately taxed depends on the account to which the stock is transferred from your 401 (k). If the transfer is to an IRA, you don't pay any tax immediately, which is helpful. But you're liable to pay income tax on the stock's full NUA when you sell it. Moving the stocks to a brokerage account, on ...
How to sell private shares?
The simplest solution for selling private shares is to approach the issuing company and determine how other investors liquidated their stakes. Some private companies have buyback programs, which allow investors to sell their shares back to the issuing company.
What Is Private Company Stock?
Private company stock includes shares issued by private companies to their employees or investors. For example, startups often use equity to compensate employees during the early stages when cash flow is limited. Public companies also use equity compensation programs. These programs are designed to motivate employees by tying a portion of their pay to the company's earnings.
What is pre IPO stock?
Pre-IPO private company stock exchanges are essentially venture capital markets for the masses. An employee who holds stock in a pre-IPO private company can list shares for sale on this market. Some of these secondary market sites offer loans to buy pre-IPO stock.
Why do companies use equity?
For example, startups often use equity to compensate employees during the early stages when cash flow is limited. Public companies also use equity compensation programs. These programs are designed to motivate employees by tying a portion of their pay to the company's earnings.
Can insiders sell stocks?
An insider may be able to provide leads about current shareholders or potential investors who have expressed interest in buying the company's shares. The seller would be wise to visit a securities lawyer to make sure the paperwork is done correctly. Although private stocks are not registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), all SEC regulations that apply to selling stocks must still be followed. 1
Do private stocks have to be registered with the SEC?
The seller would be wise to visit a securities lawyer to make sure the paperwork is done correctly. Although private stocks are not registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), all SEC regulations that apply to selling stocks must still be followed.
Do companies have to approve private stock?
A sale of private stock must be approved by the company that issued the shares. Some companies may not want their shares to be widely distributed. In addition, some employees of startups may feel pressured to hold onto their company stock as proof of loyalty.
What happens if you stop contributing to your 401(k)?
If you stop contributing to your 401 (k) during downturns, you’re not buying stocks when they’re cheap. Because the stock market has lost more than 10% so far this year, stocks (in aggregate) are cheaper than they were when 2020 started. Trying to market-time in down markets can make losses much worse.
Why do people invest in stocks?
Why do people bother investing in stocks, then? Because historically, investors who have put up with stocks’ higher volatility (as measured by standard deviation, which shows how widely a stock’s price fluctuates from its median price) have been rewarded with higher returns. Consider the below chart, which compares the returns of these different asset classes.
Why is it important to have diversified investments?
Holding broadly diversified investments is a good way to get exposure to stocks without having to worry as much that an individual company (or sector or industry) will have a large negative impact on your overall return. For instance, low-cost index funds that track the broad market provide exposure to lots of companies in different sectors and industries.
Why are stocks more prone to swinging?
Because stocks’ long-term outlooks are more uncertain than, say, investment-grade bonds that are very likely to pay a fixed amount of income over a specific time frame, stocks' prices are more prone to swing around.
Why do you need to hold international stock funds?
Holding international stock funds in addition to U.S. stock funds is another way to spread your bets and give yourself exposure to different economies and currencies.
What is company risk?
Company risk, also known as business risk, is the risk that a specific stock might plunge because of non-market-related factors such as poor company management. This is beyond overall stock market risk and is not always rewarded with higher returns.
How to reduce the risk of one failing stock negatively impacting your portfolio?
You can reduce the risk of one failing stock negatively impacting your portfolio by holding lots of stocks. The image below shows that if an investor holds 100 stocks, he has essentially eliminated the impact of “company risk” from his portfolio.
How to evaluate a company's stock?
One effective strategy is to appoint a totally independent fiduciary who will evaluate the company stock, monitor its continued performance and make recommendations to the plan’s trustee. The most significant drawback to this option is the plan sponsor loses control and influence over the decision, but this is also the greatest benefit. Independent fiduciaries generally operate under a presumption that the company stock should continue to be offered, and will only change that presumption if there is clear evidence that the organization’s financial condition is in doubt. The plan sponsor always retains liability for the selection and monitoring of the independent fiduciary.
How to discourage overinvesting in stock?
Finally, one of the best design strategies is to discourage participants from overinvesting in company stock. By imposing restrictions on the amount of company stock that can be held in a plan (for instance, 30 percent of a participant’s account), plan sponsors can reduce the risk of significant loss if the organization’s stock declines.
Why is company stock more volatile than a normal investment benchmark?
A company stock’s performance may be more volatile than a normal investment benchmark because employer stock is a single security. Therefore, the investment review must determine if there is evidence indicating that the business should stop offering company stock. The investment committee would need to clearly document its consideration of all public information available to it at the time of the investment review and should pay particular attention to the following:
Why do companies need to be carefully scrutinized?
Communications to participants must be carefully scrutinized to prevent any misrepresentations about company stock or the company’s financial outlook. Businesses that overstate the benefits of their stock and fail to advise participants of the risk of not diversifying out of company stock can find themselves in trouble.
Why did the stock market artificially inflated?
Artificially inflated its stock price because of a failure to disclose adverse information.
What is the benefit of offering stock?
However, the only benefit that matters when deciding to offer company stock is providing a secure retirement for participants. To that end, the decision to offer company stock is governed by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA), which requires that plan sponsors:
Can a plan sponsor take risks from stock?
Nothing will completely insulate a plan sponsor from the fiduciary risks that company stock presents, aside from not offering such stock. There are, however, relatively simple and effective strategies that plan sponsors can take to reduce the risk. At the end of the day, none of these steps is effective if you do not carefully document the fiduciary decision-making process surrounding company stock and make sure to follow the terms of your plan.
What is the tax rate on selling stock?
The maximum federal capital gains tax rate is currently 20%, far lower than the current 37% top income tax rate , so your potential tax savings may be substantial.
How long do you have to distribute vested funds?
You must distribute your entire vested balance in your plan within one tax year (though you don't have to take all distributions at the same time).
What tax bracket is Tony's stock in?
When Tony's required minimum distributions (RMDs) start in a few years, he's projected to be in the 22% federal tax bracket.
Do you pay taxes on 401(k) transfer?
When you transfer most types of assets from a 401 (k) plan to a taxable account, you pay income tax on their market value.
Can you roll stock into a 401(k)?
When you want to distribute company stock or its cash value out of your 401 (k), you will face a choice: Roll it into an IRA (or another 401 (k) plan), or distribute the company stock into a taxable account and roll the remaining assets into an IRA or 40 1 (k). The latter option might be more effective, depending on your circumstances, ...
Do you pay taxes on 401(k) distributions?
When company stock holdings in your 401 (k) are distributed, you must pay taxes on investment gains.
Can Tony's children inherit stock?
Down the road when Tony passes away, if he hasn’t yet sold the company stock, his children can get a step-up in basis on it (under current law). While they may be subject to estate or inheritance tax when they inherit the company stock, they will not need to worry about income or capital gains taxes on the company stock. If estate or inheritance tax is an issue, Tony could also consider the transfer of the company stock to an irrevocable trust as part of his estate planning strategy, working with a qualified estate planning attorney. Note: If the account holder dies before selling or transferring assets, the heirs do not receive a stepped-up basis on those assets because the NUA is considered "income in respect of a decedent" and is still taxable as a long-term capital gain.
/Investingjourneypic-a9bb92f557694caaaa92b761eb2cadd9.jpg)