First, identify that capital stock is an equity account and also classified as an credit account. Then, find out what transaction is involved, which is an increase in capital stock. Lastly, apply the accounting rule of debit and credit.
Is a common stock considered an asset?
Common stock is a popular type of financial asset, in which investors buy shares in a publicly traded company. Common stockholders typically receive quarterly dividends and voting rights in major corporate decisions. Common stocks vary greatly in their riskiness and price performance but tend to appreciate in value over the long term.
How to record stock transactions?
- Tracking code, optional (can be used if, e.g., you select stocks using more than one system)
- Date purchased
- Number of stocks
- Price
- Buy brokerage cost
- Total cost
- Dividends received
- Date sold
- Number of stocks
- Price
How to record capital stock?
Step 2: Record the investment
- Select + New.
- Select Bank deposit.
- From the Account ▼ drop-down menu, select the bank account you're depositing the money into.
- Enter the Date you deposited the money.
- In the Add funds to this deposit section, enter the name of the investor in the Received from field.
- Select the appropriate equity account from the drop-down list in the Account field.
Is treasury stock a debit or credit?
Treasury stock is credited for the full amount. If the retirement stock revaluation price is lower than the basis, the transaction is shown as a debit to common stock at the basis price. A credit is made to paid-in capital for the amount under the basis and a credit is made to treasury stock at the basis price.

How do you increase common stock?
However, a company commonly has the right to increase the amount of stock it's authorized to issue through approval by its board of directors. Also, along with the right to issue more shares for sale, a company has the right to buy back existing shares from stockholders.
Is common stock increased by credit?
Common stock is an equity balance. As mentioned, this account increases in most cases. Even when companies issue shares for free or at discount, the account balance will grow. As an equity balance, a company's common stock is credit.
Does common stock have credit or debit?
Shareholders' Equity For example, common stock and retained earnings have normal credit balances. This means an increase in these accounts increases shareholders' equity. The dividend account has a normal debit balance; when the company pays dividends, it debits this account, which reduces shareholders' equity.
Is issuing common stock a debit or credit?
creditIssuing common stock generates cash for a business, and this inflow is recorded as a debit in the cash account and a credit in the common stock account. The proceeds from the stock sale become part of the total shareholders' equity for the corporation but do not affect retained earnings.
How to determine if a capital stock is an equity or credit account?
Then, find out what transaction is involved, which is an increase in capital stock. Lastly, apply the accounting rule of debit and credit.
What is debit vs credit?
Debit vs. Credit. In accounting, a debit may represent an increase of value to certain accounts but a decrease of value to other accounts. For example, an increase an asset account is a debit and a decrease in a liability or equity account is also a debit. On the other hand, a credit may also represent an increase of value to certain accounts ...
What are the different types of accounts?
Accounts. In accounting, accounts are classified into five basic categories: asset accounts, liability accounts, equity accounts, revenue accounts and expense accounts. Based on the implied meaning of debit and credit, that is, a debit means the use of money and a credit means the source of money, all the asset accounts ...
What is change in capital stock?
An change in capital stock is the result of a business transaction, and all business transactions are recorded based on the rules of debit and credit. The accounting term of debit and credit does not always mean that a debit is to subtract and a credit is to add.
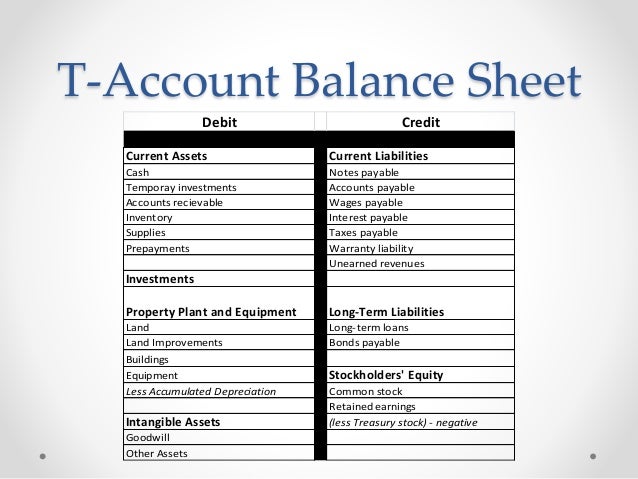
Where are debit and credit accounts on the balance sheet?
Accounting rules arbitrarily place all debit accounts on the left side and credit accounts on the right side in the layout of both the balance sheet and journal entries used to record each transaction in a pair of debit and credit accounts. Every transaction involves a change of value in two accounts. For example, an increase in capital stock results in also an increase in the cash account, a special asset account. The practical rule for identifying whether a transaction is a debit or credit to a particular account is always to record a debit for an increase in a debit account and a credit for an increase in a credit account, and to record a credit for a decrease in a debit account and a debit for a decrease in a credit account.
Is a credit an increase or decrease?
On the other hand, a credit may also represent an increase of value to certain accounts but a decrease of value to other accounts. For example, an increase in a liability or equity account is a credit and a decrease in an asset account is also a credit. Advertisement. Video of the Day.
Is a capital stock transaction a debit or credit?
The practical rule for identifying whether a transaction is a debit or credit to a particular account is always to record a debit for an increase in a debit account ...
How much cash does a corporation receive from a common stock issue?
A corporation issues common stock and receives $20,000 of cash. When a corporation issues shares of its no par, no stated value Common Stock to investors for their $20,000 of cash, the corporation's assets increase by $20,000 and its stockholders' equity increases by $20,000. As a result, the accounting equation will be in balance:
Is a T account debited?
Therefore, the Cash account is debited to increase its balance.
Does asset account have debit balance?
Since assets are on the left side of the accounting equation, the asset account Cash is expected to have a debit balance. The debit balance will decrease with a credit to Cash for $1,500. The other part of the entry involves the stockholders' equity account Retained Earnings.
What is debit in accounting?
A debit is an accounting entry that either increases an asset or expense account, or decreases a liability or equity account. It is positioned to the left in an accounting entry. A credit is an accounting entry that either increases a liability or equity account, or decreases an asset or expense account.
What is stock in business?
You own the property; the property has value and can be liquidated for cash. As a business owner, stock is something you use to get an influx of capital. The capital is used as savings, to buy machinery or property, or to pay operating expenses. What is debit and credit?
Is common stock an asset?
Furthermore, is stock an asset or expense? As an investor, common stock is considered an asset. You own the property; the property has value and can be liquidated for cash.
Is common stock a debit or credit?
Click to see full answer. Also asked, is the common stock a debit or a credit? Some of the accounts have a normal credit balance, while others have a normal debit balance. For example, common stock and retained earnings have normal credit balances. This means an increase in these accounts increases shareholders' equity.
Which side of the stockholders equity account will have the expense balance?
Therefore expense accounts will have their balances on the left side. To reduce the normal credit balance in stockholders' equity accounts, a debit will be needed. Hence, the accounts such as Rent Expense, Advertising Expense, etc. will have their balances on the left side.
What happens when you earn $400?
Revenues of $400 are earned and that causes stockholders' equity to increase. The company earns the right to receive $400. This increases the company's asset account Accounts Receivable. Here's the effect on the accounting equation and the company's balance sheet as a result of earning the revenues:
What is the equation for assets and liabilities?
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's equity (if a sole proprietorship) With double-entry accounting, the accounting equation should always be in balance. In other words, not only will debits be equal to credits, but the amount of assets will be equal to the amount of liabilities plus the amount of owner's equity.
Which side of the accounting equation should assets be?
Assets are on the left side of the accounting equation. Asset account balances should be on the left side of the accounts. In the accounting equation you can see that assets are on the left side of the equation: Earlier you learned that debit means left side. Recall our T-account that showed debits on the left side:
Which side of the account should liability be?
Liability account balances should be on the right side of the accounts. In the accounting equation you can see that liabilities are on the right side of the equation: Earlier you learned that credit means right side. Recall our T-account that showed credits on the right side: Thus liability accounts such as Accounts Payable, Notes Payable, ...
Is stockholders equity on the right side?
Stockholders' equity is on the right side of the accounting equation. Stockholders' equity account balances should be on the right side of the accounts. In the accounting equation you can see that stockholders' equity is on the right side of the equation: Again, credit means right side and our T-account showed credits on the right side.
What is debit and credit?
Debits and Credits: A Simple, Visual Guide. By Nick Zarzycki on January 23, 2019. If there’s one piece of accounting jargon that trips people up the most, it’s “debits and credits.”. What exactly does it mean to “debit” and “credit” an account?
Why do you debit furniture?
You debit your furniture account, because value is flowing into it (a desk). In double-entry accounting, every debit (inflow) always has a corresponding credit (outflow). So we record them together in one entry. In this case, the entry would be: Account. Debit.