The calculation of implied volatility can be done in the following steps:
- Gathered the inputs of the Black and Scholes model, such as the Market Price of the underlying, which could be stock,...
- Now, one has to input the above data in the Black and Scholes Model.
- Once the above steps are completed, one needs to start doing an iterative search by trial and error.
How do you calculate implied volatility?
The factors are as follows:
- The market price of the option
- The underlying stock price
- The strike price
- The time to expiration
- The risk-free interest rate
How implied volatility (VIX) can impact a trade?
How Implied Volatility (VIX) Can Impact a Trade. Implied Volatility (IV) is a measure of how much the “market place” expects the price of an underlying stock or index to move; i.e. the volatility that the market itself is implying for the underlying stock or index. The VIX index represents the Implied Volatility for the S&P 500 index (SPX ...
What exactly does implied volatility mean?
The term implied volatility refers to a metric that captures the market's view of the likelihood of changes in a given security's price. Investors can use implied volatility to project future moves and supply and demand, and often employ it to price options contracts.
What determines the volatility of a stock?
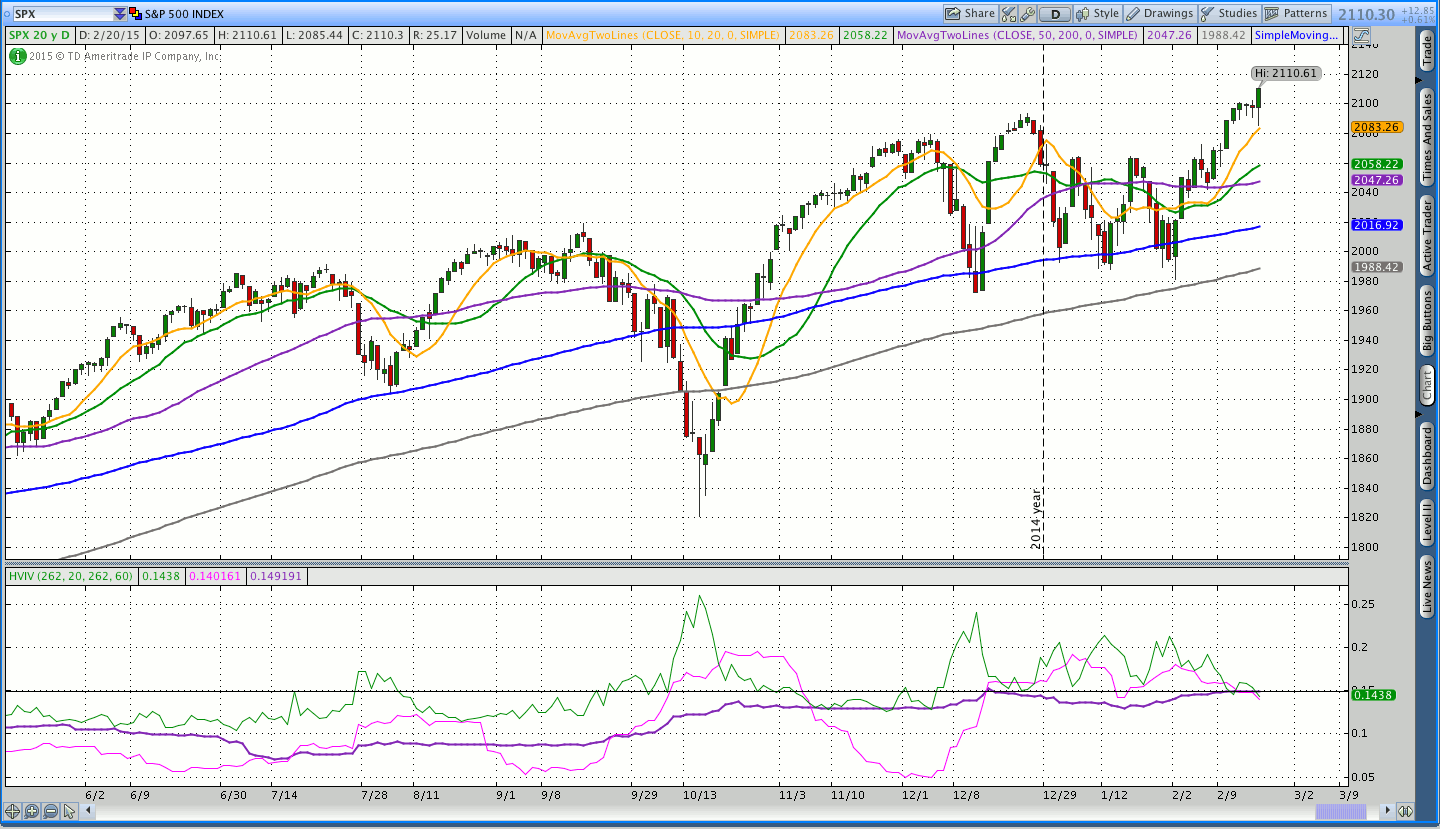
TL;DR
- Market volatility is a measure of the variance of returns on a market index over a given period.
- High volatility is associated with high risk and unpredictability.
- Historical market volatility represents the current market volatility based on historical returns. ...
- A market is considered volatile if it rises or falls more than 1% over a given period.
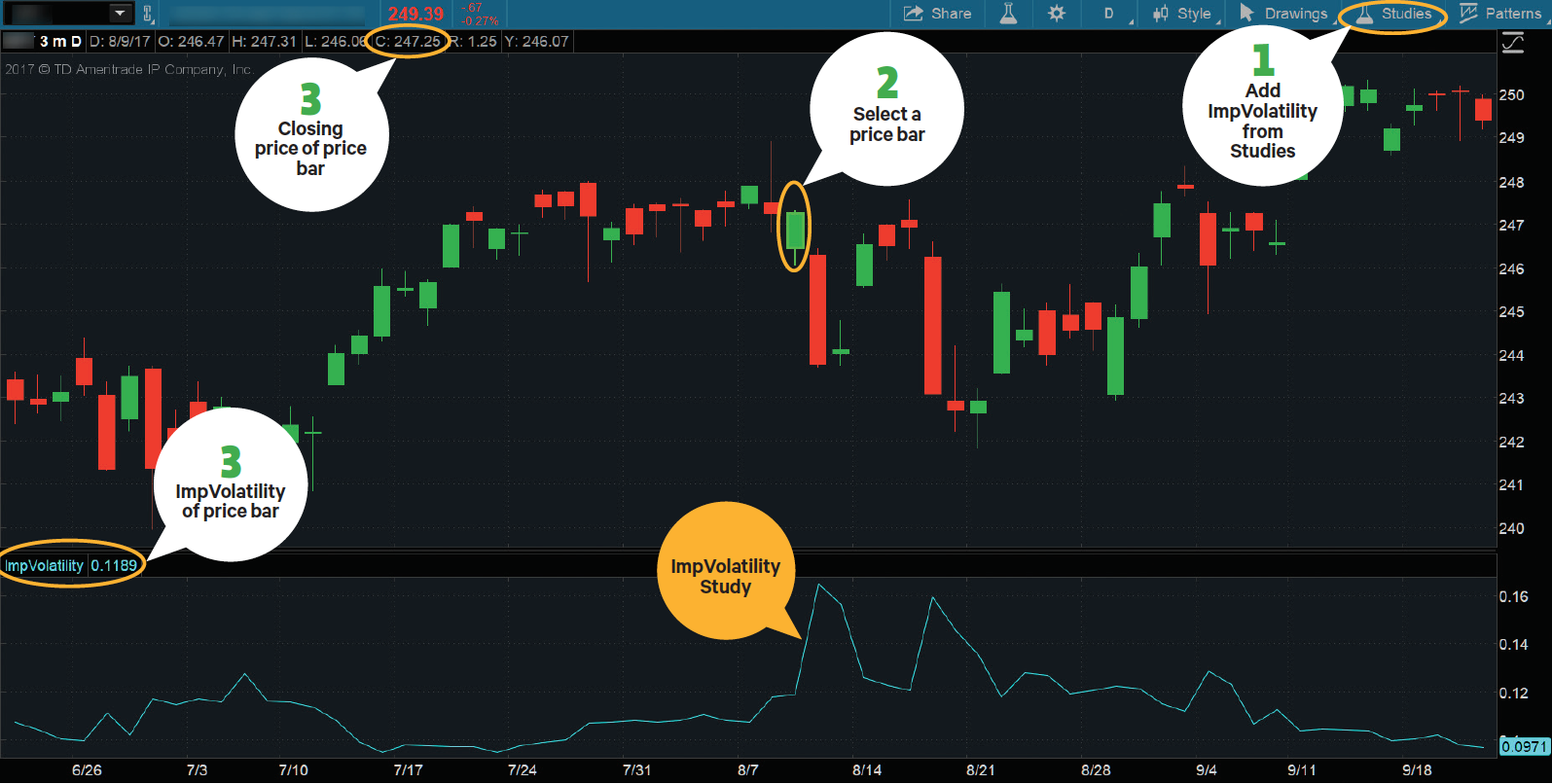
How do you find the implied volatility of a stock?
One effective way to analyze implied volatility is to examine a chart. Many charting platforms provide ways to chart an underlying option's average implied volatility, in which multiple implied volatility values are tallied up and averaged together. For example, the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is calculated similarly.
What is a good implied volatility for a stock?
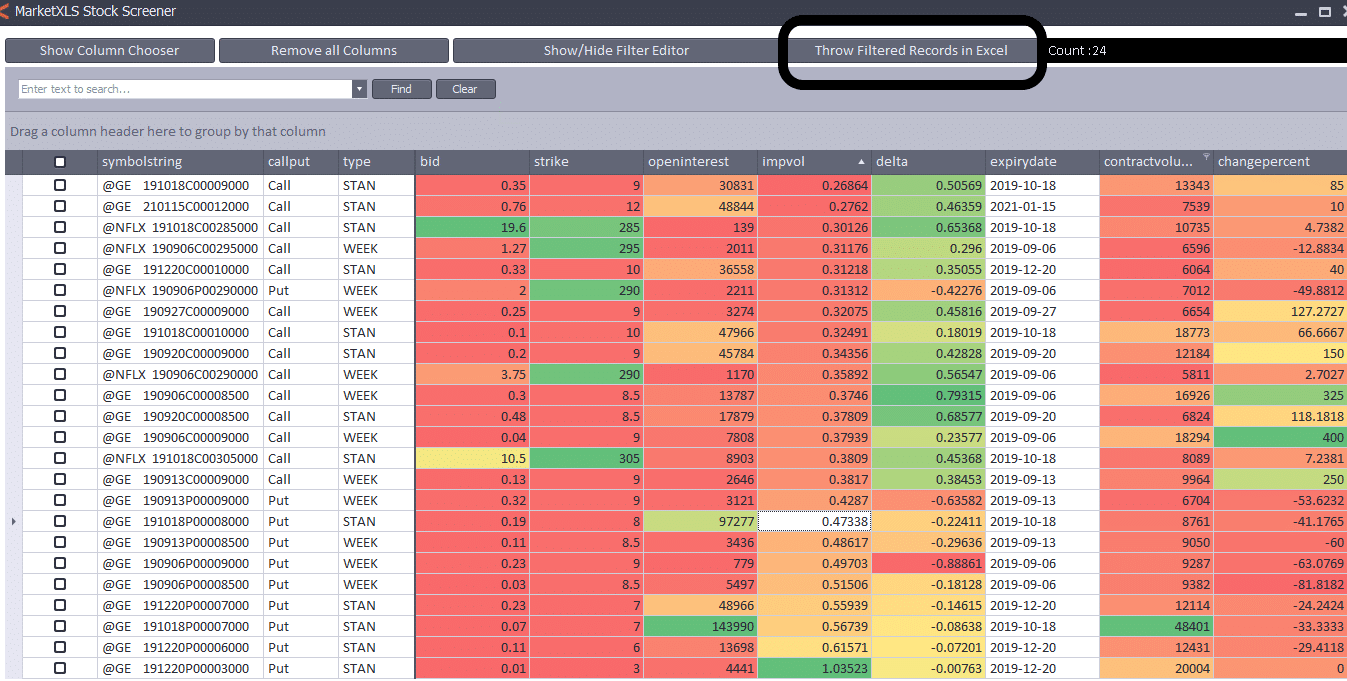
For U.S. market, an option needs to have volume of greater than 500, open interest greater than 100, a last price greater than 0.10, and implied volatility greater than 60%.
Is 80% implied volatility high?
Put simply, IVP tells you the percentage of time that the IV in the past has been lower than current IV. It is a percentile number, so it varies between 0 and 100. A high IVP number, typically above 80, says that IV is high, and a low IVP, typically below 20, says that IV is low.
How do you use implied volatility to trade stocks?
1:5518:08How to use implied volatility to trade - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow conversely if the demand drops. Right then the implied. Volatility is going to drop in that nameMoreNow conversely if the demand drops. Right then the implied. Volatility is going to drop in that name which means that the price of the option is going to drop as well so implied volatility.
Does Robinhood show implied volatility?
To find implied volatility of an option on Robinhood, follow these steps: Tap the Search icon at the bottom of your app. Search for a stock symbol. In the Stock Information Page, tap Trade, then Trade Options.
What makes IV go up?
IV typically gets high when the company has news or some event impending that could move the stock – I call it the event horizon – and I refer to this kind of volatility as event volatility. These stocks sometimes are called “situation” stocks.
Is Low IV good for options?
Low IV means cheap options. 2. Using a daily price chart, determine if we have a good reason to be strongly bullish or strongly bearish on each stock. This will be the case only if the stock is near (within an average day's range of) a high-probability turning point - a high-quality supply or demand level.
How do you profit from volatility?
10 Ways to Profit Off Stock VolatilityStart Small. The saying 'go big or go home,' while inspirational, is not for beginning day traders. ... Forget those practice accounts. ... Be choosy. ... Don't be overconfident. ... Be emotionless. ... Keep a daily trading log. ... Stay focused. ... Trade only a couple stocks.More items...
Who determines implied volatility?
Supply and demand are major determining factors for implied volatility. When an asset is in high demand, the price tends to rise. So does the implied volatility, which leads to a higher option premium due to the risky nature of the option.
What is a good IV to buy options at?
Around 20-30% IV is typically what you can expect from an ETF like SPY. While these numbers are on the lower end of possible implied volatility, there is still a 16% chance that the stock price moves further than the implied volatility range over the course of a year.
How do you know if implied volatility is high?
Implied volatility shows the market's opinion of the stock's potential moves, but it doesn't forecast direction. If the implied volatility is high, the market thinks the stock has potential for large price swings in either direction, just as low IV implies the stock will not move as much by option expiration.
Is high IV good for options?
High IV (or Implied Volatility) affects the prices of options and can cause them to swing more than even the underlying stock. Just like it sounds, implied volatility represents how much the market anticipates that a stock will move, or be volatile.
What happens to implied volatility?
Options that have high levels of implied volatility will result in high-priced option premiums. Conversely, as the market's expectations decrease, or demand for an option diminishes, implied volatility will decrease. Options containing lower levels of implied volatility will result in cheaper option prices.
How does implied volatility affect the market?
Implied volatility is directly influenced by the supply and demand of the underlying options and by the market's expectation of the share price's direction. As expectations rise, or as the demand for an option increases, implied volatility will rise.
What happens when implied volatility is relatively low?
Conversely, if you determine where implied volatility is relatively low, you might forecast a possible rise in implied volatility or a reversion to its mean.
Why are options less expensive?
As implied volatility decreases, options become less expensive. As implied volatility reaches extreme highs or lows, it is likely to revert to its mean. 2. If you come across options that yield expensive premiums due to high implied volatility, understand that there is a reason for this.
Why is implied volatility important?
This is important because the rise and fall of implied volatility will determine how expensive or cheap time value is to the option , which can, in turn, affect the success of an options trade.
Which option is more sensitive to volatility?
Options with strike prices that are near the money are most sensitive to implied volatility changes, while options that are further in the money or out of the money will be less sensitive to implied volatility changes. Vega —an option Greek can determine an option's sensitivity to implied volatility changes.
What is time value in options?
Time value is the additional premium that is priced into an option, which represents the amount of time left until expiration. The price of time is influenced by various factors, such as the time until expiration, stock price, strike price, and interest rates. Still, none of these is as significant as implied volatility.
The Black-Scholes Formula
The Black-Scholes model, also called the Black-Scholes-Merton model, was developed by three economists—Fischer Black, Myron Scholes, and Robert Merton in 1973. It is a mathematical model that projects the pricing variation over time of financial instruments, such as stocks, futures, or options contracts.
Implied Volatility Inputs
Implied volatility is not directly observable, so it needs to be solved using the five other inputs of the Black-Scholes model, which are:
The Iterative Search
Suppose that the value of an at-the-money call option for Walgreens Boots Alliance, Inc. (WBA) is $3.23 when the stock price is $83.11, the strike price is $80, the risk-free rate is 0.25%, and the time to expiration is one day.
Historical Volatility
Historical volatility, unlike implied volatility, refers to realized volatility over a given period and looks back at past movements in price. One way to use implied volatility is to compare it with historical volatility.
The Bottom Line
The Black-Scholes formula has been proven to result in prices very close to the observed market prices. And, as we've seen, the formula provides an important basis for calculating other inputs, such as implied volatility. While this makes the formula quite valuable to traders, it does require complex mathematics.
Why use implied volatility?
Investors can use implied volatility to help judge market sentiment of a company stock, but it doesn't always take into account certain market factors. Because implied volatility considers historical data and certain market conditions, it doesn't forecast larger market swings based on investor emotions.
How is implied volatility calculated?
It is calculated through a formula using several variables in market and stock price.
What is volatility in stocks?
Volatility is a measurement of how much a company's stock price rises and falls over time. Stocks with high volatility see relatively large spikes and dips in their prices, and low-volatility stocks show more consistent gains and losses.
How long do you have to know when an option expires?
When calculating for options trading, investors need the number of days until the option expires.
Can volatility be realized?
Once volatility is no longer "implied" -- it becomes "realized" -- an investor can look at historical volatility. Over a given period, a security's movement regarding its price offers a comparison from its historical volatility to its implied volatility. This comparison may help investors make investing decisions.
Determine Whether Implied Volatility Is High Or Low
Determine whether IV is high or low, rising or falling, by looking at a metrics that shows the IV rank.
Research Why Some Options Yield Higher Premiums
There will always be a reason why some options yield higher premiums due to high implied volatility. It could be a product approval, or news about a merger or acquisition.
Identifying Options With High Implied Volatility For Short Premium Strategies
After you’ve done your research, you could identify options with high implied volatility that you might consider selling. You can sell options and still be bullish or neutral.
Identifying Options With Low Implied Volatility For Long Premium Strategies
When the implied volatility is low and the premiums are low-priced, it’s typically a buyers’ market. In a low IV environment, you can consider options buying strategies such as:
What does it mean when implied volatility is high?
When implied volatility is high that can signal that a large price swing is ahead, but it won’t tell you which way the swing will move. Similarly, low implied volatility can be a sign that a security’s price is set to remain relatively stable, without any rapid up or down movements.
What are the indicators used to track the price of a stock?
When trading stocks or stock options, there are certain indicators you may use to track price momentum. Implied volatility, which measures how likely a security’s price is to change, can be useful for determining whether the market is set for bearish or bullish movements. It can also be important when pricing options contracts.
Is implied volatility accurate?
What’s important to remember is that implied volatility is not an accurate forecasting tool for determining which direction a stock’s price will move. You also need to be aware of how certain events may trigger an increase or decrease in volatility surrounding a particular security. For example, the release of a quarterly earnings report or ...
Does supply and demand affect implied volatility?
Other technical indicators. In terms of supply and demand, both can impact implied volatility so it’s important to be aware of how they’re trending when investing in a particular stock or option. Higher demand can lead to higher prices, which can trigger higher implied volatility and send option premiums higher.
Can you use implied volatility to trade options?
Using Implied Volatility for Options Trading. Implied volatility is not a magic crystal ball, though it can give you some insight into how the market as a whole views a particular security. When using implied volatility to trade stocks or options, there are other things to consider as well, including: Supply and demand balance.
The Black-Scholes Formula
Implied Volatility Inputs
- Implied volatility is not directly observable, so it needs to be solved using the five other inputs of the Black-Scholes model, which are: 1. The market priceof the option. 2. The underlying stock price. 3. The strike price. 4. The time to expiration. 5. The risk-free interest rate. Implied volatility is calculated by taking the market price of the...
The Iterative Search
- Suppose that the value of an at-the-money call option for Walgreens Boots Alliance, Inc. (WBA) is $3.23 when the stock price is $83.11, the strike price is $80, the risk-free rate is 0.25%, and the time to expirationis one day. Implied volatility can be calculated using the Black-Scholes model, given the parameters above, by entering different values of implied volatility into the option prici…
Historical Volatility
- Historical volatility, unlike implied volatility, refers to realized volatilityover a given period and looks back at past movements in price. One way to use implied volatility is to compare it with historical volatility. From the example above, if the volatility in WBA is 23.6%, we look back over the past 30 days and observe that the historical volatilityis calculated to be 23.5%, which is a mo…
The Bottom Line
- The Black-Scholes formula has been proven to result in prices very close to the observed market prices. And, as we've seen, the formula provides an important basis for calculating other inputs, such as implied volatility. While this makes the formula quite valuable to traders, it does require complex mathematics. Fortunately, traders and investors who use it do not need to do these cal…