
Place an entry in the general ledge on the date of the purchase for the redemption. List the date of the transaction; then, on the first line of the listing, write "Treasury Stock" in the column for "Account Title and Description." In the "Debit" column, list the amount paid by the company to redeem the stock.
Full Answer
What should be reported on Line 18 of Form 1120-S?
The amount reported on line 18 must be the same as the amount reported on line 8 of Schedule M-1 or line 26, column (d), in Part II of Schedule M-3 (Form 1120-S). The balance sheets should agree with the corporation's books and records.
What is a stock redemption for tax purposes?
If none of the other existing owners is interested in purchasing the shares, the shares can be sold back to the corporation. This is known as a “stock redemption for tax purposes.”
How do I enter a loss on Form 1120-S?
Enter the amount from Form 1120-S, page 1, line 21. Enter the income (loss) without reference to the shareholder's: Basis in the stock of the corporation and in any indebtedness of the corporation to the shareholders (section 1366 (d)), Passive activity limitations.
How do I report a capital inversion on Form 1120-S?
Attach a statement to Form 1120-S that shows the amount of each type of income or gain included in the inversion gain. The corporation must report each shareholder's pro rata share of the inversion gain in box 17 of Schedule K-1 using code AD.
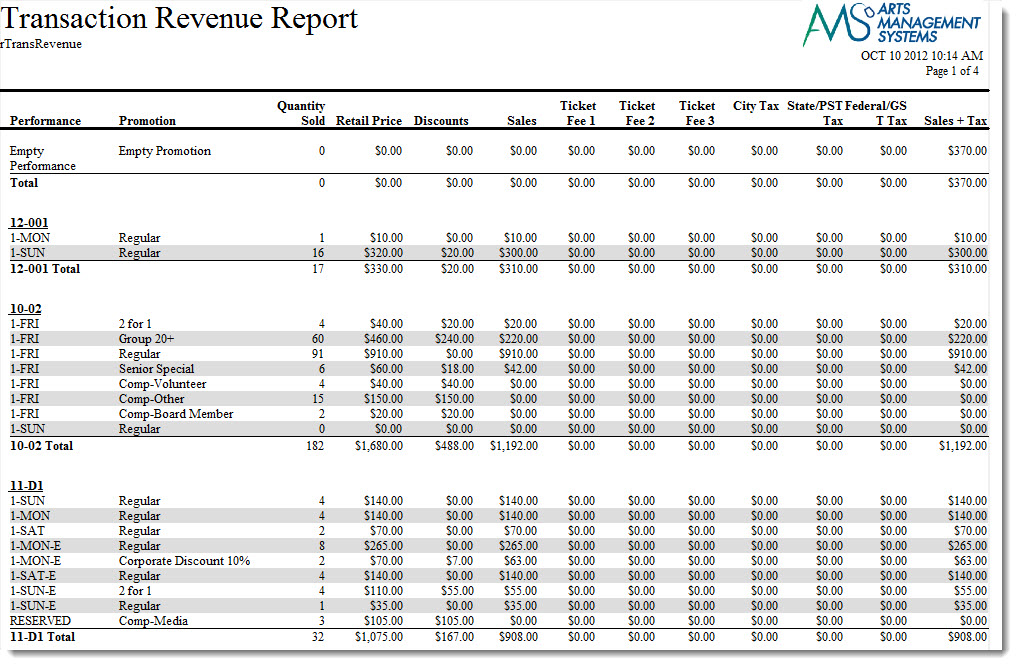
How do I report S Corp shareholder withdrawals?
Use Schedule K-1 to Complete Your Schedule E If you receive distributions from your S corporation, you'll rely on the information provided on your Form K-1 to report and pay tax on that income. You'll need to use the information from the K-1 to complete one or more required IRS schedules.
How do you record a stock redemption?
Place an entry in the general ledge on the date of the purchase for the redemption. List the date of the transaction; then, on the first line of the listing, write "Treasury Stock" in the column for "Account Title and Description." In the "Debit" column, list the amount paid by the company to redeem the stock.
How does a corporation treat the redemption of stock?
Summary. A stock redemption is a transaction in which a corporation acquires its own stock from a shareholder in exchange for cash or other property. The redeeming corporation generally does not recognize gain or loss, unless it distributes appreciated property.
How is a stock redemption treated for federal income tax purposes?
The general rule for a stock redemption payment received by a C corporation shareholder is the payment is treated as a taxable dividend to the extent of the corporation's earnings and profits (similar to the financial accounting concept of retained earnings).
Can S Corp redeem stock?
When an S corporation redeems its stock in a transaction that qualifies as a sale or exchange, the shareholder's realized and recognized gain or loss is governed by Sec. 1001. The shareholder's adjusted stock basis is subtracted from the amount of cash and the FMV of other property received from the corporation.
Is a redemption a return of capital?
The redemption of an investment may generate a capital gain or loss, both of which are recognized on fixed-income investments and mutual fund shares. Taxation of capital gains is reduced by capital losses recognized in the same year.
Is a redemption the same as a distribution?
A redemption is treated as a distribution in part or full payment in exchange for the stock redeemed and, therefore, not as a dividend if it is "not essentially equivalent to a dividend." A redemption may technically be "essentially equivalent to a dividend" as measured by this rule and still be treated as a redemption ...
Is redemption premium taxable?
"The company received premium of Rs. 2,37,60,000 on redemption of debentures of Times Guarantee Ltd during the year. This has been shown as long term capital gains because these were received for the transfer of the asset. It is therefore the Company's claim that this is taxable as capital gain."
Do you issue a 1099 for stock redemption?
Form 1099-B (Proceeds from Broker and Barter Exchange) reports proceeds from securities transactions including sales of stocks, bonds, short sales, redemptions, tenders and bond maturities.
Is a redemption of shares a distribution?
A repayment or redemption of share capital will represent a distribution by the company. The distribution can only be a capital distribution if it does not constitute income for Income Tax or Corporation Tax purposes.
Is the redemption of stock dividends a taxable event?
Redeem and be tax-free The CTA declared that redemption of shares cannot be treated as dividends unless the shares are previously issued as stock dividends and the time and manner of such redemption is essentially equivalent to dividend distribution.
What is the difference between redemption and sale?
The Bottom Line Unlike a redemption, which is compulsory, selling shares back to the company with a repurchase is voluntary. However, a redemption typically pays investors a premium built into the call price, partly compensating them for the risk of having their shares redeemed.
Why is the redeemed shareholder denied the sole shareholder beneficial tax treatment?
Because the redeemed shareholder held 100% of the stock both before and after the redemption , the Court denied the sole shareholder beneficial tax treatment. The Court also made clear that the business purpose of pro rata distributions is irrelevant in this determination.
What is the letter ruling 201918009?
75-502 discuss the before-and-after stock percentages held by the redeemed shareholder in their analyses. However, in Letter Ruling 201918009 the IRS merely states that the shareholder's ownership was reduced, with no explicit reference to whether the reduction was meaningful. Instead, taxpayers are left to ponder the significance of a diverse list of facts surrounding the transaction itself, none of which have much to do with the shareholder's economic interest in the redeeming corporation.
Is a redemption an isolated transaction?
First, the IRS makes two key points: The redemption was an isolated transaction, and no other shareholder is obligated to purchase any of the redeemed stock. These factors imply that the redemption was not made pursuant to an overall plan, and no other shareholders were redeemed simultaneously.
Is a redemption a capital loss?
If the redemption would result in a loss on the stock, it is a capital loss, so the IRS may consider recharacterizing the transaction as essentially equivalent to a dividend to reach its desired result: the less tax-favorable ordinary loss.
Does a redeemed shareholder receive notes?
Second, the IRS noted the redeemed shareholder received fair market value for his stock and will not receive notes or other obligations from the redeeming corporation. By including these factors in its analysis, the IRS indicated that the type of consideration received by the redeemed shareholder is important in determining whether a redemption is essentially equivalent to a dividend. In Rev. Proc. 2019-3, the IRS stated that it will no longer issue rulings concerning whether Sec. 302(b) applies when the consideration received by a redeemed shareholder consists of the redeeming corporation's promise to pay that is based either on future earnings or notes payable secured by the shareholder's stock.
What is stock redemption?
A stock redemption is an agreement between a corporation and a shareholder to purchase back shares of stock for cash. The stock, once purchased, goes into the corporation’s treasury stock account. Accounting for this transaction is necessary to maintain correct corporate records, with the transaction being recording in the company’s general ledger, ...
What is a record in a treasury stock account?
Record the transaction in the "Treasury Stock" account as a debit to the account, increasing the balance of treasury stock held by the company ; record the transaction in the "Cash" account as a credit, decreasing the amount of cash on hand.
How to list treasury stock?
List the date of the transaction; then, on the first line of the listing, write "Treasury Stock" in the column for "Account Title and Description." In the "Debit" column, list the amount paid by the company to redeem the stock. This shows the addition of treasury stock held by the company in that amount.
How to write cash in a ledger?
Place an entry in the next line of the ledger, slightly indented for easy readability, in the "Account Title and Description" column, writing "Cash" in the column. Write the cash outlay for the redemption in the "Credit" colum n for that line to show that the company account is less than the amount of cash for the purchase. The credit amount should be equal to the earlier "Treasury Stock" debit amount.
Do you need to show ownership change in ProSeries?
You will also need to show the ownership change (ProSeries Professional has worksheets for this but I do not know about PTO). The part year owner will get a K-1 for his/her ownership time based on pro-rated profit unless an election was made and specifically agreed to by stockholder to have K-1 based on actual profit for the days owned.
Do part year owners get a K-1?
The part year owner will get a K-1 for his/her ownership time based on pro-rated profit unless an election was made and specifically agreed to by stockholder to have K-1 based on actual profit for the days owned. 12-07-2019 01:07 AM.
What is the tax consequence of a S corporation redemption?
Tax consequence of a distribution under Sec. 301: If an S corporation redemption does not qualify as a sale or exchange under Sec. 302, it instead defaults to a Sec. 301 distribution, subject to the ordering rules of Sec. 1368, which provide that the recipient shareholder must treat the redemption in the following sequence: 1. ...
What is a redemption under Sec. 302?
Pursuant to Sec. 302, a distribution in redemption of stock is treated as a sale or exchange if the redemption: 1. Is not essentially equivalent to a dividend; 2. Is substantially disproportionate; 3. Completely terminates the shareholder's interest; or. 4.
What happens if a S corporation fails to meet the requirements of Sec 302?
301 and 1368. Given the comparative tax rates on capital gains and qualified dividends, it is easy to question what impact, if any, a failure to meet the requirements of Sec. 302 has on a redemption of C corporation stock. However, in the S corporation environment, shareholders may find more tax advantages from Sec. 301, as discussed below.
What is disproportionate redemption?
Substantially disproportionate: A redemption is substantially disproportionate if: (1) The shareholder's interest in the outstanding common stock of the redeeming company post-redemption is less than 80% of the shareholder's interest before the redemption (the 80% test must be met for both common voting, and common voting and nonvoting combined); and (2) immediately after the redemption, the shareholder owns less than 50% of the total combined voting power of all classes of stock entitled to vote .
What is the tax consequence of a sale or exchange?
302, the amount of the redemption proceeds in excess of the shareholder's basis in the redeemed stock will be taxed as a capital gain.
What is the ownership share of B and C?
However, B's and C's redemptions do not meet the substantially disproportionate test, with B's post-redemption ownership share of 16.67% exceeding the 16% threshold, and C's ownership share increasing to 23% .
Is a redemption under Sec. 301 a disproportionate distribution?
301 is considered a disproportionate distribution in violation of the identical-distribution rules under Regs. Sec. 1.1361-1 (l) (1). A redemption that fails to qualify under Sec. 302 is generally not considered a disproportionate distribution that creates a second class of stock in violation of the S corporation eligibility rules (so long as the redemption agreement was not entered into to circumvent the single-class-of-stock requirement) (Regs. Sec. 1.1361-1 (l) (2) (iii); see also IRS Letter Rulings 9810020 and 9404020). Therefore, a redemption made under Sec. 301 will generally not terminate an S election.
What happens if distributions exceed AAA?
If distributions exceed AAA at the close of the year, a portion of each distribution is allocated to AAA pro rata based on the relative size of the distributions . (§1368(c))
What is required for an S corp?
One of the requirements for an S Corporation is that the entity have only one class of stock. This requires that all corporate distributions to shareholders be pro rata.
What is initial basis?
Generally, initial basis equals the cost paid for the stock. If property was contributed for stock, then basis equals basis of property contributed, adjusted for gain recognized and boot distributed.
What is a 162(l) deduction?
Section 162(l) provides that the deduction is limited to the amount of the individual’s earned income from the trade or business with respect to which the plan providing the medical care coverage is established .
Can a shareholder use a loss or deduction in excess of the basis of the S corporation?
Section 1366(d) provides that a shareholder may not utilize losses or deductions in excess of the shareholder’s basis in (i) its stock of the S corporation, and (ii) any debt owed by the S corporation to the shareholder.
Do shareholders get basis for debt owed by the S corporation?
Shareholders get basis for debt owed by the S corporation to the shareholder, not for debt owed by the S corporation to some party other than the shareholder. This is the case even if the shareholder guarantees the debt. This is a substantial divergence from partnerships.
What is Ultratax CS/1120?
UltraTax CS/1120 transfers the amounts in the Total column of this worksheet to the respective line on Form Schedule K-1. UltraTax CS includes this worksheet in the shareholder package at print time.
When does a corporation have to treat its taxable year as if it consisted of two separate taxable years?
When a shareholder has terminated their interest in the corporation or made a qualifying disposition of their interest in the corporation , the corporation can elect, with the consent of all affected shareholders, to treat its taxable year as if it consisted of two separate taxable years, the first of which ends at the close of the day on which the shareholder's stock in the corporation changed , by following this procedure.
When to enter change of ownership in S corp?
If the change of ownership occurred on the first day of the S Corporation’s tax year, enter the second day of the tax year in the Change of Ownership dialog.
What is stock redemption?
If none of the other existing owners is interested in purchasing the shares, the shares can be sold back to the corporation. This is known as a “stock redemption for tax purposes.”. The redemption can be treated as an exchange or a sale, with the resulting gain or loss treated as a capital gain or loss. Alternatively, the redemption transaction can ...
What happens if a redemption is not equivalent to a dividend?
If the redemption is not equivalent to a dividend (a subjective test that occurs where there is no meaningful reduction in shareholder’s interest). If there is a partial liquidation. If the proceeds of the redemption are used to pay death taxes. The shareholder would compute the gain or loss as to the difference between ...
Can a shareholder eliminate ownership in an S corporation?
There are many situations where a shareholder may want to eliminate or reduce ownership in an S-corporation. One may be the need for additional cash as a result of the economic downturn stemming from the COVID-19 shutdown. If none of the other existing owners is interested in purchasing the shares, the shares can be sold back to the corporation.
Is a redemption of a corporation a distribution?
If none of the above scenarios applies, and the shareholder wishes to redeem a small percentage of ownership, then the redemption is treated as a distribution. The distribution will be treated as tax-free to the extent of the corporation’s accumulated adjustment account (AAA), then as a tax-free recovery of basis, with any remaining distribution in excess of AAA and basis, to be treated as a sale or exchange gain.
