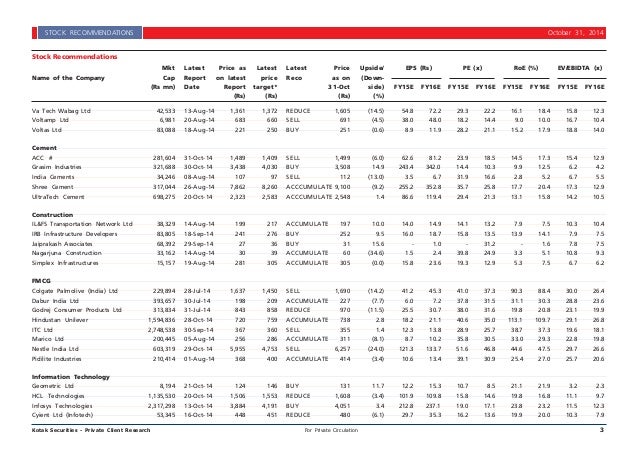
How to Report Nonqualified Stocks on a 1099
- Qualified and Nonqualified Options. The IRS allows favorable tax treatment of "statutory" stock options, on which you...
- The Price of Exercise. For nonqualified stock options, taxable income is generated on exercise -- the date that you...
- W-2 vs 1099. For a salaried, regular employee, the employer will report the compensation...
When should you exercise your nonqualified stock options?
Reasons to Consider Using Non-Qualified Stock Options
- Provide increased compensation when you can't afford to raise salaries.
- Recognize the contributions of key employees.
- Avoid the complexity of incentive stock options.
- Issue stock options to individuals who aren't eligible for qualified stock options.
How to report nonqualified stocks on a 1099?
- Generally, payments to a corporation (including a limited liability company (LLC) that is treated as a C or S corporation). ...
- Payments for merchandise, telegrams, telephone, freight, storage, and similar items.
- Payments of rent to real estate agents or property managers. ...
- Wages paid to employees (report on Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement).
How to report stock options to the IRS?
Nonstatutory Stock Options
- You can transfer the option.
- You can exercise the option immediately in full.
- The option or the property subject to the option isn't subject to any condition or restriction (other than a condition to secure payment of the purchase price) that has a ...
- The FMV of the option privilege can be readily determined.
What are tax consequences of nonqualified stock options?
Your payroll taxes on gains from exercising your NQ stock options will be 1.45% for Medicare only if and when your earned income exceeds the wage base for the given tax year. You won't pay more than 6.2% of your wage base in taxes for Social Security if you earn more than that amount.

How do I report non-qualified stock options on my taxes?
With nonqualified stock options, for employees the spread at exercise is reported to the IRS on Form W-2 For nonemployees, it is reported on Form 1099-MISC (starting with the 2020 tax year, it will be reported on Form 1099-NEC ). It is included in your income for the year of exercise.
Are nonqualified stock options included in W-2?
If you exercised nonqualified stock options (NQSOs) last year, the income you recognized at exercise is reported on your W-2. It appears on the W-2 with other income in: Box 1: Wages, tips, and other compensation.
Are NSOs reported on W-2?
In the case of a nonemployee, income from the exercise of NSOs would be reflected on Form 1099-MISC. Reporting income on the exercise of NSOs is a no-brainer. So long as the amount is reported properly on your W-2 or 1099-MISC, it should appear correctly on your tax return.
How do I report stock options on Form 8949?
Because most call options expire in less than a year, you report them on Form 8949 and Schedule D as short-term capital gains or losses.Start with Form 8949, Part I, Short-Term Capital Gains and Losses. ... Move to Column E, Sales Price, and enter the sale amount reported on your brokerage statement.More items...
How do I report Code V on my W-2?
A code of V in Box 12 of your W-2 is an amount that was exercise of non-statutory stock option. This amount is included with your taxable income in boxes 1, 3, and 5. This will need to be reported on your Schedule D. TurboTax helps you do this in the Investment section.
Where do I report stock options on tax return?
When you buy an open-market option, you're not responsible for reporting any information on your tax return. However, when you sell an option—or the stock you acquired by exercising the option—you must report the profit or loss on Schedule D of your Form 1040.
How do I file a 1099 NEC?
Form 1099-NEC can be filed online or by mail. A version of the form is downloadable and a fillable online PDF format is available on the IRS website. You can complete the form using IRS Free File or a tax filing software.
What is CODE V in box 12 on W-2?
Code V. Code V in box 12 of the W-2 indicates income from the exercise of non-statutory stock options. Per IRS General Instructions for Forms W-2 and W-3: "Code V—Income from the exercise of nonstatutory stock option(s).
What causes a non statutory stock option to be taxable upon grant?
For nonstatutory options without a readily determinable fair market value, there's no taxable event when the option is granted but you must include in income the fair market value of the stock received on exercise, less the amount paid, when you exercise the option.
What is the difference between form 8949 and Schedule D?
Use Form 8949 to reconcile amounts that were reported to you and the IRS on Form 1099-B or 1099-S (or substitute statement) with the amounts you report on your return. The subtotals from this form will then be carried over to Schedule D (Form 1040), where gain or loss will be calculated in aggregate.
Is Schedule D required if form 8949 is Used?
Key Takeaways. IRS Form 8949 is used to report capital gains and losses from investments for tax purposes. The form segregates short-term capital gains and losses from long-term ones. Filing this form also requires a Schedule D and a Form 1099-B, which is provided by brokerages to taxpayers.
Is form 8949 the same as 1099-B?
Purpose of Form. Use Form 8949 to report sales and exchanges of capital assets. Form 8949 allows you and the IRS to reconcile amounts that were reported to you and the IRS on Forms 1099-B or 1099-S (or substitute statements) with the amounts you report on your return.
How is income calculated when you exercise non qualified stock options?
One of the biggest factors you need to consider when exercising your non-qualified stock options is the compensation element. This is the difference between the exercise price and the current market value of the stock when you exercise the options.
What happens if you sell stock for more than the exercise price and compensation element?
If you sell the stock for more than the combined exercise price and compensation element, you would incur a short-term capital gain. The opposite results in a short-term capital loss.
What is the difference between the exercise price and the current market value of the stock?
This is the difference between the exercise price and the current market value of the stock when you exercise the options. The exercise price is given to you by your employer when you receive the stock options. When you exercise your options, this is the price at which you can purchase company stock, regardless of its current market value.
What does it mean when you exercise your options?
When you exercise your options, this is the price at which you can purchase company stock, regardless of its current market value. The market value of the stock is the price at which it is trading when you decide to exercise your options. The hope is that your company will continue to grow (in part due to your management and production) ...
What does it mean to bid adieu to another year's filing deadline?
Bidding adieu to another year’s filing deadline, for many, means an opportunity to breathe a sigh of relief and to not have to think about it again for another year. As an executive financial advisor, however, the topic of taxes is never far from my mind.
Is short term capital gain taxed?
A short-term capital gain is taxed at the same rate as ordinary income tax. You exercise your stock options and sell those shares within a year. In this scenario, the first taxable incident is still the compensation element. The second is the sale of your shares within a year of purchasing them. If you sell the stock for more than ...
How are non qualified stock options taxed?
When you exercise your non-qualified stock options, the value of the bargain element will be treated as earned income that is reported on your tax return the same way as your regular earned income. The bargain element is calculated as the difference between the grant price ...
What happens when you exercise non qualified stock options?
When you exercise your options, the spread between the grant price and the exercise price is taxed the same as compensation income subject to Medicare and Social Security tax. Any subsequent gain or loss from the date you exercise your options is taxed as a capital asset subject to capital asset rates.
How are stock shares taxed?
The period for which you retain ownership, and the value of the shares dictate how they will be taxed. Stock shares are subject to capital asset tax rates. Short term capital assets (assets that are held for less than one year) are taxed as ordinary income and long term capital gains (assets that are held for one year or greater) ...
What is the lifespan of options?
The lifespan of your options includes the period beginning when your shares are granted and ending when you sell the stock. During this time, you need to consider two different types of tax you may need to pay: Earned Income Tax: Earned income is taxed as ordinary income and is subject to Social Security and Medicare wage taxes.
What does advanced planning for non-qualified stock options mean?
Advanced planning for non-qualified stock options may also mean exercising in calendar years when you are also exercising or selling incentive stock options as a means to increase or decrease the alternative minimum tax.
When you exercise non-qualified stock options, should you pay attention to the price at which you exercised?
This price will dictate the cost basis of the shares moving forward. The cost basis is necessary because it is used to calculate capital gain/loss upon a subsequent sale of the exercised stock.
Is long term capital gains tax better than short term?
Long term capital gains offers a more favorable rate, considering it creates a tax bill that is over 50% lower. (While this illustration indicates that long term capital gains rates are better than short term capital gains rates, it does not mean that you should always hold your stock for one year or more.
What is a non qualified stock option?
A non-qualified stock option gives employees the right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price. There are several key elements to a stock option. Grant date: The date when the employee receives the option to buy the stock. Exercise price: The price at which the employee can buy the stock from the company.
Why are non qualified stock options important?
Non-qualified stock options are important for three reasons. Reduce current compensation expenses. Share the risks associated with a growing business. Give your employees and partners a vested interest in promoting your growth.
What is the exercise price of an option?
Exercise price: The price at which the employee can buy the stock from the company. The idea is that the stock's value will later rise and the employee will be able to buy it at a discount. Expiration date: The latest date that the employee can exercise the option. If they don't do so, they lose the option.
What happens if you don't cancel an option?
A common reason for a clawback is when the employee leaves the company before a set period of time.
How long do you have to hold a stock to sell it?
Exercise, hold for longer than one year, then sell. Exercise their option. Hold the stock for another 18 months at which time they sell it for $25 per share.
Who can you give stock options to?
Qualified stock options, also known as incentive stock options, can only be granted to employees. Non-qualified stock options can be granted to employees, directors, contractors and others. This gives you greater flexibility to recognize the contributions ...
Do qualified stock options qualify for special tax?
Qualified stock options may also qualify for special tax treatment. If eligibility and holding period requirements are met, the bargain element is taxed as a capital gain to the employee. For non-qualified stock options, the bargain element is treated as ordinary income to the employee. However, you have fewer obligations with regard to IRS ...
What is an NSO?
An NSO is an option that doesn’t qualify for the special tax treatment afforded incentive stock options (ISOs). Despite the potential tax advantages of ISOs, most employers use NSOs because they’re simpler, their tax treatment is more straightforward, and they avoid certain risks and limitations associated with ISOs.
Do brokers have to adjust basis?
Adjustments. Until recently, brokers were permitted, but not required, to adjust basis to reflect the amount of compensation income reported when options were exercised. For options granted after 2013, however, brokers are prohibited from making this adjustment.
Do NSOs have tax consequences?
NSO tax treatments. Generally, there are no tax consequences when NSOs are granted. Publication 525’s discussion of NSOs devotes several paragraphs to the circumstances under which an option grant requires you to report taxable income.
Do you have to report compensation income when exercising an NSO?
When you exercise an NSO, however, you must report compensation income equal to the spread between the exercise price and the stock’s FMV on the exercise date.
Do you report NSOs on your tax return?
Reporting income on the exercise of NSOs is a no-brainer. So long as the amount is reported properly on your W-2 or 1099-MISC, it should appear correctly on your tax return. Things get a bit more complicated, however, when you sell the stock.
What is non qualified stock option?
Companies often award employees non-qualified stock options as a form of long-term compensation. These stock options afford employees the chance to purchase stock at a predetermined price (strike price), despite the potential of the price going up over time. If an employee decides to exercise his option, profit amounts to the difference between ...
What to do if you exercise an option but do not sell the stock?
This is all you need to do, if you exercise your option but do not sell the stock. Fill out the Schedule D form, Part 1 if you choose to sell your stock before the end of the year. You will report your capital gain or capital loss according to the difference between the market price when you buy the stock and the market price when you sell ...
What line do you list the total compensation on a W-2?
On your W-2 form, in box 12 with the code “v,” your employer will list the total compensation when you exercised your option. If your employer does not include this amount in box 1, you must declare the amount on your 1040 form, on line 7. This is all you need to do, if you exercise your option but do not sell the stock.
Should I contact a financial adviser before investing?
You should always contact a financial adviser before making decisions regarding your long-term investment strategy. Warnings. You should always weigh the consequences of taxes before you choose to exercise your options, sell your stock and spend the cash.
What is taxable income when you exercise an NSO?
Going back to the example, when Steve exercises his options, he receives $5,000 in compensation, which is taxable to him as ordinary income and deductible by his employer.
How to calculate gain on option stock?
In theory, calculating and reporting gain on the sale of option stock is simple: You take the proceeds from the sale (net of any broker’s commissions or other expenses) and subtract your basis in the stock. The difference is short- or long-term capital gain, depending on how long you held the stock.
Why do employers use NSOs?
Despite the potential tax advantages of ISOs, most employers use NSOs because they’re simpler, their tax treatment is more straightforward, and they avoid certain risks and limitations associated with ISOs. Let’s look at an example: ABC Inc. grants its employee, Steve, NSOs to buy 100 shares of the company’s stock for $100 per share — ...
Do NSOs have tax consequences?
NSO tax treatments. Generally, there are no tax consequences when NSOs are granted. Publication 525’s discussion of NSOs devotes several paragraphs to the circumstances under which an option grant requires you to report taxable income.
Do brokers have to adjust basis?
Adjustments. Until recently, brokers were permitted, but not required, to adjust basis to reflect the amount of compensation income reported when options were exercised. For options granted after 2013, however, brokers are prohibited from making this adjustment.
Do you report NSOs on your tax return?
Reporting income on the exercise of NSOs is a no-brainer. So long as the amount is reported properly on your W-2 or 1099-MISC, it should appear correctly on your tax return. Things get a bit more complicated, however, when you sell the stock.
Basic Tax Treatment of Nonqualified Stock Options (NSOs)
Nonqualified Stock Options (NSOs) tax treatment isn’t too terribly complex once you become familiar with the different terms associated with them. We’ve covered the basic terms in this article so you can do a quick review.
NSO Tax Treatment - Things to Watch Out For
There are three major things to watch out for if you’ve received a grant of NSOs and are planning on exercising them.
Nonqualified Stock Option (NSO) Tax Examples
To help you figure out how to calculate the taxes you might owe from exercising NSOs or selling stock after exercising an NSO, we’ve put together three NSO Tax Examples to help you figure out which category you’d likely fall into.
Nonqualified Stock Options Tax Recommendations
Nonqualified stock options have a pretty straightforward tax calculation (eventually we’ll build a calculator for you to use). Since the spread on an NSO is treated as ordinary income when you exercise, it makes a lot of sense to sell immediately to ensure that you’ll have the funds you need to pay the taxes.
What is a non qualified stock option?
Non-qualified stock options (aka non-statutory options or NSOs) These employer stock options are often awarded at a discount or a fixed price to buy stock in the company. While both types of options are often used as bonus or reward payments to employees, they carry different tax implications. The good news is that regardless of the type ...
What is an employer stock option?
The two main types of stock options you might receive from your employer are: These employer stock options are often awarded at a discount or a fixed price to buy stock in the company. While both types of options are often used as bonus or reward payments to employees, they carry different tax implications.
What is stock option?
Stock options give you the right to buy shares of a particular stock at a specific price. The tricky part about reporting stock options on your taxes is that there are many different types of options, with varying tax implications.
Is an option sold after a one year holding period considered long term capital gains?
Options sold after a one year or longer holding period are considered long-term capital gains or losses. When you use TurboTax to prepare your taxes, we’ll do these calculations and fill in all the right forms for you. We can even directly import stock transactions from many brokerages and financial institutions, right into your tax return.
Do you have to report an open market option on your tax return?
When you buy an open-market option, you're not responsible for reporting any information on your tax return. However, when you sell an option—or the stock you acquired by exercising ...
Do you have to report stock options on taxes?
No matter how many statutory or non-statutory stock options you receive, you typically don't have to report them when you file your taxes until you exercise those options, unless the option is actively traded on an established market or its value can be readily determined. This exception is rare but does happen at times.
What is stock option?
The stock option gives you the right to buy company stock at a fixed price, after a "vesting period" has passed. While you wait for the options to fully vest, the stock should rise in value and the options will become more valuable.
What is income amount in stock options?
The income amount is the difference between the market price when you buy the stock and the original exercise price. If the option is for 1,000 shares at an exercise price of $10 a share, and the market price of the stock when you actually buy it is $15 a share, your client has paid out $5,000 of compensation and must report the payment to ...
Do you pay taxes on statutory stock options?
The IRS allows favorable tax treatment of "statutory" stock options, on which you pay tax only when you sell the stock. A statutory stock option is one your client grants under an incentive stock option plan. For what the IRS calls nonqualified or nonstatutory stock options, income tax is due when you exercise the option to purchase the stock, ...
Do you report a 1099 on a 1040?
You must report the 1099 compensation as business income on Schedule C and add it to your adjusted gross income on Form 1040.
