- Market Capitalization = Market Price per Share x Total Outstanding Shares
- Book Value per Share is calculated as = Net Assets / Outstanding Shares
- Net Assets = Total Assets – Total Liabilities. These values can be obtained from a company’s balance sheet or statement of financial position.
How do you calculate the stock valuation formula?
What is Common Stock Formula?
- Examples of Common Stock Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Common Stock in a better manner. ...
- Explanation. ...
- Relevance and Uses of Common Stock Formula. ...
- Common Stock Formula Calculator
- Recommended Articles. ...
How to choose the best stock valuation method?
Popular Stock Valuation Methods
- Dividend Discount Model (DDM) The dividend discount model is one of the basic techniques of absolute stock valuation. ...
- Discounted Cash Flow Model (DCF) The discounted cash flow model is another popular method of absolute stock valuation. ...
- Comparable Companies Analysis
What is the formula to calculate price per share?
- List the various prices at which you bought the stock, along with the number of shares you acquired in each transaction.
- Multiply each transaction price by the corresponding number of shares.
- Add the results from step 2 together.
- Divide by the total number of shares purchased.
What are the methods of stock valuation?
The singular value decomposition can be computed using the following observations:
- The left-singular vectors of M are a set of orthonormal eigenvectors of MM⁎.
- The right-singular vectors of M are a set of orthonormal eigenvectors of M⁎M.
- The non-zero singular values of M (found on the diagonal entries of Σ {\displaystyle \mathbf {\Sigma } } ) are the square roots of the non-zero eigenvalues of both M⁎M ...

How is stock valuation calculated?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
What are the three main stock valuation methods?
There are three methods for inventory valuation: FIFO (First In, First Out), LIFO (Last In, First Out), and WAC (Weighted Average Cost).
How do you determine if a stock is undervalued or overvalued?
Price-book ratio (P/B) To calculate it, divide the market price per share by the book value per share. A stock could be overvalued if the P/B ratio is higher than 1.
What are the 5 methods of stock valuation?
5 Inventory Costing Methods for Effective Stock ValuationThe retail inventory method.The specific identification method.The First In, First Out (FIFO) method.The Last In, First Out (LIFO) method.The weighted average method.
Which stock valuation method is best?
Top 7 Stock Valuation Methods to Find Winning StocksAsset Reproduction Value. Type: Balance sheet valuation, Absolute. ... Benjamin Graham Valuation Formula. ... Earnings Power Value (EPV) By Bruce Greenwald. ... PE Model For Stock Valuation. ... Discounted Cash Flow Valuation. ... Reverse Discounted Cash Flow. ... Dividend Discount Model.
How do you judge if a stock is a good buy?
Here are nine things to consider.Price. The first and most obvious thing to look at with a stock is the price. ... Revenue Growth. Share prices generally only go up if a company is growing. ... Earnings Per Share. ... Dividend and Dividend Yield. ... Market Capitalization. ... Historical Prices. ... Analyst Reports. ... The Industry.More items...
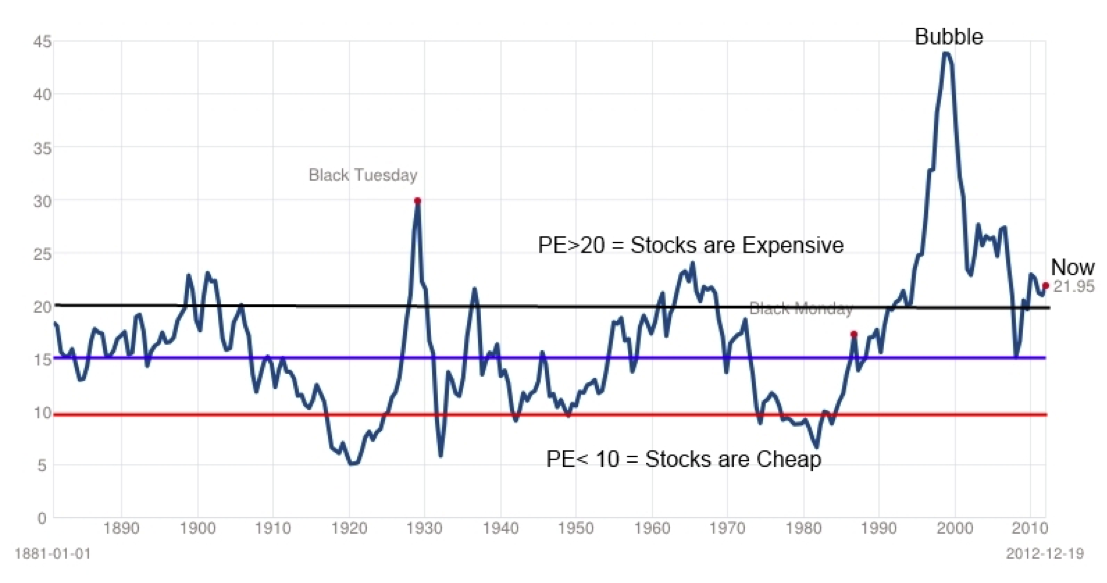
What is good PE ratio?
As far as Nifty is concerned, it has traded in a PE range of 10 to 30 historically. Average PE of Nifty in the last 20 years was around 20. * So PEs below 20 may provide good investment opportunities; lower the PE below 20, more attractive the investment potential.
How do you judge a share price?
6 Basic Financial Ratios.5 Must-Have Metrics for Value Investors.Earnings Per Share (EPS)Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)Price-To-Book Ratio (P/B Ratio)Price/Earnings-to-Growth (PEG Ratio)
Which index has the broadest representation of the total market?
However, the index with one of the broadest representations of the total market is the Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index. 4 The diagram below illustrates both the number of securities and the degree of representation of each index:
Which stock index has outperformed the other major market indexes over the last decade?
Th Nasdaq 100 has handily outperformed the other major market indexes over the last decade.
How many companies are in the Wilshire 5000?
headquartered equity securities with readily available price data." By the end of 2014, the index held 3,818 companies. As of Sept., 2020, the index contained only 3,445 components. 4
Does Wilshire 5000 include publicly traded companies?
So, if you really want to measure the "total market, you would be best advised to check out the Wilshire 5000. Although it does not include every publicly traded company, it does include a lot more than the other indices which people often refer to as "the market.".
Is the NASDAQ 100 technology based?
Meanwhile, the NASDAQ 100 is largely technology-based , with such holdings as Netflix (NFLX) and Match Group (MTCH). Thus, it's no surprise that over the longer-term (10 years in this case), the DIJA underperforms other indexes, while the Nasdaq 100 outperforms.
What is stock valuation?
Stock valuation methods can be primarily categorized into two main types: absolute and relative. 1. Absolute. Absolute stock valuation relies on the company’s fundamental information. The method generally involves the analysis of various financial information that can be found in or derived from a company’s financial statements.
What is the process of valuing stocks?
Valuing stocks is an extremely complicated process that can be generally viewed as a combination of both art and science. Investors may be overwhelmed by the amount of available information that can be potentially used in valuing stocks (company’s financials, newspapers, economic reports.
What is intrinsic valuation?
Unlike relative forms of valuation that look at comparable companies, intrinsic valuation looks only at the inherent value of a business on its own. (or theoretical value) of a stock. The importance of valuing stocks evolves from the fact that the intrinsic value of a stock is not attached to its current price.
What is intrinsic value in stock valuation?
Intrinsic Value The intrinsic value of a business (or any investment security) is the present value of all expected future cash flows, discounted at the appropriate discount rate.
What is comparable analysis?
The comparable analysis is an example of relative stock valuation. Instead of determining the intrinsic value of a stock using the company’s fundamentals, the comparable approach aims to derive a stock’s theoretical price using the price multiples of similar companies.
What is economic indicator?
Economic Indicators An economic indicator is a metric used to assess, measure, and evaluate the overall state of health of the macroeconomy. Economic indicators. , stock reports, etc.). Therefore, an investor needs to be able to filter the relevant information from the unnecessary noise. Additionally, an investor should know about major stock ...
What is dividend discount?
The dividend discount model is one of the basic techniques of absolute stock valuation. The DDM is based on the assumption that the company’s dividends represent the company’s cash flow to its shareholders.
What is book value?
The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds. With purely financial firms, the book value can fluctuate with the market as these stocks tend to have a portfolio of assets that goes up and down in value.
Why do investors use the PEG ratio?
Because the P/E ratio isn't enough in and of itself, many investors use the price to earnings growth (PEG) ratio. Instead of merely looking at the price and earnings, the PEG ratio incorporates the historical growth rate of the company's earnings. This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock.
How to calculate PEG ratio?
This ratio also tells you how company A's stock stacks up against company B's stock. The PEG ratio is calculated by taking the P/E ratio of a company and dividing it by the year-over-year growth rate of its earnings. The lower the value of your PEG ratio, the better the deal you're getting for the stock's future estimated earnings.
How long does it take to pay back a stock?
The reason for this is simple: A P/E ratio can be thought of as how long a stock will take to pay back your investment if there is no change in the business. A stock trading at $20 per share with earnings of $2 per share has a P/E ratio of 10, which is sometimes seen as meaning that you'll make your money back in 10 years if nothing changes.
Why is it important to compare P/E ratios?
The reason for this is simple: A P/E ratio can be thought of as how long a stock will take to pay back your investment if there is no change in the business.
What does a PEG ratio mean?
A PEG of 1 means you're breaking even if growth continues as it has in the past.
What is the P/B ratio?
Made for glass-half-empty people, the price-to-book (P/B) ratio represents the value of the company if it is torn up and sold today. This is useful to know because many companies in mature industries falter in terms of growth, but they can still be a good value based on their assets. The book value usually includes equipment, buildings, land and anything else that can be sold, including stock holdings and bonds.
Who performs stock valuation?
Stock valuation performed by leading financial institutions and hedge fund managers make use of highly sophisticated variations of the below valuation methods. This article seeks to provide traders with a comprehensive starting point to stock valuation for the following stock valuation methods:
Why is it important to know the value of a stock?
Knowing how to accurately value a stock enables traders to identify and take advantage of opportunities in the stock market. Stock valuation, also referred to as ‘equity valuation’, provides the framework for traders to identify when a stock is relatively cheap or expensive. The difference between a stock’s market value and its intrinsic value presents traders with an opportunity to benefit from this disparity.
Why value a stock?
Valuing a stock allows traders to acquire a solid understanding of the value of a share and whether it is appropriately priced. Once the value of the share is known, it can then be compared to the quoted price of the share in the stock market.
What is dividend discount?
The dividend discount model is similar to the previous stock valuation methods as it considers future dividends (earnings) to shareholders. However, the DDM model looks at future dividends and discounts them to establish what those dividends would be worth in today’s value otherwise referred to as the present value (PV).
What happens if the quoted share price is higher than the calculated value?
If the quoted share price is higher than the calculated value, it is seen as expensive and traders will look to short/sell the stock in anticipation of price reverting to its intrinsic value.
What is the reverse of a share?
The reverse of this is where a share trades below its intrinsic value and traders purchase the share in anticipation of the share price rising to match the intrinsic value. This is often the case for value stocks. An example of this is shown below where Aviva PLC is trading below intrinsic value.
What is equity valuation?
Stock valuation, also referred to as ‘equity valuation’, provides the framework for traders to identify when a stock is relatively cheap or expensive. The difference between a stock’s market value and its intrinsic value presents traders with an opportunity to benefit from this disparity.
How to value a stock?
The most common way to value a stock is to compute the company's price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio . The P/E ratio equals the company's stock price divided by its most recently reported earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio implies that an investor buying the stock is receiving an attractive amount of value.
What is the book value of a stock?
Price is the company's stock price and book refers to the company's book value per share. A company's book value is equal to its assets minus its liabilities (asset and liability numbers are found on companies' balance sheets). A company's book value per share is simply equal to the company's book value divided by the number of outstanding shares. ...
What is a stock?
A single share of a company represents a small ownership stake in the business. As a stockholder, your percentage of ownership of the company is determined by dividing the number of shares you own by the total number of shares outstanding and then multiplying that amount by 100. Owning stock in a company generally confers to the stock owner both corporate voting rights and income from any dividends paid.
What is GAAP earnings?
GAAP is shorthand for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, and a company's GAAP earnings are those reported in compliance with them. A company's GAAP earnings are the amount of profit it generates on an unadjusted basis, meaning without regard for one-off or unusual events such as business unit purchases or tax incentives received. Most financial websites report P/E ratios that use GAAP-compliant earnings numbers.
Why do investors use adjusted earnings to calculate P/E?
Non-repeating events can cause significant increases or decreases in the amount of profits generated, which is why some investors prefer to calculate a company's P/E ratio using a per-share earnings number adjusted for the financial effects of one-time events. Adjusted earnings numbers tend to produce more accurate P/E ratios.
How to calculate forward P/E ratio?
The forward P/E ratio is simple to compute. Using the P/E ratio formula -- stock price divided by earnings per share -- the forward P/E ratio substitutes EPS from the trailing 12 months with the EPS projected for the company over the next fiscal year . Projected EPS numbers are provided by financial analysts and sometimes by the companies themselves.
Why should investors consider companies' strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value?
Aside from metrics like the P/E ratio that are quantitatively computed, investors should consider companies' qualitative strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock's value. A company with a defensible economic moat is better able to compete with new market participants, while companies with large user bases benefit from network effects. A company with a relative cost advantage is likely to be more profitable, and companies in industries with high switching costs can more easily retain customers. High-quality companies often have intangible assets (e.g., patents, regulations, and brand recognition) with considerable value.
How to calculate book value of stock?
How it’s calculated. Divide the current share price by the stock’s book value. Then divide by the number of shares issued. The book value is worked out from the balance sheet as total assets minus total liabilities (or costs). The balance sheet with these figures can be found in the company’s latest earnings report on its website.
Why should I value stocks before buying?
No one wants to pay more than they need to. The basic goal of investing in stocks is to buy when the price is low and sell when it’s high to make a profit.
How do fundamental analysts determine the intrinsic value of a stock?
Fundamental analysts attempt to discover this intrinsic value based on the company’s financial statements, including its earnings and debt. Relative value is determined by comparing businesses against their peers, like comparing the price of Dollar General stock with Dollar Tree stock or comparing Bank of America stock with Citibank stock.
How to find P/E?
How it’s calculated. Look for a company’s EPS figures on its website. Divide the current price share by the EPS to find the P/E. If the company has adjusted EPS figures, use those instead — any one-time major expense could affect the EPS.
What does it mean when a P/E ratio increases?
Watch out for when a P/E ratio increases dramatically. This could mean investors overshot the expectations about the company’s actual earnings. Investors can get caught up in the market hype, anticipating significant growth, and push the stock price to the point it’s overvalued and due for a correction.
What is fundamental analysis?
Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, aims to determine the intrinsic, or true, value and the relative value of the stock so that an investor or trader can anticipate whether the stock price will rise or fall to realign with that value.
Why do investors use ratios?
Many investors use ratios to decide if a stock offers a good relative value compared to its peers. Here are the four most basic ways to calculate a stock value.
Core Valuation Models
We currently track five different models to evaluate whether the US stock market is accurately priced, relative to long-term historical patterns and fundamental indicators. Each model is illustrated below, with much more detail available by clicking into each. Models are updated weekly, or as data becomes available.
Yield Curve Model: Fairly Valued
If the spread between the 10-year and 3-month Treasury yield is negative (when 3mo yield is higher than 10y), it is a bearish signal that is almost always followed by economic recession.
Buffett Indicator Model: Overvalued
The ratio of the total value of the US stock market vs current GDP. Originally a favorite valuation indicator of Warren Buffett.
S&P500 Mean Reversion Model: Overvalued
This model simply assumes that over time the S&P500 will tend to revert back to its own long term trend line.
Interest Rate Model: Fairly Valued
For several reasons, low interest rates tend to push stock prices higher. This model considers current US stock market prices relative to US Treasury interest rates.
Margin Debt Model: Strongly Overvalued
The model looks at the level of margin debt that investors use to finance further stock purchases.
Posts
Shorter form blog-style posts on various stock/economy related topics, but not limited to market valuation. These are generally not updated after they are posted.
