A short-term gain will typically appear in box 1 of your W-2 as ordinary income, and you should file it as wages on Form 1040. If you buy or sell a stock option in the open market, the taxation rules are similar to options you receive from an employer.
How do I list stock options on my W-2?
Any compensation income received from your employer in the current year is included on Form W-2 in Box 1. If you sold any stock units to cover taxes, this information is included on Form W-2 as well. Review Boxes 12 and 14 as they list any income included on Form W-2 related to your employee stock options.
Do I have to report sale of stock on W2?
Since you have not sold the stock, the holding period requirements have not been determined. Therefore, the employer does not include compensation income on your Form W-2 as ordinary income. Form 3922 is issued to report the income on your tax return when you sell the units.
What is included on a W-2 form?
Your W-2 includes income from any other compensation sources you may have, such as stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, employee stock purchase plans, and cash bonuses.
How do I report nonqualified stock options on my taxes?
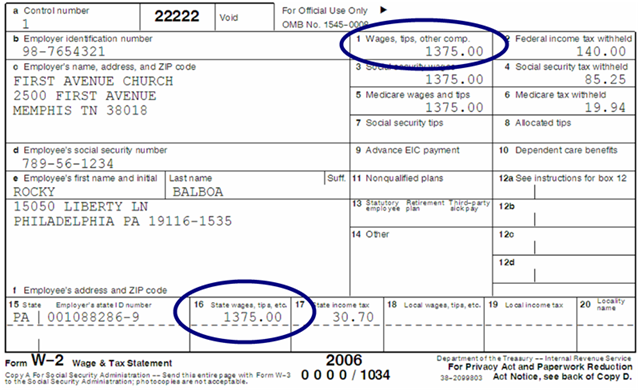
Stock Options If you exercised nonqualified stock options (NQSOs) last year, the income you recognized at exercise is reported on your W-2. It appears on the W-2 with other income in: Box 1: Wages, tips, and other compensation
How do you report income from stock options?
You should report a long-term gain on Schedule D of Form 1040. A short-term gain will typically appear in box 1 of your W-2 as ordinary income, and you should file it as wages on Form 1040.
Do stock options count as wages?
In exercising stock options, an employee incurs a tax liability equal to the difference between the market and exercise price that is reported as wages; the company receives a tax deduction for the difference between the market and exercise price, which reduces taxes paid.
Does stock compensation show up on W-2?
Form W-2. Any compensation income received from your employer in the current year is included on Form W-2 in Box 1. If you sold any stock units to cover taxes, this information is included on Form W-2 as well. Review Boxes 12 and 14 as they list any income included on Form W-2 related to your employee stock options.
How do I report employee stock options on tax return?
With nonqualified stock options, for employees the spread at exercise is reported to the IRS on Form W-2 For nonemployees, it is reported on Form 1099-MISC (starting with the 2020 tax year, it will be reported on Form 1099-NEC ). It is included in your income for the year of exercise.
Are stock options subject to payroll tax?
With NSOs, you are taxed when you exercise the stock options. You pay ordinary income and Medicare taxes and are subject to Social Security tax if you have not paid the yearly maximum on the difference between the fair market value at exercise and the grant price.
How do you account for stock options?
Stock options use equity accounts rather than liability accounts since they will be settled with stock. The same entry is made at the end of year two to account for all of the compensation expense.
How do I report stock options on Form 8949?
Start with Form 8949, Part I, Short-Term Capital Gains and Losses. Check Box C since you did not receive a Form 1099. On Line 1, Column A, Description of Property, enter the name of the company or its symbol, and after that write "call options" and the number of call options you sold.
What is CODE V in Box 12 of my W-2?
Code V in box 12 of the W-2 indicates income from the exercise of non-statutory stock options. Per IRS General Instructions for Forms W-2 and W-3: "Code V—Income from the exercise of nonstatutory stock option(s).
Do stock options get taxed twice?
If you follow IRS rules when you report the sale of stock bought through an ISO, you'll avoid being taxed twice on the same income. The broker your employer uses to handle the stocks will send you a Form 1099-B.
What are the codes in box 12 on W-2?
The W-2 box 12 codes are:A – Uncollected Social Security tax or Railroad Retirement Tax Act (RRTA) tax on tips. ... B – Uncollected Medicare tax on tips. ... C – Taxable costs of group-term life insurance over $50,000 (included in W-2 boxes 1,3 (up to Social Security wages base), and box 5); Taxable costs are information only.More items...•
What line of W-2 is income?
Since you'll have to exercise your option through your employer, your employer will usually report the amount of your income on line 1 of your Form W-2 as ordinary wages or salary and the income will be included when you file your tax return.
What is an employer stock option?
The two main types of stock options you might receive from your employer are: These employer stock options are often awarded at a discount or a fixed price to buy stock in the company. While both types of options are often used as bonus or reward payments to employees, they carry different tax implications.
How long do you have to keep stock after exercise of option?
If you satisfy the holding period requirement, by either keeping the stock for 1 year after exercising the option or 2 years after the grant date of the option, you will report a long-term capital gain, which is usually taxed at a lower rate.
What is stock option?
Stock options give you the right to buy shares of a particular stock at a specific price. The tricky part about reporting stock options on your taxes is that there are many different types of options, with varying tax implications.
What is the term for the price you pay when you exercise an option?
When you exercise an option, you agree to pay the price specified by the option for shares of stock, also called the award, strike, or exercise price.
What happens if you sell stock?
When you sell stock you've acquired via the exercise of any type of option, you might face additional taxes.
Do you pay taxes on stock options?
The underlying principle behind the taxation of stock options is that if you receive income, you will pay tax. Whether that income is considered a capital gain or ordinary income can affect how much tax you owe when you exercise your stock options.
What is included in W-2?
Remember that it’s not just for reporting your salary to you and the IRS. Your W-2 includes income from any other compensation sources you may have, such as stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, employee stock purchase plans, and cash bonuses. If you have income and withholding from what the IRS considers supplemental wage income ...
What is Section 83 B on W-2?
If you made a Section 83 (b) election to be taxed on the value of restricted stock at grant, your W-2 for the year of grant, not vesting, shows the income and withholding.
What is an incentive stock option?
With incentive stock options (ISOs), the value of the exercise income appears on Form W-2 only if you made what is technically called a disqualifying disposition. That means you sold or gifted the stock before you met the required holding periods of one year from exercise and two years from grant.
Does W-2 show compensation income?
In this situation, the income appears on the W-2 as compensation income. The amount depends on whether you sold the stock at a higher or lower price than the market price on the exercise date. Unlike with NQSOs, your company does not withhold taxes on ISO exercises, and no money is owed for Social Security and Medicare, even with a same-day sale or any later disqualifying dispositions.
Who does an employer send out W2?
An employer would normally have to send out the W2 forms to each employee in the company who have been paid a wage, salary, or offered any kind of bonuses or stock option plans.
What is a W2 form?
The form W2 is also called the informational return since it informs all the important stakeholders about the earnings that were made and the taxes that are being paid for it in a year. The stakeholders here are:
What is restricted stock unit?
The restricted stock units are another form of employee compensation. But in this plan, the employee does not get the stock during the grant. It has a particular vesting scheme that is outlined for the employee and how they would get the stock. When the stock is vested, the employee gets the shares and the FMV of the stock that the employee got on the same day is regarded as income.
How much discount is allowed on ESPP?
The maximum discount permitted in this plan is up to 15% lower than the actual market price.
What form do you get when you sell stocks?
In the year you sell the stocks, the employee would get a form 1099-B which reports all the capital gain or loss from the transactions in their tax return. In this case, they would have to analyze the investment records for verifying the cost basis amount on the form 1099-B, which is based on the details on the employee’s brokerage. In case the details are not complete, the cost basis amount might be incorrect.
What is box 1 in a tax return?
Box 1: Displays the gross wage, prizes, bonuses, tips, stock options, and other compensation that is taxable for the year in question . The amount is deducted from specific elective deferrals like payroll deductions, pre-tax benefits, and 401 (k) plans.
What box is 1040?
Boxes 2 and 17 are used by the employer to share the amount that was withheld by the company for federal and state income tax.
How to edit 1099-B?
If the Form 1099-B was already imported, you will need to go through the interview screens until you come to where you can Edit the Form 1099-B. Select Edit. Otherwise, just follow the prompts to type the information in. .
Do you get taxed on 1099B stock option income?
1099B stock option income, but already reported in W2 wages. Enter the Form 1099-B (see steps below) and it will automatically create Form 8949. You won't get taxed on the income again, because you will have a cost basis in the stock that is approximately equal to what your proceeds were.
What is a 427 stock option?
427 Stock Options. If you receive an option to buy stock as payment for your services, you may have income when you receive the option, when you exercise the option, or when you dispose of the option or stock received when you exercise the option. There are two types of stock options:
What is nonstatutory stock option?
If your employer grants you a nonstatutory stock option, the amount of income to include and the time to include it depends on whether the fair market value of the option can be readily determined.
What is a Form 3922?
Employee Stock Purchase Plan - After your first transfer or sale of stock acquired by exercising an option granted under an employee stock purchase plan, you should receive from your employer a Form 3922, Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan under Section 423 (c). This form will report important dates and values needed to determine the correct amount of capital and ordinary income to be reported on your return.
What happens if you don't meet special holding period requirements?
However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income. Add these amounts, which are treated as wages, to the basis of the stock in determining the gain or loss on the stock's disposition.
Is an option without a fair market value taxable?
For nonstatutory options without a readily determinable fair market value, there's no taxable event when the option is granted but you must include in income the fair market value of the stock received on exercise, less the amount paid, when you exercise the option. You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell ...
What is included in income when you exercise an option?
When you exercise the option, you include, in income, the fair market value of the stock at the time you acquired it, less any amount you paid for the stock. This is ordinary wage income reported on your W2, therefore increasing your tax basis in the stock. 5 .
What is stock option?
Stock options are employee benefits that enable them to buy the employer’s stock at a discount to the stock’s market price. The options do not convey an ownership interest, but exercising them to acquire the stock does. There are different types of options, each with their own tax results.
What happens if you make an AMT adjustment?
If you have to make an AMT adjustment, increase the basis in the stock by the AMT adjustment. Doing this ensures when the stock is sold in the future, the taxable gain for AMT purposes is limited, which means you don’t pay tax twice on the same amount.
How many events are there in a stock option?
For this type of stock option, there are three events, each with their own tax results: The grant of the option, the exercise of the option, and the sale of stock acquired through the exercise of the option.
When you sell stock, do you report capital gains?
When you sell the stock, you report capital gains or losses for the difference between your tax basis and what you receive on the sale.
Do you have to report the fair market value of a stock when you sell it?
When you sell the stock, you report capital gains or losses for the difference between your tax basis and what you receive on the sale.
Do stock options have to be taxed?
Tax Rules for Statutory Stock Options. The grant of an ISO or other statutory stock option does not produce any immediate income subject to regular income taxes. Similarly, the exercise of the option to obtain the stock does not produce any immediate income as long as you hold the stock in the year you acquire it.