Dividends from C corporations are reported on the 1099-DIV. For smaller, closely held C corporations, it is important that you file the 1099-DIV for dividends paid, even if there is only one owner of the C corporation. Failure to file a 1099-DIV can result in a penalty starting at $50 per form.These forms are due by March 31 each year.
Full Answer
What is the C Corp dividend tax rate for S corporations?
The C corp dividend tax rate is a major reason why many small business owners consider instead forming their company as an S corporation. C corporations are taxed both at the initial corporate level and then when proceeds are distributed to its owners. In contrast, S corporations are only taxed at the individual level as the
What is the cheapest way for a C corporation to distribute profits?
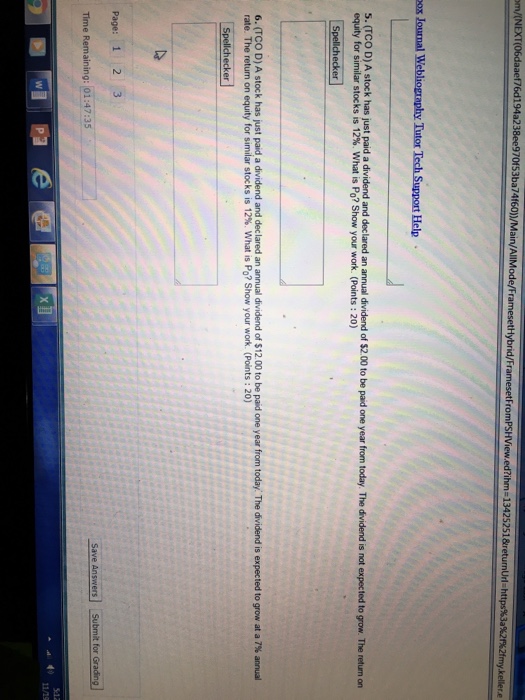
The cheapest way for C corporations to distribute profits to their owners and lower their tax liability remains through dividends. Dividends do not have many tax benefits, as while the dividend is taxed on the recipient, the corporation is not able to deduct the dividend's cost.
Is sale of C Corp stock held by LLC subject to tax?
Is sale of C corp stock held by LLC subject to Net Investment Income Tax if I materially participated? In 2015, a C corp that I worked at was sold. The stock of the C corp was held by an LLC which I was a partner in, and the proceeds will be reported on a K-1 as a combination of long term capital gains and dividend income.
How can I withdraw cash from my closely held C corporation?
Business owners are often concerned about how to withdraw cash from their closely-held C corporations at a minimum tax cost. The simplest way to withdraw cash from the corporation is to distribute cash as a dividend.
How do I report dividends from C corp?
Dividends paid by C corporations will be reported to shareholders using Form 1099-DIV. The C corporation will also send a copy of the form listing dividends to the IRS and other income tax agencies The recipient of the dividends is required to report these dividends using the information on the 1099-DIV.
Where do I report dividends paid on 1120?
Where do I enter dividends received by or paid by the corporation on an 1120 return? Enter dividends received by the corporation, and special deductions, on screen C, Schedule C Dividends Received.
Do C corporations get a deduction for dividends paid?
A business set up as a traditional corporation, known in tax language as a "C corporation," must pay corporate income taxes on its profit. Profit is simply the company's revenue minus its expenses. Dividends, however, are not a business expense, meaning you can't deduct them on your corporate income tax return.
Do C corporation dividends have to be pro rata?
They need not be paid pro rata to all shareholders. Legally, they do not even have to be a dividend under state law; all that is required is a finding by the IRS that a shareholder received some benefit from the corporation.
Where does a corporation report dividends paid?
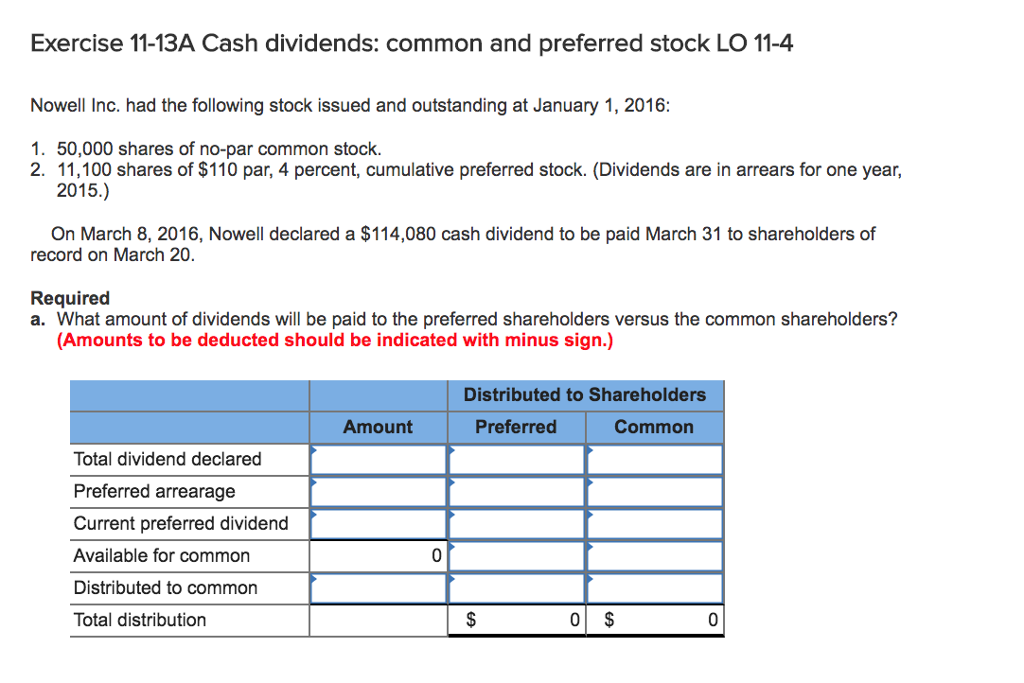
If you receive over $1,500 of taxable ordinary dividends, you must report these dividends on Schedule B (Form 1040), Interest and Ordinary Dividends. If you receive dividends in significant amounts, you may be subject to the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) and may have to pay estimated tax to avoid a penalty.
Are dividends taxed when declared or paid?
Investors pay taxes on the dividend the year it is announced, not the year they are paid the dividend.
How do C Corp distributions work?
A distribution in excess of the corporation's earnings and profits is generally viewed as a nontaxable return of capital to the shareholder. In other words, it is seen as merely a recovery or return of the shareholder's investment in the corporation.
Are dividends an expense for a corporation?
Cash or stock dividends distributed to shareholders are not recorded as an expense on a company's income statement. Stock and cash dividends do not affect a company's net income or profit. Instead, dividends impact the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet.
How are corporations taxed on dividends received?
A US corporation generally may deduct 50% of dividends received from other US corporations in determining taxable income. The dividends received deduction (DRD) is increased from 50% to 65% if the recipient of the dividend distribution owns at least 20% but less than 80% of the distributing corporation.
What happens when a corporation pays a dividend?
Dividends are corporate earnings that companies pass on to their shareholders. Paying dividends sends a message about a company's future prospects and performance. Its willingness and ability to pay steady dividends over time provides a solid demonstration of financial strength.
How is stock basis calculated in C corporation?
A shareholder's initial basis in the stock of a C Corporation is either the cost of the stock purchased or, for qualifying Section 351 transactions, the adjusted basis of the assets transferred plus the gain recognized, and minus boot received and liabilities transferred.
Do dividends count as capital gains?
Key Takeaways Dividend income is paid out of the profits of a corporation to the stockholders. As a practical matter, most stock dividends in the U.S. qualify to be taxed as capital gains.
What is S corp dividend?
S corp dividends. There are technically two forms of S corp dividends that an owner can receive. The first is through distributions. S corporation distributions act and work very similarly to draws that a member in an LLC, a partner in a partnership, or a sole proprietor receives.
What is dividend for owners?
For owners, the dividend can represent an additional form of compensation or a reward for a company’s positive financial performance. Subscribe. Get the latest articles, info, and advice to help you run your small business. Delivered weekly.
Can compensation be reclassified as dividends?
If compensation is excessive, that compensation can be reclassified as dividends to the owner. Due to the lower tax rates for C corporations (currently at 21 percent), this is less of an issue than it has been in the past.
When are 1099-DIV due?
Failure to file a 1099-DIV can result in a penalty starting at $50 per form.These forms are due by March 31 each year.
Do people know dividends?
Most people know and understand dividends by the pennies on the share they get from some of their stock holdings. However, we will look at dividends not from the passive investor point of view, but the active business owners’ point of view. For owners, the dividend can represent an additional form of compensation or a reward for a company’s ...
Is an S corporation a pass through entity?
Since the S corporation is a pass-through tax entity like the LLC, partnership, and sole proprietorship, the earnings are passed through to the owners and taxed on the owner’s personal income tax return. S corporation owners can take these distributions tax-free to the extent that they have basis in the company.
Do C corporations pay taxes?
C corporations pay taxes at the corporate level and any dividends paid from the corporation are taxed again at the shareholder level, which results in double taxation. Because of this double taxation, C corporation owners may not want to receive dividends as a form of compensation, particularly for smaller, closely held corporations.
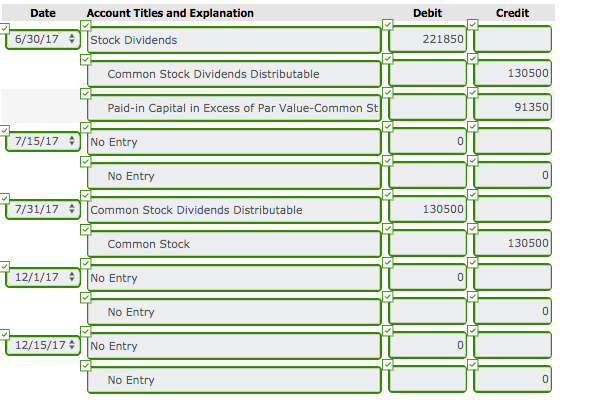
Definition of Dividend Payment to Stockholders
A dividend payment to stockholders is usually a cash payment which reduces the corporation's asset cash and the corporation's stockholders' equity. There are actually two steps required for a corporation to make a dividend payment:
Example of Recording a Dividend Payment to Stockholders
On the date that the board of directors declares the dividend, the stockholders' equity account Retained Earnings is debited for the total amount of the dividend that will be paid and the current liability account Dividends Payable is credited for the same amount.
How do C corporations pay their employees?
C corporations have two main ways of distributing their earnings. The first is by paying employees, of which you or other owners may be a part. The other major way is by distributing a dividend to all of the corporation's owners in proportion to their ownership.
Why is a C corp taxed?
C corporations are taxed both at the initial corporate level and then when proceeds are distributed to its owners.
How do C corporations reduce their taxable income?
C corporations can reduce their taxable income through the use of salaries as well as reinvesting profits in the business. One major benefit of corporations is that they can be easily transferred or have ownership structures in ways that are more flexible than many other types of business models.
What is an S corporation?
An S corporation is an alternate type of corporate entity subject to a variety of strict qualifications and criteria. The S corporation is generally intended for small businesses, due to restrictions in shareholder number and type.
Do dividends have payroll taxes?
The tax comparison is complex, as employees will be subject to various taxes including business payroll taxes and individual payroll taxes. Dividends do not have any payroll taxes, and the rate varies depending on current tax law governing dividends. C corporations are their own business and have their own tax issues to determine.
Do S corporations have lower tax liability?
S corporation's profits and losses pass through to the owners. However, S corporations don 't always result in lower tax liability, as it varies depending on the specific corporate and individual tax rates. The cheapest way for C corporations to distribute profits to their owners and lower their tax liability remains through dividends.
Can a C corporation deduct salary?
Whether the C corporation pays its earnings as salary, dividends, or keeps the earnings will have also a tax impact on the business itself. The C corporation will be permitted to deduct any salary they pay. Given that corporations face a significant tax rate on their own, any salary paid through this method will proportionally reduce ...
Can you withdraw cash from a corporation?
You may withdraw cash from the corporation by selling property to the corporation. However, certain types of sales should be avoided. For instance, you should not sell property at a loss to a corporation you constructively own more than 50% of, since the loss on the sale will be disallowed.
Can you withdraw money from a corporation without paying taxes?
You may withdraw cash from the corporation without being taxed by borrowing money from the corporation. However, to avoid re-characterization of the loan as a dividend, the loan must be properly documented and made on terms (including a provision for interest) comparable to those on which an unrelated third party would lend money to you. All payments of interest and principal on the loan should be made under the loan agreement.
Is interest paid on a corporation debt deductible?
Additionally, interest paid on the debt is deductible by the corporation . The debt must have been properly documented with certain terms that characterize it as debt instead of equity. The corporation must also not have a disproportionately high debt-to-equity ratio.
Is compensation taxable to a corporation?
Reasonable compensation you, or members of your family, receive for services actually rendered to the corporation is taxable to you or your family member and deductible to the corporation. The same rule applies to any compensation (i.e., rent) you receive from the corporation for the use of property. In both cases the compensation must be reasonably related to the services rendered or the value of the property provided. To the extent the compensation is excessive; the excess will be nondeductible to the corporation. However, remember compensation payments require payroll taxes to be paid by both the individual and the corporation.
Is a dividend distribution taxable?
However, a dividend distribution is generally not tax efficient because it is taxable to the recipient to the extent of the corporation's "earnings and profits," but NOT deductible by the corporation. There are, however, several alternative methods that allow you to withdraw cash from a corporation while avoiding dividend treatment:
Is debt a dividend?
Otherwise, the repayment of the "debt" could be re-characterized and taxed as a dividend. If you make additional cash contributions to the corporation in the future, you may wish to consider structuring such contributions as debt to facilitate later withdrawals on a tax-advantaged basis.
Can a corporation repay debt without a dividend?
To the extent you have capitalized the corporation with debt, including any amounts you have advanced to the corporation, the corporation may repay the debt without the repayment being treated as a dividend. Additionally, interest paid on the debt is deductible by the corporation.
What is the tax dilemma for a C corporation?
Shareholders of closely-held C Corporations often find themselves in a tax dilemma when it comes to creating liquidity from their investment . Generally, the shareholder is compensated for work performed (Ordinary income to the shareholder) or for risk taken and paid in the form of dividends. Compensating a shareholder has many tax considerations that are not covered in this post. For dividends, the issue is double taxation whereby the corporation is not allowed to deduct the dividend from taxable income and the shareholder is taxed on the dividend received. By limiting the deduction of the dividend at the corporate level and taxing the recipients of the dividend, any dividends paid are subject to taxation at the corporate and individual levels. This double taxation can push the combined effective federal tax rate to over 60%. Based on this, you can see why S Corporation status has become the standard for small to medium size businesses. However, there are many small to medium size C Corporations that continue to exist today.
How much of the voting power of all voting stock must be disproportionate?
the shareholder must possess less than 50% of the voting power of all voting stock after the redemption.
What is the test for a shareholder to have less than 50% of voting power?
the shareholder must possess less than 50% of the voting power of all voting stock after the redemption. Thus, if a shareholder owned 50% of the only class of stock of the corporation before the redemption, the test is satisfied if their interest is less than 40% (80% times 50%) after the redemption,. Keep in mind that when computing the ownership ...
What is attribution of stock?
Shareholders are treated as owning shares owned by a partnership, S corporation, trust, or estate, in proportion to his or her interest in the entity. Stock is also attributed through a regular (“C”) corporation if 50% or more of its stock is owned directly or indirectly by (or for) the shareholder.
Is compensating a shareholder a tax issue?
Compensating a shareholder has many tax considerations that are not covered in this post. For dividends, the issue is double taxation whereby the corporation is not allowed to deduct the dividend from taxable income and the shareholder is taxed on the dividend received. By limiting the deduction of the dividend at the corporate level and taxing ...
Can a corporation deduct reacquisition of stock?
Corporations cannot deduct any amount paid or incurred in connection with the reacquisition of its stock or the stock of any related person. This includes transactions treated as redemptions. However, interest and other fees on debt incurred to finance the redemption are deductible.
Is stock redemption taxable?
Stock redemptions can be structured in a manner that lets shareholders take cash out of the corporation while minimizing the tax cost. While dividends are taxable to non-corporate taxpayers at capital gains rates, the advantage of property structuring a stock redemption is that shareholders are only taxed on the “gain,” i.e., ...
Do target tax attributes come under the buyer's control?
382–383 limitation rules. If the buyer makes a direct asset purchase, the target’s tax attributes do not come under the buyer’s control. Unwanted assets and/or unknown or contingent liabilities are unimportant to the buyer.
Can a corporation have capital receipts of $1 million?
The corporation cannot have capital receipts in excess of $1 million on the day the stock is issued for the stock to be considered Sec. 1244 stock. This test is applied each time new stock is issued. If new shares are issued in exchange for cash or property transferred to the corporation and the $1 million capital receipts limit is not ...
Can a seller shelter gains from a stock sale?
The seller can shelter gains from the stock sale with NOLs or capital loss carryovers. The seller can recognize a loss (perhaps an ordinary loss under Sec. 1244, as discussed below) on the sale of the target’s stock. A tax-free reorganization is unattractive because the seller wants cash, or a limited market exists for the stock ...
Is a C corporation stock sale taxable?
Buying or Selling C Corporation Stock. Unlike an asset sale, a taxable stock sale does not result in the recognition of taxable income or loss at the corporate level. The differences between the basis and fair market value (FMV) of corporate assets are deferred instead of recognized immediately, as they are in an asset sale.
Can you exclude gain on a stock sale?
If the stock is sold at a gain, the seller may be able to exclude some of the gain under Sec. 1202. If the stock is sold at a loss, the seller can treat some or all of a loss as ordinary rather than capital under Sec. 1244. In a stock sale for cash, the seller recognizes gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount realized ...
Is Sec 1244 stock netted before the dollar limit?
Gains and losses on Sec. 1244 stock are not nett ed before applying the annual dollar limitation, and the annual dollar limitation can apply to the sale of Sec. 1244 stock of the same corporation in different (e.g., succeeding) tax years.
What is a redemption of stock?
A redemption of stock owned by a shareholder of a corporation may be characterized as a “sale or exchange” under IRC Section 302 or as a “dividend” payment under IRC Section 301. The manner in which the redemption is characterized will determine the tax treatment afforded the redemption and, more specifically, may impact whether the shareholder must report the income realized on the transaction as capital gain or ordinary income as well as the amount of income that must be reported.
Is a redemption a dividend?
the redemption is “not essentially equivalent to a dividend”; the redemption is “substantially disproportionate”; the redemption is for all the shareholder’s stock; the redemption is a “partial liquidation” of the distributing corporation; or. the redemption is for stock of a public regulated investment company.
Is a dividend a qualified dividend?
Thus, if the dividend is a “qualified dividend,” then the dividend will be taxed at the same tax rate as an IRC Section 302 distribution. However, the amount of gain included in the shareholder’s income may differ given the specific rules under IRC Section 301 vis-à-vis IRC Section 302. It is important that a shareholder be aware ...